Review Article
Transcriptional regulation of seed storage protein genes in Arabidopsis and cereals
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2011, pp. 247-254
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Article
The reduction of seed-specific dehydrins reduces seed longevity in Arabidopsis thaliana
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2011, pp. 165-173
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Review
Progress in research on dry afterripening†
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2011, pp. 69-80
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Opinion
Making the case for plant diversity
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2010, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Invited Review
Starch biosynthesis in developing seeds
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2010, pp. 5-32
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Article
Oxygen interacts with priming, moisture content and temperature to affect the longevity of lettuce and onion seeds
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2011, pp. 175-185
-
- Article
- Export citation
Seed dormancy and germination in Vitis amurensis and its variation
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2011, pp. 255-265
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Opinion
Granivore seed-size preferences
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2011, pp. 81-83
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Article
Non-deep complex morphophysiological dormancy in seeds of the Iberian Peninsula endemic geophyte Merendera montana (Colchicaceae)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2011, pp. 267-281
-
- Article
- Export citation
Temperature control of seed germination in Fritillaria tubiformis subsp. moggridgei (Liliaceae) a rare endemic of the South-west Alps
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2010, pp. 33-38
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Papers
Tight translational control by the initiation factors eIF4E and eIF(iso)4E is required for maize seed germination
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2011, pp. 85-93
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Article
Cathodic amelioration of the adverse effects of oxidative stress accompanying procedures necessary for cryopreservation of embryonic axes of recalcitrant-seeded species
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2011, pp. 187-203
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Papers
Rice seed quality development and temperature during late development and maturation
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2011, pp. 95-101
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Article
Germination characteristics of Syngonanthus seeds (Eriocaulaceae) in campos rupestres vegetation in south-eastern Brazil
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2010, pp. 39-45
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pea and bean germination and seedling responses to temperature and water potential
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2011, pp. 205-213
-
- Article
- Export citation
Morphology, anatomy and germination response of heteromorphic achenes of Anthemis chrysantha J. Gay (Asteraceae), a critically endangered species
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2011, pp. 283-294
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Papers
Timing of seed dispersal and dormancy, rather than persistent soil seed-banks, control seedling recruitment of woody plants in Neotropical savannas
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2011, pp. 103-116
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Article
Deep simple morphophysiological dormancy in seeds of the basal taxad Cephalotaxus
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2011, pp. 215-226
-
- Article
- Export citation
Seed persistence in the soil on eroded slopes in the hilly-gullied Loess Plateau region, China
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2011, pp. 295-304
-
- Article
- Export citation
Seed mass and shape are related to persistence in a sandy soil in northern China
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2010, pp. 47-53
-
- Article
- Export citation

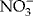 ) or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD
) or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD