Non-communicable diseases (NCD) are the main causes of death worldwide. CVD, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases and diabetes account for 60 % of all deaths worldwide and 80 % in low- or middle-income countries( Reference Yach, Hawkes and Gould 1 ). Several dietary factors including whole grains, fruits and vegetables have been shown to contribute to the risk for NCD( Reference Erkkila, Herrington and Mozaffarian 2 – Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 ). Moreover, it seems that fibres from these dietary components have an important role in the aetiology of NCD and mortality( Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 – Reference Pereira, O’Reilly and Augustsson 9 ).
Earlier studies have shown that fibre intakes are inversely associated with all-cause mortality and CVD and cancer mortalities( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 , Reference Larsson and Wolk 7 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Krishnamurthy, Wei and Baird 11 ). A pooled analysis of ten prospective studies indicated that a 10 g/d higher intake of total dietary fibre was associated with 17 and 27 % reductions in the risk of all coronary events and coronary mortality, respectively( Reference Pereira, O’Reilly and Augustsson 9 ). However, the results are inconsistent based on different food sources of dietary fibres( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 – Reference Buil-Cosiales, Zazpe and Toledo 6 , Reference Pereira, O’Reilly and Augustsson 9 ). It is suggested that greater intakes of cereal fibre are associated with a lower risk of CVD and all-cause mortalities( Reference Pereira, O’Reilly and Augustsson 9 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 ). Similar results have been reported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)-AARP Diet and Health Study, which found that dietary fibre from grains, but not from other sources, was inversely related to cause-specific death in men and women( Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 ). In addition, in a cohort study on 3588 elderly, cereal fibre consumption was associated with a lower risk of CVD events( Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 ). However, some observational studies have not found a significant association between cereal fibre intake and CVD mortality( Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 ). Threapleton et al.( Reference Threapleton, Greenwood and Burley 14 ) in UK Women’s Cohort Study observed no significant association between cereal fibre intake and CVD mortality. Moreover, in the cohort study of Women’s Health Study among the US population, no significant association was observed between cereal fibre intake and CVD-specific death( Reference Liu, Buring and Sesso 4 ). It is also suggested by the Blue Mountain Eye Study that cereal fibre intake is not associated with CHD or stroke mortality( Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 ). Two recent meta-analyses of cohort studies( Reference Kim and Je 16 , Reference Yang, Zhao and Wu 17 ) have reported the inverse associations of total dietary fibre intake with all-cause mortality; however, some relevant cohort studies were not included in these meta-analyses( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 ). In addition, the relation between cereal fibre intake and cause-specific mortality was not examined in these meta-analyses. Nevertheless, in another meta-analysis by Liu et al.( Reference Liu, Wang and Liu 18 ), which assessed the association of total dietary fibre intake with cause-specific mortality, different sources of dietary fibres were not considered. Given the lack of any clear meta-analysis of the association of cereal fibre intake with cause-specific mortality, as well as the conflicting evidence in this regard, we aimed to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of the prospective cohort studies to assess the relation between cereal fibre intake and mortality from all causes, CVD, cancer and inflammatory diseases.
Methods
Search strategy
A systematic literature search was conducted in medical databases including Medline/PubMed, SCOPUS, EMBASE, ISI web of Science and Google scholar up to April 2015 using the following medical subject headings (MeSH) and non-MeSH keywords relevant to ‘whole grain’, ‘cereals’ and ‘dietary fiber’ in combination with ‘mortality’, ‘fatal’, ‘death’ and ‘survive’. No restriction was set on the time of publication and language. The reference lists of related articles were hand-searched for additional relevant studies. Titles/abstracts were screened for relevant studies by two independent investigators (M. H. and P. S.).
Inclusion criteria
Published studies were included if they were prospective cohort studies that reported relative risks (RR) or hazard ratio (HR) for the association of cereal fibre intakes and mortality from all causes, CVD, cancer and inflammatory diseases as the main outcomes of interest. In case of multiple published reports from the same study population, we included the one reporting the largest number of mortality cases( Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 ).
