Multidimensional forced-choice (MFC) tests are increasing in popularity but their construction is complex. The Thurstonian item response model (Thurstonian IRT model) is most often used to score MFC tests that contain dominance items. Currently, in a frequentist framework, information about the latent traits in the Thurstonian IRT model is computed for binary outcomes of pairwise comparisons, but this approach neglects stochastic dependencies. In this manuscript, it is shown how to estimate Fisher information on the block level. A simulation study showed that the observed and expected standard errors based on the block information were similarly accurate. When local dependencies for block sizes \documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$>\,2$$\end{document}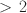 were neglected, the standard errors were underestimated, except with the maximum a posteriori estimator. It is shown how the multidimensional block information can be summarized for test construction. A simulation study and an empirical application showed small differences between the block information summaries depending on the outcome considered. Thus, block information can aid the construction of reliable MFC tests.
were neglected, the standard errors were underestimated, except with the maximum a posteriori estimator. It is shown how the multidimensional block information can be summarized for test construction. A simulation study and an empirical application showed small differences between the block information summaries depending on the outcome considered. Thus, block information can aid the construction of reliable MFC tests.