Volume 39 - December 1973
Research Article
Crystal structures of some double hydroxide minerals
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 377-389
-
- Article
- Export citation
Quetzalcoatlite, Cu4Zn8(TeO3)3(OH)18, a New Mineral from Moctezuma, Sonora
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 261-263
-
- Article
- Export citation
The origin and petrogenetic significance of hour-glass zoning in titaniferous clinopyroxenes
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 133-144
-
- Article
- Export citation
The geochemistry of the Devonian lavas of the northern Lorne Plateau, Scotland
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 621-640
-
- Article
- Export citation
Other
Arthur William Gerald Kingsbury (1906–1968)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Article
Glaukosphaerite: A new nickel analogue of rosasite
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 737-743
-
- Article
- Export citation
Correction
Errata
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. ii-iii
-
- Article
- Export citation
Obituary
Cecil Edgar Tilley (1894–1973)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 493-497
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Research Article
The crystal structure of buttgenbachite
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 264-270
-
- Article
- Export citation
A solid solution series between xenotime (YtPO4) and chernovite (YtAsO4)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 145-151
-
- Article
- Export citation
Supercooling and the crystallization of plagioclase from a basaltic magma
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 641-653
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cesbronite, a new copper tellurite from Moctezuma, Sonora
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 744-746
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nigerite in the tin-tantalum pegmatites of Amapá, Brazil
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 837-846
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mineral Analysis and Analysts
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 4-24
-
- Article
- Export citation
The crystal chemistry of the amphiboles II Refinement of the crystal structure of oxy-kaersutite
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 390-400
-
- Article
- Export citation
The crystallization history and mechanism of emplacement of the western part of the Galway Granite, Connemara, Western Ireland
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 498-513
-
- Article
- Export citation
Polytypism of heterogenite
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 152-157
-
- Article
- Export citation
The cause of the colour of Blue John and other purple fluorites
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 401-411
-
- Article
- Export citation
The crystal structure of julgoldite
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 271-281
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reverse zoning between myrmekite and albite in a quartzofeldspathic gneiss from Broken Hill, New South Wales
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 654-657
-
- Article
- Export citation

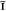 0};
0}; 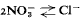 . The crystal structure of buttgenbachite is closely related to that of connellite. The mechanism of forming an isomorphous series is discussed: the present study shows that the replacement is more complicated than was supposed in the literature.
. The crystal structure of buttgenbachite is closely related to that of connellite. The mechanism of forming an isomorphous series is discussed: the present study shows that the replacement is more complicated than was supposed in the literature.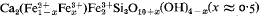 , has been determined and refined to an
, has been determined and refined to an