Excluded studies
We excluded editorial letters, comments, ecological studies and meta-analyses. The study selection process is illustrated in Fig. 1. Our search strategy identified 9895 human studies. After removing duplicates, 4798 abstracts were selected for a more detailed review; 181 citations were left after screening for title and abstracts. After scrutinising the full-text papers and based on our inclusion criteria, eighteen prospective studies were selected for the systematic review. However, we included only fourteen studies( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 – Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Pereira, O’Reilly and Augustsson 9 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 – Reference Threapleton, Greenwood and Burley 14 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 , Reference Crowe, Key and Appleby 19 – Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 ) in the meta-analysis, and the other four studies were excluded from the meta-analysis because of the following reasons. Two studies conducted by Rimm et al.( Reference Rimm, Ascherio and Giovannucci 24 ) and Wolk et al.( Reference Wolk, Manson and Stampfer 25 ) were not included because they had reported RR or HR for all CVD events simultaneously and had not separated the findings for fatal and non-fatal outcomes. Moreover, two studies were excluded because they had duplicated data from the same cohort studies( Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 , Reference Kaushik, Wang and Wong 26 ).

Fig. 1 The flow diagram of study selection. RR, relative risk.
Data extraction
Two authors (M. H. and P. S.) extracted the required information independently. We used HR or RR as a measure of the association. First author’s last name, publication year, cohort name, the country in which the study was conducted, sample size, age range of participants at baseline, methods of assessment of cereal fibre intake, duration of follow-up, main outcome, covariates adjusted for in the analyses and RR or HR with the corresponding 95 % CI were extracted. From each study, we extracted RR or HR estimates that reflected the greatest degree of adjustments for potential confounders. In case of disagreements between the two investigators, principal investigator (A. E.) was consulted.
Quality assessment
We assessed study quality with the Newcastle–Ottawa quality assessment scale( Reference Wells, Shea and O’connell 27 ). This system allowed a total score of up to 9 points as the highest quality. Scores were derived through three aspects of each study including selection, comparability and outcome in eight questions. Each study could be awarded a maximum score of 1 for each question in selection and outcome categories. However, a maximum score of 2 could be given for comparability.
Statistical methods
RR and HR, and their 95 % CI for the comparison of the highest v. the lowest category of cereal fibre intake, were used to calculate log RR and its standard error. The analyses were performed using random-effects model, calculating both Q-statistic and I 2 as indicators of heterogeneity. In case of significant between-study heterogeneity, we performed subgroup analysis, based on the location of the study, participants’ sex, duration of follow-up and adjustment for energy intake, to find out possible sources of heterogeneity. Between-subgroup heterogeneity was examined through fixed-effects modelling. We also performed random-effects meta-regression analysis to assess the overall linear relationship between cereal fibre intake and mortality. RR (95 % CI) comparing mortality from all causes, CVD, cancer and inflammatory diseases, in different categories of cereal fibre intake compared with the reference group, were extracted, converted to log RR (se) and used in this meta-regression. Depending on the available information in the included studies, the median or means of cereal fibre intake (g/d) in the categories were used. For studies in which a range of cereal fibre intake was reported, the mid-point of each category of intake was calculated. For categories with the open-ended ranges, half the width of the adjacent category was used. One study by Holmes et al.( Reference Holmes, Chen and Hankinson 21 ) was not included in the meta-regression, because they had not reported the amount of cereal fibre intake across different categories. Moreover, the studies by Baer et al.( Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 ), Streppel et al.( Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 ) and Pereira et al.( Reference Pereira, O’Reilly and Augustsson 9 ), which had reported linear estimates (RR or HR for 4 or 10 g/d increment in cereal fibre intake), were included in the meta-regression but not in the meta-analysis of the highest v. lowest intake. The publication bias was examined by visual inspection on Begg’s funnel plots. Formal statistical assessment of funnel plot asymmetry was also carried out using Egger’s regression asymmetry test. We also conducted a sensitivity analysis in which each prospective cohort study was excluded to examine the influence of that study on the overall estimate. Statistical analyses were conducted using Stata version 11.2 (StataCorp LP). P values<0·05 were considered statistically significant for all tests including Cochran’s Q test.
