Abbreviations: TV, television
Short Communication
Iodine concentration of organic and conventional milk: implications for iodine intake
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2011, pp. 935-940
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Molecular Nutrition
Full Papers
Inhibition of advanced glycation end-product formation on eye lens protein by rutin
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2011, pp. 941-949
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Metabolism and metabolic studies
Full Papers
The protective effect of supplemental calcium on colonic permeability depends on a calcium phosphate-induced increase in luminal buffering capacity
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2011, pp. 950-956
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Urinary excretion of in vivo13C-labelled milk oligosaccharides in breastfed infants
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2011, pp. 957-963
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Developmental Biology
Full Papers
Glucose intolerance associated with early-life exposure to maternal cafeteria feeding is dependent upon post-weaning diet
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2011, pp. 964-978
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nutritional Endocrinology
Full Papers
Calcium supplementation prevents obesity, hyperleptinaemia and hyperglycaemia in adult rats programmed by early weaning
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2011, pp. 979-988
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Microbiology
Full Papers
Alterations in microbiota and fermentation products in equine large intestine in response to dietary variation and intestinal disease
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2011, pp. 989-995
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Perialveolar bacterial microbiota and bacteraemia after dental alveolitis in adult rats that had been subjected to neonatal malnutrition
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2011, pp. 996-1005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anticarcinogenic effect of probiotic fermented milk and chlorophyllin on aflatoxin-B1-induced liver carcinogenesis in rats
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2011, pp. 1006-1016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Human and Clinical Nutrition
Full Papers
Study of potential cardioprotective effects of Ganoderma lucidum (Lingzhi): results of a controlled human intervention trial
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2011, pp. 1017-1027
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Home and neighbourhood correlates of BMI among children living in socioeconomically disadvantaged neighbourhoods
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2011, pp. 1028-1036
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of 6 weeks' consumption of β-glucan-rich oat products on cholesterol levels in mildly hypercholesterolaemic overweight adults
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2011, pp. 1037-1047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Oral hydroxycitrate supplementation enhances glycogen synthesis in exercised human skeletal muscle
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2011, pp. 1048-1055
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enteral n-3 fatty acids and micronutrients enhance percentage of positive neutrophil and lymphocyte adhesion molecules: a potential mediator of pressure ulcer healing in critically ill patients
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 November 2011, pp. 1056-1061
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dietary Surveys and Nutritional Epidemiology
Full Papers
High disaccharide intake associates with atherogenic lipoprotein profile
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2011, pp. 1062-1069
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Linoleic acid intake, plasma cholesterol and 10-year incidence of CHD in 20 000 middle-aged men and women in the Netherlands
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2011, pp. 1070-1076
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Determination of fluoride concentration in powdered milk in Iran 2010
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2011, pp. 1077-1079
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vitamin D status and pain: analysis from the Health Survey for England among English adults aged 65 years and over
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2011, pp. 1080-1084
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Behaviour, Appetite and Obesity
Full Papers
Longitudinal changes in body composition associated with healthy ageing: men, aged 20–96 years
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2011, pp. 1085-1091
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Corrigenda
The impact of the catechol-O-methyltransferase genotype on the acute responsiveness of vascular reactivity to a green tea extract – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2011, p. 1092
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation


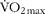 and received HCA or placebo in a crossover design repeated after a 7 d washout period. They consumed 500 mg HCA or placebo with a high-carbohydrate meal (2 g carbohydrate/kg body weight, 80 % carbohydrate, 8 % fat, 12 % protein) for a 3-h post-exercise recovery. Muscle biopsy samples were obtained from vastus lateralis immediately and 3 h after the exercise. We found that HCA supplementation significantly lowered post-meal insulin response with similar glucose level compared to placebo. The rate of glycogen synthesis with the HCA meal was approximately onefold higher than that with the placebo meal. In contrast, GLUT4 protein level after HCA supplementation was significantly decreased below the placebo level, whereas expression of fatty acid translocase (FAT)/CD36 mRNA was significantly increased above the placebo level. Furthermore, HCA supplementation significantly increased energy reliance on fat oxidation, estimated by the gaseous exchange method. However, no differences were found in circulating NEFA and glycerol levels with the HCA meal compared with the placebo meal. The present study reports the first evidence that HCA supplementation enhanced glycogen synthesis rate in exercised human skeletal muscle and improved post-meal insulin sensitivity.
and received HCA or placebo in a crossover design repeated after a 7 d washout period. They consumed 500 mg HCA or placebo with a high-carbohydrate meal (2 g carbohydrate/kg body weight, 80 % carbohydrate, 8 % fat, 12 % protein) for a 3-h post-exercise recovery. Muscle biopsy samples were obtained from vastus lateralis immediately and 3 h after the exercise. We found that HCA supplementation significantly lowered post-meal insulin response with similar glucose level compared to placebo. The rate of glycogen synthesis with the HCA meal was approximately onefold higher than that with the placebo meal. In contrast, GLUT4 protein level after HCA supplementation was significantly decreased below the placebo level, whereas expression of fatty acid translocase (FAT)/CD36 mRNA was significantly increased above the placebo level. Furthermore, HCA supplementation significantly increased energy reliance on fat oxidation, estimated by the gaseous exchange method. However, no differences were found in circulating NEFA and glycerol levels with the HCA meal compared with the placebo meal. The present study reports the first evidence that HCA supplementation enhanced glycogen synthesis rate in exercised human skeletal muscle and improved post-meal insulin sensitivity.