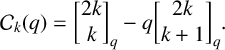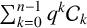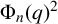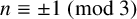1 Introduction
There are several possible q-analogues of the Catalan numbers
![]() $(k+1)^{-1}\binom{2k}{k}$
. Here, we consider MacMahon’s q-Catalan polynomials which are defined by
$(k+1)^{-1}\binom{2k}{k}$
. Here, we consider MacMahon’s q-Catalan polynomials which are defined by
 $$ \begin{align*} \mathcal{C}_k(q):=\frac{1-q}{1-q^{k+1}}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2k}\\ {k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q=\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2k}\\ {k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q-q\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2k}\\ {k+1}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q, \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \mathcal{C}_k(q):=\frac{1-q}{1-q^{k+1}}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2k}\\ {k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q=\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2k}\\ {k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q-q\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2k}\\ {k+1}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q, \end{align*} $$
where
![]() $[\begin {smallmatrix}{n}\\ {k}\end {smallmatrix}]_q$
denotes the q-binomial coefficient recalled in Section 2. The first few q-Catalan polynomials are
$[\begin {smallmatrix}{n}\\ {k}\end {smallmatrix}]_q$
denotes the q-binomial coefficient recalled in Section 2. The first few q-Catalan polynomials are
Notice that
![]() $\mathcal {C}_k(q)$
is a polynomial in q and it reduces to the ordinary Catalan number as
$\mathcal {C}_k(q)$
is a polynomial in q and it reduces to the ordinary Catalan number as
![]() $q\to 1$
. Moreover,
$q\to 1$
. Moreover,
![]() $\mathcal {C}_k(q)$
has a natural enumerative meaning. Indeed, MacMahon [Reference MacMahon4, Volume 2, page 214] established that
$\mathcal {C}_k(q)$
has a natural enumerative meaning. Indeed, MacMahon [Reference MacMahon4, Volume 2, page 214] established that
where w ranges over all ballot sequences
![]() $a_1a_2\dots a_{2k}$
(that is, any permutation of the multiset
$a_1a_2\dots a_{2k}$
(that is, any permutation of the multiset
![]() $\{0^k, 1^k\}$
such that in any subword
$\{0^k, 1^k\}$
such that in any subword
![]() $a_1a_2\dots a_{i}$
, there are at least as many
$a_1a_2\dots a_{i}$
, there are at least as many
![]() $0$
s as there are
$0$
s as there are
![]() $1$
s) and
$1$
s) and
 $$ \begin{align*}\operatorname{maj}(w):=\sum_{\{i: a_i>a_{i+1}\}}\!\!\!\! i\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\operatorname{maj}(w):=\sum_{\{i: a_i>a_{i+1}\}}\!\!\!\! i\end{align*} $$
is the major index of w (see also the survey [Reference Fürlinger and Hofbauer1, Section 3] and [Reference Stanley7, Problem A43]).
In the present work, however, we focus on a problem of number-theoretic interest. The second author in [Reference Tauraso8, Theorem 6.1] proved that, modulo
![]() $\Phi _n(q)$
,
$\Phi _n(q)$
,
 $$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}q^k \mathcal{C}_k(q)\equiv \begin{cases} \displaystyle q^{\lfloor {n}/{3}\rfloor}&\text{if } n\equiv 0,1 \pmod{3},\\ \displaystyle -1-q^{{(2n-1)}/{3}}&\text{if } n\equiv 2 \pmod{3}, \end{cases} \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}q^k \mathcal{C}_k(q)\equiv \begin{cases} \displaystyle q^{\lfloor {n}/{3}\rfloor}&\text{if } n\equiv 0,1 \pmod{3},\\ \displaystyle -1-q^{{(2n-1)}/{3}}&\text{if } n\equiv 2 \pmod{3}, \end{cases} \end{align*} $$
where
 $$ \begin{align*} \Phi_n(q)=\prod_{\substack{1\le k \le n\\ (n,k)=1}}(q-e^{{2k\pi i}/{n}}) \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \Phi_n(q)=\prod_{\substack{1\le k \le n\\ (n,k)=1}}(q-e^{{2k\pi i}/{n}}) \end{align*} $$
denotes the cyclotomic polynomial of order n. Afterwards, a stronger version was proved by Liu in [Reference Liu2, Theorem 1]: modulo
![]() $\Phi _n(q)^2$
,
$\Phi _n(q)^2$
,
 $$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}q^k \mathcal{C}_k(q)\equiv \begin{cases} q^{{(n^2-1)}/{3}}-\dfrac{n-1}{3}(q^n-1)\;&\text{if } n\equiv 1\pmod{3}, \\[3pt] -q^{{(n^2-1)}/{3}}-q^{{n(2n-1)}/{3}}\;&\text{if } n\equiv 2\pmod{3}, \end{cases} \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}q^k \mathcal{C}_k(q)\equiv \begin{cases} q^{{(n^2-1)}/{3}}-\dfrac{n-1}{3}(q^n-1)\;&\text{if } n\equiv 1\pmod{3}, \\[3pt] -q^{{(n^2-1)}/{3}}-q^{{n(2n-1)}/{3}}\;&\text{if } n\equiv 2\pmod{3}, \end{cases} \end{align*} $$
where the case
![]() $n\equiv 0\pmod {3}$
is not covered. Our main aim is to fill this gap as stated next.
$n\equiv 0\pmod {3}$
is not covered. Our main aim is to fill this gap as stated next.
Theorem 1.1. If n is a positive integer divisible by
![]() $3$
, then
$3$
, then
 $$ \begin{align*}\sum_{k=0}^{n-1}q^k \mathcal{C}_k(q)\equiv q^{{n(2n+1)}/{3}} +\frac{1}{3}(q^n-1)(2+(n+1)q^{{2n}/{3}}) \pmod{\Phi_n(q)^2}.\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\sum_{k=0}^{n-1}q^k \mathcal{C}_k(q)\equiv q^{{n(2n+1)}/{3}} +\frac{1}{3}(q^n-1)(2+(n+1)q^{{2n}/{3}}) \pmod{\Phi_n(q)^2}.\end{align*} $$
As we will explain in more detail below, this theorem holds as soon as we prove the following more manageable identity, which is of interest in its own right.
Theorem 1.2. If n is a positive integer divisible by
![]() $3$
and q is a primitive nth root of unity, then
$3$
and q is a primitive nth root of unity, then
 $$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=1}^{{n}/{3}}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k-1)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k-1}} +\sum_{k=1}^{{n}/{3}-1}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k+5)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k}} =\frac{1}{6}(2+(n+1)q^{{2n}/{3}}). \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=1}^{{n}/{3}}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k-1)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k-1}} +\sum_{k=1}^{{n}/{3}-1}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k+5)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k}} =\frac{1}{6}(2+(n+1)q^{{2n}/{3}}). \end{align} $$
Notice that, according to [Reference Liu2, Lemma 3], our Theorem 1.2 mirrors
 $$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {n}/{3}\rfloor}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k-1)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k-1}} +\sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {(n-1)}/{3}\rfloor}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k+5)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k}} \equiv \begin{cases} -\dfrac{n-1}{6}\quad &\text{if } n\equiv 1\pmod{3},\\ 0\quad &\text{if } n\equiv 2\pmod{3}. \end{cases} \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {n}/{3}\rfloor}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k-1)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k-1}} +\sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {(n-1)}/{3}\rfloor}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k+5)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k}} \equiv \begin{cases} -\dfrac{n-1}{6}\quad &\text{if } n\equiv 1\pmod{3},\\ 0\quad &\text{if } n\equiv 2\pmod{3}. \end{cases} \end{align*} $$
The remainder of the paper is organised as follows. In Section 2, we present a reduction of our main result Theorem 1.1 to Theorem 1.2. Section 3 contains preliminary results which we need towards the proof of Theorem 1.2. Sections 4 and 5 split up Theorem 1.2 according to the parity of n and contain the corresponding proofs. Finally, in Section 6, we consider a conversion of one particular identity coming from (1.1) into a trigonometric format and a remarkable implication in the language of character sums.
2 Reducing Theorem 1.1 to Theorem 1.2
We recall that the Gaussian q-binomial coefficients are defined by
 $$ \begin{align*} \bigg[\begin{matrix}{n}\\ {k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q=\begin{cases} \displaystyle\frac{(q;q)_n}{(q;q)_k(q;q)_{n-k}} &\text{if } 0\leq k\leq n,\\ 0 &\text{otherwise,} \end{cases} \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \bigg[\begin{matrix}{n}\\ {k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q=\begin{cases} \displaystyle\frac{(q;q)_n}{(q;q)_k(q;q)_{n-k}} &\text{if } 0\leq k\leq n,\\ 0 &\text{otherwise,} \end{cases} \end{align*} $$
where the q-shifted factorial is given by
![]() $(a;q)_n=(1-a)(1-aq)\dots (1-aq^{n-1})$
for
$(a;q)_n=(1-a)(1-aq)\dots (1-aq^{n-1})$
for
![]() $n\ge 1$
and
$n\ge 1$
and
![]() $(a;q)_0=1$
.
$(a;q)_0=1$
.
By [Reference Liu and Petrov3, Theorem 1.2],
 $$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}q^k\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2k}\\ {k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q\equiv \genfrac{(}{)}{}{}{n}{3}q^{{(n^2-1)}/{3}}\pmod{\Phi_n(q)^2}, \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}q^k\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2k}\\ {k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q\equiv \genfrac{(}{)}{}{}{n}{3}q^{{(n^2-1)}/{3}}\pmod{\Phi_n(q)^2}, \end{align} $$
where
![]() $\genfrac {(}{)}{}{}{\,\cdot \,}{\cdot }$
denotes the Legendre symbol. In the same vein, we also recall the identity [Reference Tauraso9, Theorem 4.2],
$\genfrac {(}{)}{}{}{\,\cdot \,}{\cdot }$
denotes the Legendre symbol. In the same vein, we also recall the identity [Reference Tauraso9, Theorem 4.2],
 $$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}q^{k+1}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2k}\\ {k+1}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q=\sum_{k=1}^{n}\genfrac{(}{)}{}{}{k-1}{3} q^{(2k^2-k(k-1)/3)/3}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2n}\\ {n+k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}q^{k+1}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2k}\\ {k+1}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q=\sum_{k=1}^{n}\genfrac{(}{)}{}{}{k-1}{3} q^{(2k^2-k(k-1)/3)/3}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2n}\\ {n+k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q. \end{align*} $$
Let
![]() $1\leq k\leq n-1$
. Then, the q-analogue [Reference Sagan6, Theorem 2.2]
$1\leq k\leq n-1$
. Then, the q-analogue [Reference Sagan6, Theorem 2.2]
 $$ \begin{align*}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{an+b}\\ {cn+d}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q\equiv \binom{a}{c} \bigg[\begin{matrix}{b}\\ {d}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q \pmod{\Phi_n(q)}\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{an+b}\\ {cn+d}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q\equiv \binom{a}{c} \bigg[\begin{matrix}{b}\\ {d}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q \pmod{\Phi_n(q)}\end{align*} $$
of Lucas’ classical binomial congruence combined with
![]() $(1-q^n)\equiv 0 \pmod {\Phi _n(q)}$
, and the fact that
$(1-q^n)\equiv 0 \pmod {\Phi _n(q)}$
, and the fact that
 $$ \begin{align*}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{n-1}\\ {k-1}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q= \prod_{j=1}^{k-1}\frac{1-q^{n-j}}{1-q^j} =q^{-{k(k-1)}/{2}} \prod_{j=1}^{k-1}\frac{q^j-q^{n}}{1-q^j} \equiv (-1)^{k-1} q^{-{k(k-1)}/{2}} \pmod{\Phi_n(q)},\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{n-1}\\ {k-1}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q= \prod_{j=1}^{k-1}\frac{1-q^{n-j}}{1-q^j} =q^{-{k(k-1)}/{2}} \prod_{j=1}^{k-1}\frac{q^j-q^{n}}{1-q^j} \equiv (-1)^{k-1} q^{-{k(k-1)}/{2}} \pmod{\Phi_n(q)},\end{align*} $$
immediately imply that
 $$ \begin{align*} \bigg[\begin{matrix}{2n}\\ {n+k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q&=\frac{1-q^{2n}}{1-q^{n+k}}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2n-1}\\ {n+k-1}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q \equiv (1-q^{n})\cdot \frac{2}{1-q^{k}}\binom{1}{1}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{n-1}\\ {k-1}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q\\ &\equiv (q^{n}-1)\cdot \frac{2(-1)^k q^{-{k(k-1)}/{2}}}{1-q^{k}} \pmod{\Phi_n(q)^2}. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \bigg[\begin{matrix}{2n}\\ {n+k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q&=\frac{1-q^{2n}}{1-q^{n+k}}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2n-1}\\ {n+k-1}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q \equiv (1-q^{n})\cdot \frac{2}{1-q^{k}}\binom{1}{1}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{n-1}\\ {k-1}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q\\ &\equiv (q^{n}-1)\cdot \frac{2(-1)^k q^{-{k(k-1)}/{2}}}{1-q^{k}} \pmod{\Phi_n(q)^2}. \end{align*} $$
Therefore, modulo
![]() $\Phi _n(q)^2$
,
$\Phi _n(q)^2$
,
 $$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}q^{k+1}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2k}\\ {k+1}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q&\equiv \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}\genfrac{(}{)}{}{}{k-1}{3}q^{(2k^2-k(k-1)/3)/3}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2n}\\ {n+k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q\\ &\equiv 2(q^n-1)\sum_{k=1}^{n-1} \genfrac{(}{)}{}{}{k-1}{3} q^{(2k^2-k(k-1)/3)/3}\frac{(-1)^kq^{-{k(k-1)}/{2}}}{1-q^k}\\ &\equiv -2(q^n-1)\bigg(\sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {n}/{3}\rfloor}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k-1)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k-1}} +\sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {(n-1)}/{3}\rfloor}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k+5)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k}}\bigg). \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}q^{k+1}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2k}\\ {k+1}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q&\equiv \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}\genfrac{(}{)}{}{}{k-1}{3}q^{(2k^2-k(k-1)/3)/3}\bigg[\begin{matrix}{2n}\\ {n+k}\end{matrix}\bigg]_q\\ &\equiv 2(q^n-1)\sum_{k=1}^{n-1} \genfrac{(}{)}{}{}{k-1}{3} q^{(2k^2-k(k-1)/3)/3}\frac{(-1)^kq^{-{k(k-1)}/{2}}}{1-q^k}\\ &\equiv -2(q^n-1)\bigg(\sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {n}/{3}\rfloor}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k-1)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k-1}} +\sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {(n-1)}/{3}\rfloor}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k+5)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k}}\bigg). \end{align*} $$
By substituting this congruence together with (2.1) into the definition of
![]() $\mathcal {C}_k(q)$
, we easily see that, when n is divisible by
$\mathcal {C}_k(q)$
, we easily see that, when n is divisible by
![]() $3$
, Theorem 1.1 is indeed equivalent to Theorem 1.2.
$3$
, Theorem 1.1 is indeed equivalent to Theorem 1.2.
3 Preparing our proof of Theorem 1.2
Henceforth, we replace n with
![]() $3n$
so that our target in (1.1) amounts to proving
$3n$
so that our target in (1.1) amounts to proving
 $$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=1}^{n}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k-1)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k-1}} +\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k+5)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k}} =\frac{1}{3}+\frac{3n+1}{6}\,q^{2n}. \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=1}^{n}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k-1)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k-1}} +\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}\frac{(-1)^kq^{{k(3k+5)}/{2}}}{1-q^{3k}} =\frac{1}{3}+\frac{3n+1}{6}\,q^{2n}. \end{align} $$
To establish this identity, we need the next two results.
Lemma 3.1. For any complex number z,
 $$ \begin{align} &\sum_{k=1}^n \frac{(-1)^k z^{{k(3k-1)}/2}}{1-z^{3k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}\frac{(-1)^k z^{{k(3k+5)}/2}}{1- z^{3k}} \nonumber\\ &\quad= \frac{(-1)^{n-1}}{2}\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}\frac{z^{{k(3n+2)}/{2}}}{1+z^{{3k}/{2}}} +\frac{1}{2}\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}\frac{(-1)^k z^{{k(3n+2)}/{2}}}{1- z^{{3k}/{2}}} \nonumber\\ &\qquad + \, \sum_{k=1}^n\frac1{1-z^{3k-1}}-\sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {(n+1)}/{2}\rfloor}\frac{1}{1-z^{3k-2}} -\frac{2n-1+(-1)^n}{4}. \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} &\sum_{k=1}^n \frac{(-1)^k z^{{k(3k-1)}/2}}{1-z^{3k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}\frac{(-1)^k z^{{k(3k+5)}/2}}{1- z^{3k}} \nonumber\\ &\quad= \frac{(-1)^{n-1}}{2}\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}\frac{z^{{k(3n+2)}/{2}}}{1+z^{{3k}/{2}}} +\frac{1}{2}\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}\frac{(-1)^k z^{{k(3n+2)}/{2}}}{1- z^{{3k}/{2}}} \nonumber\\ &\qquad + \, \sum_{k=1}^n\frac1{1-z^{3k-1}}-\sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {(n+1)}/{2}\rfloor}\frac{1}{1-z^{3k-2}} -\frac{2n-1+(-1)^n}{4}. \end{align} $$
Proof. Employing partial fractions and after further rearrangement, we obtain
 $$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=1}^n & \frac{(-1)^k z^{{k(3k-1)}/2}}{1-z^{3k-1}} = \frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \frac{(-1)^k z^{{k(3k-1)}/2}}{1-z^{{(3k-1)}/2}}+ \frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \frac{(-1)^k z^{{k(3k-1)}/2}}{1+z^{{(3k-1)}/2}} \\ &= \frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \frac{(-1)^k ((z^{{(3k-1)}/2})^k-1+1)}{1-z^{{(3k-1)}/2}}- \frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \frac{-(-z^{{(3k-1)}/2})^k+1-1}{1-(-z^{{(3k-1)}/2})} \\ & = -\frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \sum_{j=0}^{k-1}((-1)^k+(-1)^j) z^{{j(3k-1)}/2} + \frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \bigg(\frac1{1+z^{{(3k-1)}/2}}+\frac{(-1)^k}{1-z^{{(3k-1)}/2}}\bigg)\\ & = -\frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \sum_{j=0}^{k-1}((-1)^k+(-1)^j) z^{{j(3k-1)}/2} + \sum_{k=1}^n\frac1{1-z^{3k-1}}-\sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {(n+1)}/{2}\rfloor}\frac{1}{1-z^{3k-2}}. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=1}^n & \frac{(-1)^k z^{{k(3k-1)}/2}}{1-z^{3k-1}} = \frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \frac{(-1)^k z^{{k(3k-1)}/2}}{1-z^{{(3k-1)}/2}}+ \frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \frac{(-1)^k z^{{k(3k-1)}/2}}{1+z^{{(3k-1)}/2}} \\ &= \frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \frac{(-1)^k ((z^{{(3k-1)}/2})^k-1+1)}{1-z^{{(3k-1)}/2}}- \frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \frac{-(-z^{{(3k-1)}/2})^k+1-1}{1-(-z^{{(3k-1)}/2})} \\ & = -\frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \sum_{j=0}^{k-1}((-1)^k+(-1)^j) z^{{j(3k-1)}/2} + \frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \bigg(\frac1{1+z^{{(3k-1)}/2}}+\frac{(-1)^k}{1-z^{{(3k-1)}/2}}\bigg)\\ & = -\frac12\sum_{k=1}^n \sum_{j=0}^{k-1}((-1)^k+(-1)^j) z^{{j(3k-1)}/2} + \sum_{k=1}^n\frac1{1-z^{3k-1}}-\sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {(n+1)}/{2}\rfloor}\frac{1}{1-z^{3k-2}}. \end{align*} $$
Continuing with additional algebraic manipulation leads to
 $$ \begin{align*} &\sum_{k=1}^n\sum_{j=0}^{k-1}((-1)^k+(-1)^j) z^{{j(3k-1)}/2} = \sum_{j=0}^{n-1}\sum_{k=j+1}^n((-1)^k+(-1)^j) z^{{j(3k-1)}/2} \\ &\quad= \frac{2n-1+(-1)^n}2+ 2\sum_{j=1}^{n-1}\frac{(-1)^j z^{{j(3j+5)}/2}}{1-z^{3j}} + \sum_{j=1}^{n-1}\bigg(\frac{(-1)^n z^{{j(3n+2)}/2}}{1+ z^{{3j}/2}}-\frac{(-1)^j z^{{j(3n+2)}/2}}{1-z^{{3j}/2}}\bigg). \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} &\sum_{k=1}^n\sum_{j=0}^{k-1}((-1)^k+(-1)^j) z^{{j(3k-1)}/2} = \sum_{j=0}^{n-1}\sum_{k=j+1}^n((-1)^k+(-1)^j) z^{{j(3k-1)}/2} \\ &\quad= \frac{2n-1+(-1)^n}2+ 2\sum_{j=1}^{n-1}\frac{(-1)^j z^{{j(3j+5)}/2}}{1-z^{3j}} + \sum_{j=1}^{n-1}\bigg(\frac{(-1)^n z^{{j(3n+2)}/2}}{1+ z^{{3j}/2}}-\frac{(-1)^j z^{{j(3n+2)}/2}}{1-z^{{3j}/2}}\bigg). \end{align*} $$
Combining the last two calculations, we find (3.2).
Lemma 3.2. If
![]() $\alpha $
is a primitive mth root of unity, then
$\alpha $
is a primitive mth root of unity, then
 $$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=1}^m\frac1{1-z^{-1}\alpha^k}=\frac{m}{1-z^{-m}}. \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=1}^m\frac1{1-z^{-1}\alpha^k}=\frac{m}{1-z^{-m}}. \end{align} $$
Proof. We introduce the function
![]() $f(z):=z^m-1=\prod _{k=1}^m(z-\alpha ^k)$
. Then, taking the logarithmic derivative, we obtain
$f(z):=z^m-1=\prod _{k=1}^m(z-\alpha ^k)$
. Then, taking the logarithmic derivative, we obtain
 $$ \begin{align*}\frac{f'(z)}{f(z)}=\sum_{k=1}^m\frac1{z-\alpha^k},\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\frac{f'(z)}{f(z)}=\sum_{k=1}^m\frac1{z-\alpha^k},\end{align*} $$
which means
 $$ \begin{align*} \frac{m}{1-z^{-m}}=\sum_{k=1}^m\frac1{1-z^{-1}\alpha^k}.\\[-34pt] \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \frac{m}{1-z^{-m}}=\sum_{k=1}^m\frac1{1-z^{-1}\alpha^k}.\\[-34pt] \end{align*} $$
We set
![]() $q=\exp ({2\pi ij}/{3n})$
with
$q=\exp ({2\pi ij}/{3n})$
with
![]() $\gcd (j,3n)=1$
. Applying (3.3) with
$\gcd (j,3n)=1$
. Applying (3.3) with
![]() $\alpha =q^3$
, and
$\alpha =q^3$
, and
![]() $z=q$
and
$z=q$
and
![]() $m=n$
,
$m=n$
,
 $$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=1}^{n}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}=\frac{n}{1-q^{-n}} =\frac{n}{3}(1-q^{n}). \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=1}^{n}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}=\frac{n}{1-q^{-n}} =\frac{n}{3}(1-q^{n}). \end{align} $$
By substituting (3.4) in the right-hand side of (3.2) with
![]() $z=q$
, we can put the target (3.1) in a form that is more convenient for our method of proof:
$z=q$
, we can put the target (3.1) in a form that is more convenient for our method of proof:
 $$ \begin{align} &\frac{(-1)^{n-1}}{2}\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}\frac{q^{{k(3n+2)}/{2}}}{1+q^{{3k}/{2}}} +\frac{1}{2}\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}\frac{(-1)^k q^{{k(3n+2)}/{2}}}{1- q^{{3k}/{2}}} + \frac{n}3(1-q^n)\nonumber\\ &\quad -\sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {(n+1)}/{2}\rfloor}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}} -\frac{2n-1+(-1)^n}{4} = \frac13+\frac{3n+1}6\, q^{2n}. \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} &\frac{(-1)^{n-1}}{2}\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}\frac{q^{{k(3n+2)}/{2}}}{1+q^{{3k}/{2}}} +\frac{1}{2}\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}\frac{(-1)^k q^{{k(3n+2)}/{2}}}{1- q^{{3k}/{2}}} + \frac{n}3(1-q^n)\nonumber\\ &\quad -\sum_{k=1}^{\lfloor {(n+1)}/{2}\rfloor}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}} -\frac{2n-1+(-1)^n}{4} = \frac13+\frac{3n+1}6\, q^{2n}. \end{align} $$
Next, we proceed to study (3.5) by distinguishing two cases:
![]() $n=2N$
and
$n=2N$
and
![]() $n=2N-1$
. This allows us to circumvent fractional powers of q.
$n=2N-1$
. This allows us to circumvent fractional powers of q.
(a) If
![]() $n=2N$
, then
$n=2N$
, then
![]() $q^{3N}=(-1)^{\,j}=-1$
because j is odd. With some algebraic simplifications, (3.5) yields
$q^{3N}=(-1)^{\,j}=-1$
because j is odd. With some algebraic simplifications, (3.5) yields
 $$ \begin{align*} q^{2N}\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{k}}{1-q^{6k}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{q^{2k-1}}{1-q^{6k-3}}+\frac{2N}{3}(1-q^{2N}) & -\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}} - N \\ & =\frac{1}{3}-\bigg(N+\frac{1}{6}\bigg)\,q^{N}. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} q^{2N}\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{k}}{1-q^{6k}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{q^{2k-1}}{1-q^{6k-3}}+\frac{2N}{3}(1-q^{2N}) & -\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}} - N \\ & =\frac{1}{3}-\bigg(N+\frac{1}{6}\bigg)\,q^{N}. \end{align*} $$
(b) If
![]() $n=2N-1$
, then we determine that (3.5) is equivalent to
$n=2N-1$
, then we determine that (3.5) is equivalent to
 $$ \begin{align*} &q^{2N-1}\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{k}}{1-q^{6k}} +\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{2k}}{1-q^{6k}}+\frac{2N-1}{3}(1-q^{2N-1})\\ &\quad -\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}} - (N-1)= \frac{1}{3}+\bigg(N-\frac{1}{3}\bigg)\,q^{2(2N-1)}. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} &q^{2N-1}\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{k}}{1-q^{6k}} +\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{2k}}{1-q^{6k}}+\frac{2N-1}{3}(1-q^{2N-1})\\ &\quad -\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}} - (N-1)= \frac{1}{3}+\bigg(N-\frac{1}{3}\bigg)\,q^{2(2N-1)}. \end{align*} $$
In the next two sections, we furnish the proofs for these two cases.