Results
Findings from the systematic review
The characteristics of the studies included in the systematic review are presented in Table 1. Out of eighteen cohort studies published between 1996 and 2015, ten were conducted in the USA( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 – Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 , Reference Holmes, Chen and Hankinson 21 , Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 – Reference Wolk, Manson and Stampfer 25 ), two in the UK( Reference Threapleton, Greenwood and Burley 14 , Reference Crowe, Key and Appleby 19 ), two in Australia( Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 , Reference Kaushik, Wang and Wong 26 ) and the rest in Japan( Reference Eshak, Iso and Date 20 ), Finland( Reference Pietinen, Rimm and Korhonen 22 ) and Netherlands( Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 ), and one pooled analysis based on cohorts in the USA and UK( Reference Pereira, O’Reilly and Augustsson 9 ). The total number of participants in these studies ranged from 1373( Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 ) to 388 122( Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 ), with age ranging from 30 to 99 years. Three( Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 , Reference Pietinen, Rimm and Korhonen 22 , Reference Rimm, Ascherio and Giovannucci 24 ) studies were restricted to male subjects and six others to female subjects( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 , Reference Liu, Buring and Sesso 4 , Reference Threapleton, Greenwood and Burley 14 , Reference Holmes, Chen and Hankinson 21 , Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 , Reference Wolk, Manson and Stampfer 25 ). However, the remaining nine papers had examined both sexes, with three examining males and females separately( Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 , Reference Eshak, Iso and Date 20 ) and six in combination( Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Pereira, O’Reilly and Augustsson 9 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 , Reference Crowe, Key and Appleby 19 , Reference Kaushik, Wang and Wong 26 ). From eighteen studies included in the systematic review, one study was conducted exclusively in patients with myocardial infarction (MI)( Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 ), and two studies were conducted in patients with type 2 diabetes and breast cancer, respectively( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 , Reference Holmes, Chen and Hankinson 21 ). From eighteen citations, six papers had reported RR for all-cause mortality( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 , Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 , Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 , Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 ), seventeen publications for CVD mortality( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 – Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 – Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 – Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 , Reference Crowe, Key and Appleby 19 , Reference Eshak, Iso and Date 20 , Reference Pietinen, Rimm and Korhonen 22 , Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 – Reference Kaushik, Wang and Wong 26 ), four studies for cancer mortality( Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Holmes, Chen and Hankinson 21 , Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 ) and three papers for inflammation-related mortality( Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 ). In some publications, cereal fibre was defined as fibre or NSP from flour, rice, pasta, pastry, bread, dark bread and breakfast cereals( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 , Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 , Reference Threapleton, Greenwood and Burley 14 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 , Reference Crowe, Key and Appleby 19 , Reference Eshak, Iso and Date 20 ). However, others did not precisely report how they defined cereal fibre( Reference Liu, Buring and Sesso 4 , Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 , Reference Pereira, O’Reilly and Augustsson 9 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 , Reference Holmes, Chen and Hankinson 21 , Reference Pietinen, Rimm and Korhonen 22 , Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 – Reference Kaushik, Wang and Wong 26 ). Most studies had assessed dietary intakes by using a validated FFQ, whereas the remaining studies had used dietary questionnaire( Reference Rimm, Ascherio and Giovannucci 24 ) and diet history( Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 ). During the follow-up periods ranging from 6( Reference Liu, Buring and Sesso 4 , Reference Rimm, Ascherio and Giovannucci 24 ) to 40 years( Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 ), there was a report of total number of 85 531 death from all causes, 29 352 from CVD, 35 021 from cancer and 1590 inflammation-related deaths. Corresponding HR for all-cause mortality across the highest v. lowest categories of cereal fibre intake were between 0·73 and 0·92. HR for CVD and cancer mortalities ranged from 0·66 to 2·13 and 0·82 to 1, respectively. Moreover, reported HR for inflammation-related mortality ranged from 0·48 to 0·98. Out of six citations with HR for all-cause mortality as the main outcome, four studies found a significant inverse association between cereal fibre intake and all-cause mortality in men and women( Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 , Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 ). However, the remaining two studies did not show a significant association( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 , Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 ). From seventeen publications that reported HR for CVD mortality, nine studies reported a significant inverse association between cereal fibre intake and CVD mortality( Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 – Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 , Reference Crowe, Key and Appleby 19 , Reference Pietinen, Rimm and Korhonen 22 – Reference Wolk, Manson and Stampfer 25 ), whereas seven others did not( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 – Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 – Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 , Reference Kaushik, Wang and Wong 26 ). It is worth noting that one study found an inverse association between cereal fibre intake and CVD mortality in women but not in men( Reference Eshak, Iso and Date 20 ). Two out of four studies that examined the association of cereal fibre intake with cancer mortality reported a significant inverse association( Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 ). From three publications that reported HR for inflammation-related mortality, two studies did not find any significant association( Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 ), whereas one study reported a significant inverse association between cereal fibre intake and inflammation-related mortality in men but not in women( Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 ). Most studies had performed adjustments for important confounding factors including age (n 17), BMI (n 16), smoking (n 17) and alcohol consumption (n 16). Moreover, some studies had also made adjustments for physical activity (n 15) and energy intake (n 15) or other dietary variables or nutrients (n 15). In terms of the quality of the study, out of eighteen publications included in the systematic review six studies had a score <7 (0–6) and the rest had a score of ≥7 (7–9).
