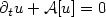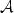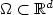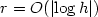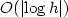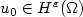Research Article
The existence of a solution and a numerical method for the Timoshenko nonlinear wave system
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2004, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
- Export citation
The effect of reduced integrationin the Steklov eigenvalue problem
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2004, pp. 27-36
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fast deterministic pricing of optionson Lévy driven assets
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2004, pp. 37-71
-
- Article
- Export citation
A quasi-dual Lagrange multiplier space for serendipity mortar finite elements in 3D
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2004, pp. 73-92
-
- Article
- Export citation
Numerical solution of parabolic equationsin high dimensions
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2004, pp. 93-127
-
- Article
- Export citation
A posteriori error control for the Allen–Cahn problem: circumventing Gronwall's inequality
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2004, pp. 129-142
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dynamical behavior of Volterra model with mutual interferenceconcerning IPM
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2004, pp. 143-155
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nouvelles formulations intégrales pour les problèmesde diffraction d'ondes
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2004, pp. 157-175
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mixed formulations for a class of variational inequalities
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2004, pp. 177-201
-
- Article
- Export citation