4 Proof of the case
 $n=2N$
$n=2N$
The condition
![]() $\gcd (j,6N)=1$
forces
$\gcd (j,6N)=1$
forces
![]() $j=\pm 1 \pmod {6}$
. We set
$j=\pm 1 \pmod {6}$
. We set
![]() $\omega :=q^{N}$
so that we have
$\omega :=q^{N}$
so that we have
![]() $1-\omega +\omega ^2=0$
and
$1-\omega +\omega ^2=0$
and
![]() $\omega ^3=-1$
. Therefore, it suffices to show the following result.
$\omega ^3=-1$
. Therefore, it suffices to show the following result.
Lemma 4.1. We have
 $$ \begin{align} \omega^2 \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{k}}{1-q^{6k}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{q^{2k-1}}{1-q^{6k-3}}-\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}}=-\frac{N}{3}(1+\omega)+\frac{1}{3}-\frac{\omega}{6}. \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \omega^2 \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{k}}{1-q^{6k}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{q^{2k-1}}{1-q^{6k-3}}-\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}}=-\frac{N}{3}(1+\omega)+\frac{1}{3}-\frac{\omega}{6}. \end{align} $$
Proof. We find it convenient to express our claim in terms of the quantities
 $$ \begin{align*} &A_1=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{k}},\quad A_2=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-\omega q^{k}},\quad A_3=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-\omega^2 q^{k}},\\ &A_4=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1+q^{k}},\quad A_5=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1+\omega q^{k}},\quad A_6=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1+\omega^2 q^{k}}. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} &A_1=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{k}},\quad A_2=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-\omega q^{k}},\quad A_3=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-\omega^2 q^{k}},\\ &A_4=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1+q^{k}},\quad A_5=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1+\omega q^{k}},\quad A_6=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1+\omega^2 q^{k}}. \end{align*} $$
(i) By partial fraction decomposition,
 $$ \begin{align} \frac{6x}{1-x^6}=\frac{1}{1-x}-\frac{\omega}{1-\omega^2 x}+\frac{\omega^2}{1+\omega x} -\frac{1}{1+x}+\frac{\omega}{1+\omega^2 x}-\frac{\omega^2}{1-\omega x}. \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \frac{6x}{1-x^6}=\frac{1}{1-x}-\frac{\omega}{1-\omega^2 x}+\frac{\omega^2}{1+\omega x} -\frac{1}{1+x}+\frac{\omega}{1+\omega^2 x}-\frac{\omega^2}{1-\omega x}. \end{align} $$
Hence, taking
![]() $x=q^k$
results in
$x=q^k$
results in
 $$ \begin{align*}6\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{k}}{1-q^{6k}}=A_1-\omega^2 A_2-\omega A_3-A_4+\omega^2 A_5+\omega A_6.\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}6\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{k}}{1-q^{6k}}=A_1-\omega^2 A_2-\omega A_3-A_4+\omega^2 A_5+\omega A_6.\end{align*} $$
(ii) Again by partial fraction decomposition,
 $$ \begin{align} \frac{3x}{1-x^3}=\frac{1}{1-x}-\frac{\omega}{1-\omega^2 x}+\frac{\omega^2}{1+\omega x}. \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \frac{3x}{1-x^3}=\frac{1}{1-x}-\frac{\omega}{1-\omega^2 x}+\frac{\omega^2}{1+\omega x}. \end{align} $$
Thus, the choice
![]() $x=q^{2k-1}$
gives
$x=q^{2k-1}$
gives
 $$ \begin{align*}3\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{q^{2k-1}}{1-q^{6k-3}}=B_1-\omega B_2+\omega^2B_3,\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}3\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{q^{2k-1}}{1-q^{6k-3}}=B_1-\omega B_2+\omega^2B_3,\end{align*} $$
where
 $$ \begin{align*}B_1=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac{1}{1-q^{2k-1}},\quad B_2=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac{1}{1-\omega^2 q^{2k-1}},\quad B_3=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac{1}{1+\omega q^{2k-1}}.\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}B_1=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac{1}{1-q^{2k-1}},\quad B_2=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac{1}{1-\omega^2 q^{2k-1}},\quad B_3=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac{1}{1+\omega q^{2k-1}}.\end{align*} $$
It is easy to check that
![]() $B_2={N}/2$
and
$B_2={N}/2$
and
![]() $B_1+B_3=N$
directly from
$B_1+B_3=N$
directly from
 $$ \begin{align*} 2\operatorname{Re}(B_2)=B_2+\overline{B_2}&=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac1{1+\omega^{-1}q^{2k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^N\frac1{1+\omega q^{1-2k}}, \\ B_1+B_3&=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac1{1-q^{2k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^N\frac1{1+q^Nq^{2N+2-2k-1}}. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} 2\operatorname{Re}(B_2)=B_2+\overline{B_2}&=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac1{1+\omega^{-1}q^{2k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^N\frac1{1+\omega q^{1-2k}}, \\ B_1+B_3&=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac1{1-q^{2k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^N\frac1{1+q^Nq^{2N+2-2k-1}}. \end{align*} $$
Consequently,
 $$ \begin{align*}3\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{q^{2k-1}}{1-q^{6k-3}}=B_1-\frac{\omega N}{2}+\omega^2(N-B_1)=(2-\omega) \bigg(B_1-\frac{N}{2}\bigg).\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}3\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{q^{2k-1}}{1-q^{6k-3}}=B_1-\frac{\omega N}{2}+\omega^2(N-B_1)=(2-\omega) \bigg(B_1-\frac{N}{2}\bigg).\end{align*} $$
Moreover, we recognise that
 $$ \begin{align*} B_1=\sum_{k=1}^{2N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^k}-\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{2k}}=A_1+\frac{1}{1-q^N}+A_2-\frac{A_1+A_4}{2} =\frac{A_1}{2}+A_2-\frac{A_4}{2}+\omega. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} B_1=\sum_{k=1}^{2N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^k}-\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{2k}}=A_1+\frac{1}{1-q^N}+A_2-\frac{A_1+A_4}{2} =\frac{A_1}{2}+A_2-\frac{A_4}{2}+\omega. \end{align*} $$
(iii) Introducing the values
 $$ \begin{align*}C_1:=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}},\quad C_2:=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}}\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}C_1:=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}},\quad C_2:=\sum_{k=1}^N\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}}\end{align*} $$
and using a partial fraction decomposition of
![]() $1/{(1-x^3)}$
,
$1/{(1-x^3)}$
,
 $$ \begin{align*} C_1+C_2&=\sum_{k=1}^{3N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^k}-\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k}}\\ &=A_1+\frac{1}{1-q^N}+A_2+\frac{1}{1-q^{2N}}+A_3-\frac{A_1+A_3+A_5}{3}\\&=\frac{2A_1}{3}+A_2+\frac{2A_3}{3}-\frac{A_5}{3}+\frac{4\omega+1}{3}. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} C_1+C_2&=\sum_{k=1}^{3N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^k}-\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k}}\\ &=A_1+\frac{1}{1-q^N}+A_2+\frac{1}{1-q^{2N}}+A_3-\frac{A_1+A_3+A_5}{3}\\&=\frac{2A_1}{3}+A_2+\frac{2A_3}{3}-\frac{A_5}{3}+\frac{4\omega+1}{3}. \end{align*} $$
Taking advantage of (3.4) yields
 $$ \begin{align*} \frac{2N}{3}(1-q^{2N}) &=\sum_{k=1}^{2N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}} =\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3(2N+1-k)-1}}\\ &=C_1+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{-3k+2}} =C_1 - \sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{q^{3k-2}}{1-q^{3k-2}} =C_1+N-C_2. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \frac{2N}{3}(1-q^{2N}) &=\sum_{k=1}^{2N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}} =\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3(2N+1-k)-1}}\\ &=C_1+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{-3k+2}} =C_1 - \sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{q^{3k-2}}{1-q^{3k-2}} =C_1+N-C_2. \end{align*} $$
The last two evaluations lead to
Finally, by using items (i), (ii) and (iii), we reduce (4.1) to
which holds because of the symmetry
![]() $A_{\ell }+A_{7-\ell }=N-1$
for
$A_{\ell }+A_{7-\ell }=N-1$
for
![]() $\ell =1, 2$
and
$\ell =1, 2$
and
![]() $3$
.
