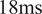Research in lower limb wearable robotic control has largely focused on reducing the metabolic cost of walking or compensating for a portion of the biological joint torque, for example, by applying support proportional to estimated biological joint torques. However, due to different musculotendon unit (MTU) contractile speed properties, less attention has been given to the development of wearable robotic controllers that can steer MTU dynamics directly. Therefore, closed-loop control of MTU dynamics needs to be robust across fiber phenotypes, that is ranging from slow type I to fast type IIx in humans. The ability to perform closed-loop control the in-vivo dynamics of MTUs could lead to a new class of wearable robots that can provide precise support to targeted MTUs for preventing onset of injury or providing precision rehabilitation to selected damaged tissues. In this paper, we introduce a novel closed-loop control framework that utilizes nonlinear model predictive control to keep the peak Achilles tendon force within predetermined boundaries during diverse range of cyclic force production simulations in the human ankle plantarflexors. This control framework employs a computationally efficient model comprising a modified Hill-type MTU contraction dynamics component and a model of the ankle joint with parallel actuation. Results indicate that the closed-form muscle-actuation model’s computational time is in the order of microseconds and is robust to different muscle contraction velocity properties. Furthermore, the controller achieves tendon force control within a time frame below 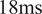 $ 18\mathrm{ms} $, aligning with the physiological electromechanical delay of the MTU and facilitating its potential for future real-world applications.
$ 18\mathrm{ms} $, aligning with the physiological electromechanical delay of the MTU and facilitating its potential for future real-world applications.