Table 1 Main characteristics of prospective studies examined the association of cereal fibre intake with all-cause, CVD, cancer and inflammation-related mortalities (Mean values and standard errors; odds ratios (OR) or relative risk (RR) and 95 % confidence intervals)

NIH, National Institutes of Health; M, male; F, female; MI, myocardial infarction; NDI, national death index; NHS+HPFS, Nurse’s Health Study+Health Professionals Follow-up Study; BMES, Blue Mountains Eye Study; 1, age; 2, BMI; 3, smoking status; 4, alcohol consumption; 5, physical activity; 6, energy intake; 7, dietary intakes; 8, education or socio-economic status; 9, marital status; 10, diseases history; 11, hormone therapy or using drugs; Q1, quartile 1; Q5, quartile 5; T1, tertile 1; T3, tertile 3.
* Mean age.
Findings from the meta-analysis on cereal fibre intake and all-cause mortality
Three effect sizes from three publications( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 ), including 379 362 participants and 48 052 cases of death, were included in this analysis (Fig. 2). Subjects with the highest intake of cereal fibre had 19 % lower risk of all-cause mortality (RR 0·81; 95 % CI 0·79, 0·83), compared with those with the lowest intake. It should be taken into account that two studies from these three publications had been conducted on diabetic patients( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 ) and individuals with MI( Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 ). No significant between-study heterogeneity was seen (I 2=0·0 %, P=0·60). Meta-regression of the five observational studies( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 , Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 , Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 ) revealed that there is a significant inverse linear trend between cereal fibre intake (g/d) and risk of all-cause mortality (β=−0·019, P=0·02) (Fig. 3(a)). Findings from the sensitivity analysis revealed that the exclusion of any single study from the analysis did not alter the overall association. Moreover, no evidence of publication bias was observed (P=0·80 by Egger’s test, P=0·60 by Begg’s test).

Fig. 2 Forest plots of the association between cereal fibre intake and risk of all-cause mortality. RR, relative risk.

Fig. 3 (a) Association between the risk of all-cause mortality and cereal fibre intake: dose–response meta-regression. The levels of cereal fibre intake (g/d) were modelled using a linear trend with random-effects meta-regression models. ![]() , Weighted regression line based on variance-weighted least squares.
, Weighted regression line based on variance-weighted least squares. ![]() , 95 % CI around the regression line.
, 95 % CI around the regression line. ![]() , Relative risk (RR) in each study. The circle size is proportional to the precision of the RR. The vertical axis is on a log scale. For all-cause mortality, β=−0·019, P=0·02, I
2 residual=50·77 %. (b) Association between the risk of CVD mortality and cereal fibre intake: β=−0·007, P=0·06, I
2 residual=0·00 %. (c) Association between the risk of cancer mortality and cereal fibre intake: β=−0·016, P=0·09, I
2 residual=0·00 %. (d) Association between the risk of mortality from inflammatory diseases and cereal fibre intake: β=−0·024, P=0·31, I
2 residual=3·86 %.
, Relative risk (RR) in each study. The circle size is proportional to the precision of the RR. The vertical axis is on a log scale. For all-cause mortality, β=−0·019, P=0·02, I
2 residual=50·77 %. (b) Association between the risk of CVD mortality and cereal fibre intake: β=−0·007, P=0·06, I
2 residual=0·00 %. (c) Association between the risk of cancer mortality and cereal fibre intake: β=−0·016, P=0·09, I
2 residual=0·00 %. (d) Association between the risk of mortality from inflammatory diseases and cereal fibre intake: β=−0·024, P=0·31, I
2 residual=3·86 %.
Findings from the meta-analysis on cereal fibre intake and CVD mortality
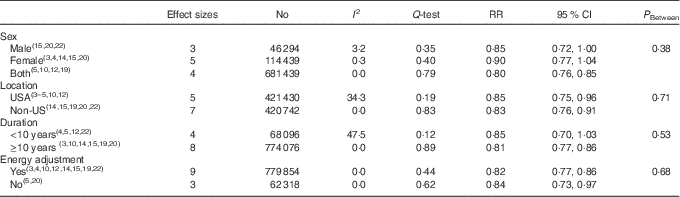
Results from the meta-analysis on cereal fibre intake and CVD mortality are presented in Fig. 4. Overall, twelve effect sizes from ten studies( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 – Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 , Reference Threapleton, Greenwood and Burley 14 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 , Reference Crowe, Key and Appleby 19 , Reference Eshak, Iso and Date 20 , Reference Pietinen, Rimm and Korhonen 22 ) were included. These studies had totally included 842 172 participants at the time of study, out of which 16 882 incident CVD deaths were reported. A significant inverse association was seen between highest consumption of cereal fibre and CVD mortality (RR 0·82; 95 % CI 0·78, 0·86). After excluding two studies that had been performed on patients with MI( Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 ) and diabetes( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 ), no significant changes occurred in the overall effect size (RR 0·82; 95 % CI 0·78, 0·86). Although no evidence of between-study heterogeneity was found (I 2=0·0 %, P=0·62), we performed a subgroup analysis based on sex, study location, follow-up duration and energy adjustment (Table 2). By sex, the inverse association tended to be stronger for men and women combined (RR 0·80; 95 % CI 0·76, 0·85) compared with women (RR 0·90; 95 % CI 0·77, 1·04) or men (RR 0·85; 95 % CI 0·72, 1·00) separately. However, the difference was not statistically significant (P=0·38). According to study location, no significant difference was found between US and non-US countries (P=0·71). For the duration of follow-up, no statistical differences was seen between long-term (≥10 years) and short-term (<10 years) studies (P=0·53). On the basis of energy adjustments, RR for studies with energy adjustments tended to be stronger (RR 0·82; 95 % CI 0·77, 0·86) than studies without energy adjustments (RR 0·84; 95 % CI 0·73, 0·97). However, there was no statistically significant difference (P=0·68). As shown in Fig. 3(b), meta-regression of the studies( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 – Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Pereira, O’Reilly and Augustsson 9 , Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 – Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 , Reference Crowe, Key and Appleby 19 , Reference Eshak, Iso and Date 20 , Reference Pietinen, Rimm and Korhonen 22 , Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 ) indicated that cereal fibre intake (g/d) was marginally associated with a lower risk of CVD mortality in a dose–response manner (β=−0·007, P=0·06). No single study influenced the final association, and no evidence of publication bias was found (P=0·16 by Egger’s test, P=0·34 by Begg’s test).

Fig. 4 Forest plots of the association between cereal fibre intake and risk of CVD mortality. RR, relative risk.
Table 2 Subgroup analysis for the association of cereal fibre intake and CVD mortality in prospective studies (Relative risks (RR) and 95 % confidence intervals)
Findings from the meta-analysis on cereal fibre intake and cancer mortality
Results from two studies( Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Holmes, Chen and Hankinson 21 ), including 371 288 participants and 19 489 cancer death cases, revealed a significant inverse relationship between cereal fibre consumption and cancer mortality (RR 0·85; 95 % CI 0·81, 0·89). However, one of these studies had included patients with breast cancer( Reference Holmes, Chen and Hankinson 21 ). No evidence of between-study heterogeneity was found (I 2=0·0 %, P=0·35). Findings from the meta-regression, using log RR of two studies( Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 ), demonstrated a marginally significant inverse relationship between cereal fibre intake (g/d) and risk of mortality from cancer (β=−0·016, P=0·09) (Fig. 3(c)). Excluding any single study did not affect this finding. In addition, no evidence of publication bias was seen (P=0·32 by Begg’s test).
