No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 August 2017
From an analytical solution to the Boltzmann-Poisson equations for a thin, vertically isothermal self-gravitating disk with the assumptions that the mass spectrum of stars is expressible as an inverse power-law and the velocity dispersion perpendicular to the plane follows a law of the form  we have obtained a vertical height distribution of planetary nebulae:
we have obtained a vertical height distribution of planetary nebulae: 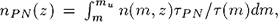 where
where  being the potential at z. Figure 1 shows a normalised height distribution for various values of V0 where we have assumed a Salpeter slope, a ρ(o) = 0.10M ⊙ pc −3 and set m∗ = m l = 1.0m ⊙. Figure 2 shows filled circles obtained from the observational sample of Daub (1982, ApJ 260, 612) superposed on the theoretical distributions. Although there is agreement for large values of z, closer to the plane the observational sample falls below the theoretical curves. Since the observational sample is size-limited, we may be missing a larger fraction of small nebulae closer to the plane. It is also possible a single value of V o is not a correct representation of reality as these nebulae originate from stars of greatly differing ages and V o may have changed over the lifetime of the Galactic disk.
being the potential at z. Figure 1 shows a normalised height distribution for various values of V0 where we have assumed a Salpeter slope, a ρ(o) = 0.10M ⊙ pc −3 and set m∗ = m l = 1.0m ⊙. Figure 2 shows filled circles obtained from the observational sample of Daub (1982, ApJ 260, 612) superposed on the theoretical distributions. Although there is agreement for large values of z, closer to the plane the observational sample falls below the theoretical curves. Since the observational sample is size-limited, we may be missing a larger fraction of small nebulae closer to the plane. It is also possible a single value of V o is not a correct representation of reality as these nebulae originate from stars of greatly differing ages and V o may have changed over the lifetime of the Galactic disk.