Annual Issue: Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019
JMR Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019
Introduction
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 January 2019, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019
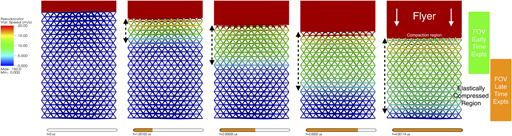
In situ dynamic compression wave behavior in additively manufactured lattice materials
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2018, pp. 2-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019: REVIEW
Chemical modification of degenerate eutectics: A review of recent advances and current issues
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2018, pp. 20-34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019
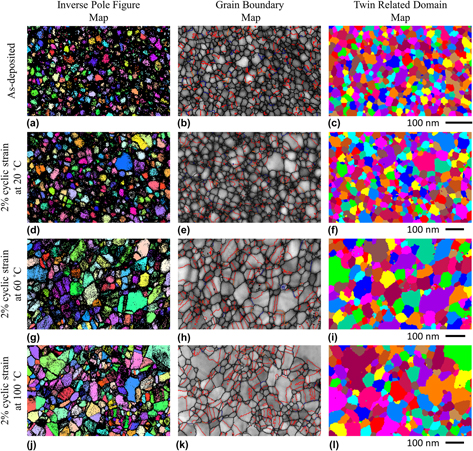
Pronounced grain boundary network evolution in nanocrystalline Cu subjected to large cyclic strains
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2018, pp. 35-47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
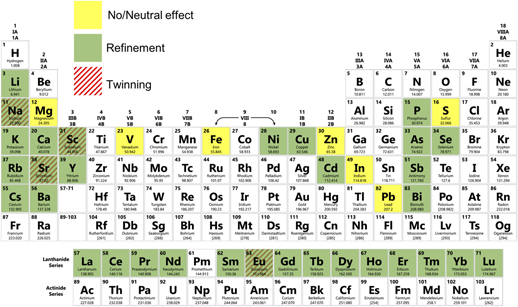
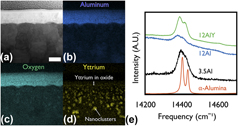
Coupled oxidation resistance and thermal stability in sputter deposited nanograined alloys
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2018, pp. 48-57
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High strength nanocrystalline Cu–Co alloys with high tensile ductility
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2018, pp. 58-68
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Creep behavior of gold thin films investigated by bulge testing at room and elevated temperature
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 October 2018, pp. 69-77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019: REVIEW
A review on friction-based joining of dissimilar aluminum–steel joints
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2018, pp. 78-96
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019
Role of binders in solid electrolyte interphase formation in lithium ion batteries studied with hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2018, pp. 97-106
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019: Invited Review
Double perovskite (Sr2B′B″O6) oxides for high-temperature thermoelectric power generation—A review
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 November 2018, pp. 107-125
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019
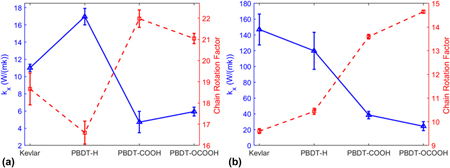
Chain rotation significantly reduces thermal conductivity of single-chain polymers
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 October 2018, pp. 126-133
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019: REVIEW
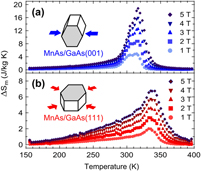
Magnetocaloric materials: From micro- to nanoscale
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2018, pp. 134-157
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019
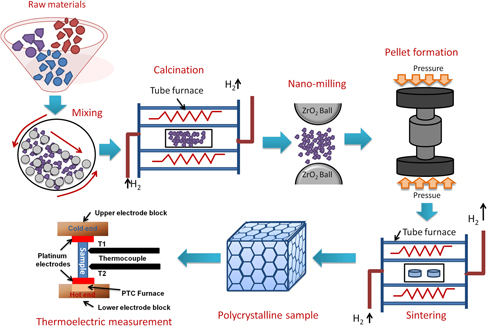
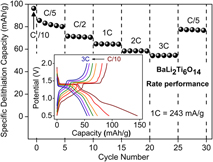
Diffusional and electrochemical investigation of combustion synthesized BaLi2Ti6O14 titanate anode for rechargeable batteries
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 November 2018, pp. 158-168
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019: REVIEW
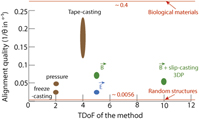
External fields for the fabrication of highly mineralized hierarchical architectures
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2018, pp. 169-193
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Synchrotron X-ray characterization of materials synthesized under microwave irradiation
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 January 2019, pp. 194-205
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019
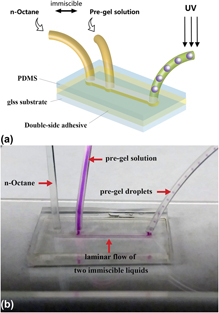
Surfactant-free fabrication of pNIPAAm microgels in microfluidic devices
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2018, pp. 206-213
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Career Scholars in Materials Science 2019: Invited Feature Paper
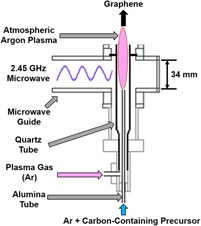
Graphene synthesized in atmospheric plasmas—A review
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2019, pp. 214-230
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Front Cover (OFC, IFC) and matter
JMR volume 34 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 January 2019, pp. f1-f5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Back Cover (OBC, IBC) and matter
JMR volume 34 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 January 2019, pp. b1-b4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation