Editorial
Editorial
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, p. 81
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Research Article
IR hybrid dysgenesis increases the frequency of recombination in Drosophila melanogaster
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 167-174
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Isolation, characterization and RFLP linkage mapping of a DNA repeat family of Solanum spegazzinii by which chromosome ends can be localized on the genetic map of potato
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Molecular analysis of opaque-2 alleles from Zea mays L. reveals the nature of mutational events and the presence of a hypervariable region in the 5′ part of the gene
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 11-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Thirteen genes (Cebpb, E2f1, Tcf4, Cyp24, Pck1, Acra4, Edn3, Kcnb1, Mc3r, Ntsr, Cd40, Plcg1 and Rcad) that probably lie in the distal imprinting region of mouse Chromosome 2 are not monoallelically expressed
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 83-93
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Preserving genes: a model of the maintenance of genetic variation in a metapopulation under frequency-dependent selection
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 175-191
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Genotype-specific modifiers of transgene methylation and expression in the zebrafish, Danio rerio
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 21-28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Mating system, bottlenecks and genetic polymorphism in hermaphroditic animals
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 193-207
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Comparative population structuring of molecular and allozyme variation of Drosophila melanogaster Adh between Europe, West Africa and East Africa
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 95-103
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Linkage analysis of the gene encoding precursor protein of diapause hormone and pheromone biosynthesis-activating neuropeptide in the silkmoth, Bombyx mori
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 105-111
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A stochastic model of selection on selfing rates in structured populations
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 209-222
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A maternal genetic effect on the composition of mouse aggregation chimaeras
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 29-40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Short Paper
Mouse endogenous X-linked genes do not show lineage-specific delayed inactivation during development
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 223-227
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Research Article
The inbreeding decline and average dominance of genes affecting male life-history characters in Drosophila melanogaster
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 41-52
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Dynamics of unconditionally deleterious mutations: Gaussian approximation and soft selection
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 113-121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A general model for the evolution of recombination
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 123-144
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Estimation of inbreeding coefficients from genotypic data on multiple alleles, and application to estimation of clonality in malaria parasites
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 53-61
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Short Paper
Partial deletion of the Y chromosome removes the effect of paternal genome imprinting on periovum sensitivity to hyaluronidase in mice
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 229-231
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Research Article
Dynamics of polygenic variability under stabilizing selection, recombination, and drift
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 63-74
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Abstracts of Papers
Abstracts of papers presented at the fifth Mammalian Genetics and Development Workshop held at the Wellcome Trust Building, Euston Road, London on 23–25 November 1994
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2009, pp. 233-245
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation

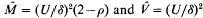 where
where