Findings from the meta-analysis on cereal fibre intake and inflammation-related mortality
Results from the meta-analysis on cereal fibre consumption in relation to mortality from inflammatory diseases are presented in Fig. 5. No significant association was observed between cereal fibre intake and inflammation-related mortality (RR 0·83; 95 % CI 0·69, 1·01). Between-study heterogeneity was not statistically significant (I 2=0·0 %, P=0·73). We found that for the included studies( Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 ) there was no significant linear association between cereal fibre intake and inflammation-related mortality (β=−0·024, P=0·32) (Fig. 3(d)). Moreover, excluding no single study affected the overall effect size. No evidence of publication bias was found (P=0·96 by Egger’s test, P=0·60 by Begg’s test).

Fig. 5 Forest plots of the association between cereal fibre intake and risk of mortality from inflammatory diseases. RR, relative risk.
Discussion
We found that high cereal fibre intake was inversely associated with mortality from all causes, CVD and cancer. However, no significant association was found between cereal fibre intake and inflammation-related mortality. The inverse association with CVD mortality did not vary by sex, study location, follow-up duration and energy adjustment.
In the interpretation of our findings, it should be taken into account that in this meta-analysis the highest v. the lowest categories of cereal fibre intake have been used to demonstrate potentially important biological effects. We have also provided linear associations between cereal fibre intake and mortality. However, most nutritionists are wanting to know the appropriate amount of cereal fibre to recommend to the general population. As the range of intakes appeared to vary considerably between included studies, with the highest values in some studies being below the lowest values in other studies, current limited data did not allow us to determine a certain value to recommend. It seems that further studies are required to shed light on this issue in the future.
Several observational studies have shown that dietary fibre intake, in particular cereal fibres, have protective effects against all-cause mortality, CVD events and different types of cancers( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 , Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 , Reference Eshak, Iso and Date 20 , Reference Holmes, Chen and Hankinson 21 , Reference Rimm, Ascherio and Giovannucci 24 , Reference Wolk, Manson and Stampfer 25 ). Findings of our meta-analysis were also in line with most previous publications. However, our findings about all-cause mortality, cancer mortality and inflammation-related mortality should be interpreted with caution, because few studies were available to be included in the analysis. In addition, some studies had included subjects with diabetes and MI in their analysis( Reference He, van Dam and Rimm 3 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 ). Although the majority of studies that were included in our systematic review had reported a significant inverse association between cereal fibre intake and all-cause and CVD mortalities( Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 – Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 , Reference Crowe, Key and Appleby 19 , Reference Pietinen, Rimm and Korhonen 22 , Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 – Reference Wolk, Manson and Stampfer 25 ), some studies did not reach a protective effect of cereal fibre intake on cancer and inflammation-related mortalities( Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 , Reference Holmes, Chen and Hankinson 21 , Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 ). Such results were also seen in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study, in which cereal fibre intake was associated with a lower risk of total and cause-specific death in healthy men and women( Reference Park, Subar and Hollenbeck 8 ). Findings from the Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta-Carotene Cancer Prevention study revealed that cereal fibre intake had stronger inverse association with coronary death than fibre from other sources in Finnish men( Reference Pietinen, Rimm and Korhonen 22 ). Moreover, a study from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition revealed a protective association between cereal fibre intake and CVD mortality. However, there was no significant difference in the association with outcome for fibre from different sources( Reference Crowe, Key and Appleby 19 ). These findings are consistent with a recent meta-analysis in which cereal fibre intake, compared with other sources of dietary fibre, had the strongest inverse association with total mortality( Reference Kim and Je 16 ). Mozaffarian et al.( Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 ) showed that cereal fibre intake was related to a lower risk of CVD events in the elderly, but reported no significant association between cereal fibre intake and CVD mortality. Other investigators have also failed to find a significant association between cereal fibre intake and CVD mortality( Reference Liu, Buring and Sesso 4 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 ). Similar results have also been reached in UK Women’s Cohort study in which neither total dietary fibre nor cereal fibre intake was associated with CVD mortality( Reference Threapleton, Greenwood and Burley 14 ). In the Nurses’ Health Study and Health Professionals Follow-up study with a large healthy population and long-term follow-up duration, an inverse association was seen between cereal fibre intake and mortality( Reference Baer, Glynn and Hu 23 , Reference Rimm, Ascherio and Giovannucci 24 ). Moreover, pooled data of survivors of MI in these two large cohort studies revealed an inverse significant association between cereal fibre intake and all-cause and CVD mortalities( Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 ). Small study population, small number of events( Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 ) and short-term follow-up duration( Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 ) in some of these mentioned studies might explain the lack of a significant association between cereal fibre intake and CVD mortality. It must be noted that when FFQ was used to assess fibre intake in earlier studies an inverse association of dietary fibre intake with risk of mortality from all-causes, CVD and cancer( Reference Liu, Buring and Sesso 4 , Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Threapleton, Greenwood and Burley 14 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 ) was found; however, this protective effect was not reached when diet history was applied for assessment of dietary fibre( Reference Streppel, Ocké and Boshuizen 13 ). Moreover, different dietary fibre definitions among included studies could be problematic, and it might affect the estimates.