$3$
.
5 Proof of the case
 $n=2N-1$
$n=2N-1$
Let
![]() $\omega :=-q^{2(2N-1)}=e^{{\pi i}/3}$
so that
$\omega :=-q^{2(2N-1)}=e^{{\pi i}/3}$
so that
![]() $\omega ^2=q^{2N-1}$
,
$\omega ^2=q^{2N-1}$
,
![]() $1-\omega +\omega ^2=0$
and
$1-\omega +\omega ^2=0$
and
![]() $\omega ^3=-1$
.
$\omega ^3=-1$
.
Lemma 5.1. We have
 $$ \begin{align} \omega^2 \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{k}}{1-q^{6k}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{2k}}{1-q^{6k}}-\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}}=-\frac{N}{3}(1+\omega). \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \omega^2 \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{k}}{1-q^{6k}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{2k}}{1-q^{6k}}-\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}}=-\frac{N}{3}(1+\omega). \end{align} $$
Proof. We adopt the notation
![]() $A_i$
from the previous section.
$A_i$
from the previous section.
(i) By the partial fraction decomposition (4.2),
 $$ \begin{align*}6q^{2N-1}\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{k}}{1-q^{6k}} =\omega^2(A_1-A_4-\omega (A_3-A_6)+\omega^2 (A_5- A_2)).\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}6q^{2N-1}\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{k}}{1-q^{6k}} =\omega^2(A_1-A_4-\omega (A_3-A_6)+\omega^2 (A_5- A_2)).\end{align*} $$
(ii) By the partial fraction decomposition (4.3),
 $$ \begin{align*}6\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{2k}}{1-q^{6k}}= A_1+A_4-\omega(A_2+A_5) +\omega^2(A_3+A_6).\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}6\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^{2k}}{1-q^{6k}}= A_1+A_4-\omega(A_2+A_5) +\omega^2(A_3+A_6).\end{align*} $$
(iii) We have
 $$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}} &= \sum_{k=1}^{3N-2}\frac{1}{1-q^{k}}-\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k}}\\ &=A_1+\sum_{k=0}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{N+k}}+A_3-\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k}}\\ &=A_1+\sum_{k=0}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{2N-1-k}}+A_3-\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k}}\\ &=A_1+\bigg(N-\frac{1}{1+\omega}-A_5\bigg)+A_3-\frac{A_1+A_3+A_5}3\\ &=\frac{2A_1}{3}+\frac{2A_3}{3}-\frac{4A_5}{3}+N-\frac{2-\omega}{3} \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}} &= \sum_{k=1}^{3N-2}\frac{1}{1-q^{k}}-\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k}}\\ &=A_1+\sum_{k=0}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{N+k}}+A_3-\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k}}\\ &=A_1+\sum_{k=0}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{2N-1-k}}+A_3-\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k}}\\ &=A_1+\bigg(N-\frac{1}{1+\omega}-A_5\bigg)+A_3-\frac{A_1+A_3+A_5}3\\ &=\frac{2A_1}{3}+\frac{2A_3}{3}-\frac{4A_5}{3}+N-\frac{2-\omega}{3} \end{align*} $$
and invoking (3.4) yields
 $$ \begin{align*} \frac{2N-1}{3}(1-q^{2N-1}) &=\sum_{k=1}^{2N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3(2N-1+1-k)-1}}\\ &=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{-3k+2}} \\ &=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}-\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{q^{3k-2}}{1-q^{3k-2}}\\ &=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}+N-\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}}. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \frac{2N-1}{3}(1-q^{2N-1}) &=\sum_{k=1}^{2N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3(2N-1+1-k)-1}}\\ &=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{-3k+2}} \\ &=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}-\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{q^{3k-2}}{1-q^{3k-2}}\\ &=\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-1}}+N-\sum_{k=1}^{N}\frac{1}{1-q^{3k-2}}. \end{align*} $$
The last two results imply that
 $$ \begin{align*} 6\sum_{k=1}^N\frac1{1-q^{3k-2}} &=2A_1+2A_3-4A_5+6N+\omega-2+(2N-1)(w^2-1). \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} 6\sum_{k=1}^N\frac1{1-q^{3k-2}} &=2A_1+2A_3-4A_5+6N+\omega-2+(2N-1)(w^2-1). \end{align*} $$
Now, by items (i), (ii) and (iii), we are able to restate (5.1) in terms of
![]() $A_i$
. So, the problem reduces to exhibiting a proof for the relation
$A_i$
. So, the problem reduces to exhibiting a proof for the relation
Since
we have
 $$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^k(1-q^k)}{1+(q^k)^3} & =A_6+A_2-2A_4,\\ \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{\omega q^k(1-\omega q^k)}{1+(\omega q^k)^3} & =A_1+A_3-2A_5,\\ \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{\omega^2 q^k(1-\omega^2 q^k)}{1+(\omega^2 q^k)^3} & =A_2+A_4-2A_6. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{q^k(1-q^k)}{1+(q^k)^3} & =A_6+A_2-2A_4,\\ \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{\omega q^k(1-\omega q^k)}{1+(\omega q^k)^3} & =A_1+A_3-2A_5,\\ \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{\omega^2 q^k(1-\omega^2 q^k)}{1+(\omega^2 q^k)^3} & =A_2+A_4-2A_6. \end{align*} $$
Therefore, we arrive at the following equivalent form of (5.2):
 $$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=1}^{N-1} \bigg(\frac{q^k(1-q^k)}{1+(q^k)^3} +3\, \frac{\omega q^k(1-\omega q^k)}{1+(\omega q^k)^3} - \frac{\omega^2 q^k(1-\omega^2 q^k)}{1+(\omega^2 q^k)^3} \bigg)=0. \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=1}^{N-1} \bigg(\frac{q^k(1-q^k)}{1+(q^k)^3} +3\, \frac{\omega q^k(1-\omega q^k)}{1+(\omega q^k)^3} - \frac{\omega^2 q^k(1-\omega^2 q^k)}{1+(\omega^2 q^k)^3} \bigg)=0. \end{align} $$
