Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 June 2015
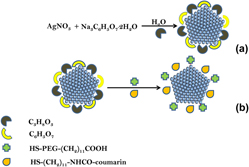
The study reports the functionalization of the size-controlled synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with coumarin derivative. The size and the morphology of the as-synthesized AgNPs were obtained in the presence of glycerol and sodium citrate which acted as the reducing agent which led to nucleation of silver ions thus yielding different sizes of AgNPs. The obtained AgNPs were functionalized with different stoichiometric ratios of [HS-(CH2)11-NHCO-coumarin:HS-PEG-(CH2)11COOH] to form mixed monolayer protected silver clusters and their Raman activities were evaluated to determine the effect of particle size on the enhancement factor (EF). The functionalization and the stability of AgNPs were confirmed using a combination of techniques, namely UV–Visible spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, Zetasizer, and Raman spectroscopy. The obtained Raman spectra were used to calculate the EF of the HS-(CH2)11-NHCO-coumarin adsorbed on AgNPs, which was observed to increase with an increase in size of AgNPs from 16 to 30 nm. Increasing the particle size to 43 nm lowered the EF by 10-fold and hence an optimal size of ∼30 nm was achieved for the coumarin derivative adsorbate.