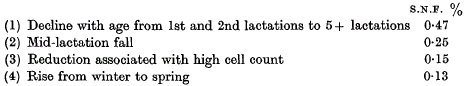Original Articles
Some volatile compounds in New Zealand Cheddar cheese and their possible significance in flavour formation: III. Time of first appearance of volatile carbonyl compounds during ripening
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 335-340
-
- Article
- Export citation
Incorporation of [1-14C] and [3-14C] butyrate into milk constituents by the perfused cow's udder
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 151-160
-
- Article
- Export citation
Methods for investigating the bacteria in young Cheddar cheese: inhibition of starter streptococci with bacteriophage and α-bromopropionic acid
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
- Export citation
The colloidal phosphate of milk: II. Influence of citrate
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 9-17
-
- Article
- Export citation
The distribution of bacteria in New Zealand Cheddar cheese
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 341-351
-
- Article
- Export citation
Phage resistance in pure strains of cheese starter streptococci
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 161-164
-
- Article
- Export citation
Microscopic observation of the effect of some reagents on the physical state of casein
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 353-360
-
- Article
- Export citation
A quantitative evaluation of some factors affecting the non-fatty solids of cow's milk
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 19-32
-
- Article
- Export citation
Studies on the manufacture of sweet cream starter butter: III. Effect of age of starter cultures at time of inoculation
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 165-169
-
- Article
- Export citation
The use of ultrafiltration and dialysis in isolating the aqueous phase of milk and in determining the partition of milk constituents between the aqueous and disperse phases
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 171-190
-
- Article
- Export citation
Genetical aspects of maximum rate of flow during milking
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 361-371
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identification of lactobacilli from Cheddar cheese by chromatography
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 33-39
-
- Article
- Export citation
Production of acetone and acetaldehyde by lactic streptococci
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 41-45
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fishy flavour in dairy products: III. The volatile compounds associated with fishy flavour in washed cream
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 373-380
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bulk feeds for milk Production: I. The influence of level of concentrate feeding in addition to silage and hay on milk yield and milk composition
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 191-204
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fishy flavour in dairy products: I. General studies on fishy butterfat
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 205-209
-
- Article
- Export citation
Strontium-90 from fallout in the diet and milk of a dairy herd*
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 47-57
-
- Article
- Export citation
The volatile compounds associated with tallowy and painty flavours in butterfat
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 381-387
-
- Article
- Export citation
The effect of various sampling intervals on the estimation of lactation milk yield and composition
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 389-398
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chemical changes in dried skim-milk during storage
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2009, pp. 59-66
-
- Article
- Export citation