Mechanisms by which cereal fibre intake might lower mortality from different causes are unknown. Cereals are one of the richest sources of insoluble fibres with laxative benefits( Reference Slavin 28 ). Dietary fibres have particular effects on the composition of intestinal microbiota( Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 ). Decreased faecal transit time and stool-bulking effect of insoluble fibre might also result in a lower contact of potential carcinogens to the colon( Reference Larsson and Wolk 7 , Reference Stevenson, Phillips and O’Sullivan 29 , Reference Todd, Woodward and Tunstall-Pedoe 30 ). Cereal fibre intake is a marker of other micronutrient and mineral-rich diet related to death caused by chronic diseases( Reference Erkkila, Herrington and Mozaffarian 2 , Reference Mozaffarian, Kumanyika and Lemaitre 5 , Reference Larsson and Wolk 7 , Reference Li, Flint and Pai 12 ). Diets high in cereal fibre are rich in folate, antioxidants, Se, Mg, Cu, phenolic acids, lignans and phytochemicals( Reference Liu, Stampfer and Hu 31 , Reference McEligot, Largent and Ziogas 32 ), which might have a role in the protective association of cereal fibre with mortality. Cereal fibre might lead to lower levels of inflammatory markers including C-reactive protein and TNF-α receptor 2( Reference Huang, Xu and Lee 10 , Reference Buyken, Flood and Empson 15 ). Lower levels of inflammation markers might explain, at least in part, the inverse association of cereal fibre intake with death. Moreover, it has been shown that high intake of cereal fibre was associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes( Reference Slavin 28 ). High intake of cereals rich in insoluble fibres also has protective effects on postprandial blood glucose responses and insulin sensitivity( Reference Ames, Blewett and Storsley 33 ). The interference of cereal fibres with the absorption and digestion of dietary protein and the modulation of the metabolic signature of amino acids by inhibiting the activation of rapamycin/S6 kinase 1 signalling pathway are among the possible mechanisms( Reference Hattersley, Pfeiffer and Roden 34 , Reference Weickert, Roden and Isken 35 ).
This study had several strengths. The first strength is the inclusion of prospective cohort studies that resulted in a large sample size with high statistical power. Although some studies had included patients as subjects in their analysis, we excluded them to reach findings generalisable to a healthy population. Most studies included in our meta-analysis had adjusted for confounding factors. However, the possibility of residual confounders cannot be excluded. Some limitations also need to be considered. Differences in sampling methods and dietary intake assessment tools might contribute to the variation in study findings. Because cereal fibre intake was assessed by FFQ in most included studies, measurement errors were inevitable. Moreover, different definitions used for categorisation of fibre consumption might result in mis-classifications. In addition, different definitions of cereal fibre among studies might also affect the associations. The possible relationship between cereal fibre consumption and healthier lifestyle might also attenuate true associations. Although we did not find publication bias, it is not easy to exclude such bias in any meta-analysis.
In conclusion, we found an inverse association between cereal fibre intake and mortality from all causes, CVD and cancer. No significant association was observed between cereal fibre and inflammation-related mortality.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Research Council of the Food Security Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran.
The financial support for conception, design, data analysis and manuscript drafting comes from Food Security Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran.
M. H. and P. S. contributed to conception, design, search, statistical analyses, data interpretation and manuscript drafting. S. B. K. contributed to design, search and data interpretation. A. E. contributed to conception, design, statistical analyses, data interpretation and manuscript drafting. A. E. supervised the study. All the authors approved the final manuscript for submission.
M. H., P. S., S. B. K. and A. E. declared no potential conflicts of interest.