Since
![]() $1+(\omega q^k)^3=1-q^{3k}$
and
$1+(\omega q^k)^3=1-q^{3k}$
and
![]() $1+(\omega ^2q^k)^3=1+q^{3k}$
, further algebraic manipulation converts (5.3) into
$1+(\omega ^2q^k)^3=1+q^{3k}$
, further algebraic manipulation converts (5.3) into
 $$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=1}^{N-1} \frac{q^k(1+\omega q^{3k})(1-\omega q^k)}{1-q^{6k}} =0. \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \sum_{k=1}^{N-1} \frac{q^k(1+\omega q^{3k})(1-\omega q^k)}{1-q^{6k}} =0. \end{align} $$
However, we note that
 $$ \begin{align*}\frac{z(1+\omega z^3)(1-\omega z)}{1-z^6} = \frac{1-\omega^2}{3}\bigg(\frac{1}{1-z^{-2}} + \frac{1}{1+\omega z^2} - \frac{1}{1-z^{-1}} -\frac{1}{1+\omega z}\bigg).\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\frac{z(1+\omega z^3)(1-\omega z)}{1-z^6} = \frac{1-\omega^2}{3}\bigg(\frac{1}{1-z^{-2}} + \frac{1}{1+\omega z^2} - \frac{1}{1-z^{-1}} -\frac{1}{1+\omega z}\bigg).\end{align*} $$
Letting
![]() $z=q^k$
and
$z=q^k$
and
![]() $\omega =-\omega ^{-2}=- q^{-(2N-1)}$
, our summand can be written as
$\omega =-\omega ^{-2}=- q^{-(2N-1)}$
, our summand can be written as
 $$ \begin{align*}\frac{1-\omega^3}{3} \bigg(\frac{1}{1-q^{-2k}} + \frac{1}{1- q^{-(2N-1-2k)}} - \frac{1}{1-q^{-k}} - \frac{1}{1-q^{-(2N-1-k)}}\bigg).\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\frac{1-\omega^3}{3} \bigg(\frac{1}{1-q^{-2k}} + \frac{1}{1- q^{-(2N-1-2k)}} - \frac{1}{1-q^{-k}} - \frac{1}{1-q^{-(2N-1-k)}}\bigg).\end{align*} $$
Hence, the claim now becomes
 $$ \begin{align*}\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{-2k}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1- q^{-(2(N-k)-1)}}= \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{-k}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1- q^{-(2N-1-k)}},\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{-2k}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1- q^{-(2(N-k)-1)}}= \sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{-k}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1- q^{-(2N-1-k)}},\end{align*} $$
which in turn translates to
 $$ \begin{align*}\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{-2k}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{-(2k-1)}} =\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{-k}}+\sum_{k=N}^{2N-2}\frac{1}{1-q^{-k}}.\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{-2k}}+\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{-(2k-1)}} =\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}\frac{1}{1-q^{-k}}+\sum_{k=N}^{2N-2}\frac{1}{1-q^{-k}}.\end{align*} $$
Indeed, equality follows here since both sides of the last equation are equal to
![]() $\sum _{k=1}^{2N-2}{1}/{(1-q^{-k})}$
. In fact, this is reminiscent of the set-theoretic identity
$\sum _{k=1}^{2N-2}{1}/{(1-q^{-k})}$
. In fact, this is reminiscent of the set-theoretic identity
 $$ \begin{align*} &\ \{k: 1 \leq k \leq N-1\} \cup \{2N-1-k: 1 \leq k \leq N-1\} \\ &\quad = \{2k: 1 \leq k \leq N-1\} \cup \{2N-1-2k: 1 \leq k \leq N-1\}. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} &\ \{k: 1 \leq k \leq N-1\} \cup \{2N-1-k: 1 \leq k \leq N-1\} \\ &\quad = \{2k: 1 \leq k \leq N-1\} \cup \{2N-1-2k: 1 \leq k \leq N-1\}. \end{align*} $$
The proof is complete.
6 Conclusion
For the trigonometric functions enthusiast, the particular equation in (5.4) can be converted to one that involves only these circular functions. To this end, we use the identities
and we rewrite
![]() $\pi /6=\pi /2-(2N-1)x$
followed by replacing
$\pi /6=\pi /2-(2N-1)x$
followed by replacing
![]() $\tan $
with
$\tan $
with
![]() $\cot $
via
$\cot $
via
![]() $\tan (\pi /2-t)=\cot (t)$
. Here,
$\tan (\pi /2-t)=\cot (t)$
. Here,
![]() $x=\pi /(6N-3)$
and the outcome is
$x=\pi /(6N-3)$
and the outcome is
 $$ \begin{align*} &\frac{q^k(1+\omega q^{3k})(1-\omega q^k)}{1-q^{6k}} =\frac{1-\omega^2}{3}\bigg(\frac{q^k}{1-q^{2k}} -\frac{1}{1+\omega q^k} + \frac{1}{1+\omega q^{2k}} \bigg) \\ &\qquad= \frac{i(1-\omega^2)}6 \bigg(\csc(2kx)+\tan\bigg(\frac{\pi}6+kx\bigg)-\tan\bigg(\frac{\pi}6+2kx\bigg) \bigg) \\ &\qquad= \frac{i(1-\omega^2)}6 (\csc(2kx)+\cot((2N-1-k)x)-\cot((2N-1-2k)x). \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} &\frac{q^k(1+\omega q^{3k})(1-\omega q^k)}{1-q^{6k}} =\frac{1-\omega^2}{3}\bigg(\frac{q^k}{1-q^{2k}} -\frac{1}{1+\omega q^k} + \frac{1}{1+\omega q^{2k}} \bigg) \\ &\qquad= \frac{i(1-\omega^2)}6 \bigg(\csc(2kx)+\tan\bigg(\frac{\pi}6+kx\bigg)-\tan\bigg(\frac{\pi}6+2kx\bigg) \bigg) \\ &\qquad= \frac{i(1-\omega^2)}6 (\csc(2kx)+\cot((2N-1-k)x)-\cot((2N-1-2k)x). \end{align*} $$
Hence, (5.4) reduces to verifying the trigonometric identity
 $$ \begin{align*}\sum_{k=1}^{N-1} (\csc(2kx)+\cot((2N-1-k)x)-\cot((2N-1-2k)x)=0.\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\sum_{k=1}^{N-1} (\csc(2kx)+\cot((2N-1-k)x)-\cot((2N-1-2k)x)=0.\end{align*} $$
For the more number-theoretic minded reader, we present below a consequence of the identity in (5.4). We appreciate Terence Tao for allowing us to include his derivation in this paper. For the remainder of this section, specialise to the case where
![]() $2N-1$
is coprime to
$2N-1$
is coprime to
![]() $3$
.
$3$
.
Introduce the cube root of unity
![]() $\epsilon : = \omega ^2= e^{2\pi i/3} = q^{2N-1}$
, where
$\epsilon : = \omega ^2= e^{2\pi i/3} = q^{2N-1}$
, where
![]() $q=e^{{2\pi i}/{(6N-3)}}$
. Expand the numerator in (5.4):
$q=e^{{2\pi i}/{(6N-3)}}$
. Expand the numerator in (5.4):
 $$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=1}^{N-1} \frac{q^k + \epsilon^2 q^{2k} - \epsilon^2 q^{4k} - \epsilon q^{5k}}{1-q^{6k}} = 0.\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \sum_{k=1}^{N-1} \frac{q^k + \epsilon^2 q^{2k} - \epsilon^2 q^{4k} - \epsilon q^{5k}}{1-q^{6k}} = 0.\end{align*} $$
From the easily verified ‘discrete sawtooth Fourier series’ identity, for any k not divisible by
![]() $2N-1$
,
$2N-1$
,
 $$ \begin{align*} \frac{1}{1-q^{6k}} = -\frac{1}{2N-1} \sum_{j=0}^{2N-2} j q^{6jk}\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \frac{1}{1-q^{6k}} = -\frac{1}{2N-1} \sum_{j=0}^{2N-2} j q^{6jk}\end{align*} $$
(proven by multiplying out the denominator, cancelling terms and applying the geometric series formula), we can write the preceding identity to be proven as
 $$ \begin{align*} \sum_{j=0}^{2N-2} j \sum_{k=1}^{N-1} (q^{(6j+1)k} + \epsilon^2 q^{(6j+2)k} - \epsilon^2 q^{(6j+4)k} - \epsilon q^{(6j+5)k}) = 0.\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \sum_{j=0}^{2N-2} j \sum_{k=1}^{N-1} (q^{(6j+1)k} + \epsilon^2 q^{(6j+2)k} - \epsilon^2 q^{(6j+4)k} - \epsilon q^{(6j+5)k}) = 0.\end{align*} $$
Since
![]() $\gcd (2N-1,3)=1$
, we can write
$\gcd (2N-1,3)=1$
, we can write
![]() $q = \epsilon ^{2N-1} \zeta $
for some primitive
$q = \epsilon ^{2N-1} \zeta $
for some primitive
![]() $(2N-1)$
th root
$(2N-1)$
th root
![]() $\zeta $
of unity. We then reduce to
$\zeta $
of unity. We then reduce to
 $$ \begin{align*} &\sum_{j=0}^{2N-2} j\sum_{k=1}^{N-1} ( \epsilon^{(2N-1)k} \zeta^{(6j+1)k} + \epsilon^{2(2N-1)k+2} \zeta^{(6j+2)k}) \\ &\quad = \sum_{j=0}^{2N-2}j\sum_{k=1}^{N-1} ( \epsilon^{(2N-1)k+2} \zeta^{(6j+4)k} + \epsilon^{2(2N-1)k+1} \zeta^{(6j+5)k} ). \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} &\sum_{j=0}^{2N-2} j\sum_{k=1}^{N-1} ( \epsilon^{(2N-1)k} \zeta^{(6j+1)k} + \epsilon^{2(2N-1)k+2} \zeta^{(6j+2)k}) \\ &\quad = \sum_{j=0}^{2N-2}j\sum_{k=1}^{N-1} ( \epsilon^{(2N-1)k+2} \zeta^{(6j+4)k} + \epsilon^{2(2N-1)k+1} \zeta^{(6j+5)k} ). \end{align*} $$
From Galois theory, we can see that the net coefficient of
![]() $\zeta ^a$
would have to be independent of a for each primitive residue class a mod
$\zeta ^a$
would have to be independent of a for each primitive residue class a mod
![]() $2N-1$
. We summarise this discussion in the next declaration.
$2N-1$
. We summarise this discussion in the next declaration.
Corollary 6.1. Let
![]() $N>1$
be a natural number such that
$N>1$
be a natural number such that
![]() $2N-1$
is not divisible by
$2N-1$
is not divisible by
![]() $3$
, let
$3$
, let
![]() $\chi : \mathbb {Z} \to \mathbb {C}$
be a nonprincipal Dirichlet character of period
$\chi : \mathbb {Z} \to \mathbb {C}$
be a nonprincipal Dirichlet character of period
![]() $2N-1$
and let
$2N-1$
and let
![]() $\epsilon := e^{2\pi i/3}$
. Then, we have the character sum identity
$\epsilon := e^{2\pi i/3}$
. Then, we have the character sum identity
 $$ \begin{align} & \bigg(\sum_{j=0}^{2N-2} j \cdot \chi(6j+1)\bigg) \bigg(\sum_{k=1}^{2N-2} \epsilon^{(2N-1)k} \cdot \chi(k)\bigg) \nonumber \\ & \quad= -\bigg(\sum_{j=0}^{2N-2} j \cdot \chi(6j+2)\bigg) \bigg(\sum_{k=1-N}^{N-1} \epsilon^{2(2N-1)k+2} \cdot \chi(k)\bigg). \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} & \bigg(\sum_{j=0}^{2N-2} j \cdot \chi(6j+1)\bigg) \bigg(\sum_{k=1}^{2N-2} \epsilon^{(2N-1)k} \cdot \chi(k)\bigg) \nonumber \\ & \quad= -\bigg(\sum_{j=0}^{2N-2} j \cdot \chi(6j+2)\bigg) \bigg(\sum_{k=1-N}^{N-1} \epsilon^{2(2N-1)k+2} \cdot \chi(k)\bigg). \end{align} $$
We conclude with a problem proposed by Terence Tao.