Article contents
ANALYTICAL RESULTS ON THE SERVICE PERFORMANCE OF STOCHASTIC CLEARING SYSTEMS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 November 2020
Abstract
Stochastic clearing theory has wide-spread applications in the context of supply chain and service operations management. Historical application domains include bulk service queues, inventory control, and transportation planning (e.g., vehicle dispatching and shipment consolidation). In this paper, motivated by a fundamental application in shipment consolidation, we revisit the notion of service performance for stochastic clearing system operation. More specifically, our goal is to evaluate and compare service performance of alternative operational policies for clearing decisions, as quantified by a measure of timely service referred to as Average Order Delay (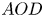 $AOD$). All stochastic clearing systems are subject to service delay due to the inherent clearing practice, and
$AOD$). All stochastic clearing systems are subject to service delay due to the inherent clearing practice, and 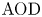 $\textrm {AOD}$ can be thought of as a benchmark for evaluating timely service. Although stochastic clearing theory has a long history, the existing literature on the analysis of
$\textrm {AOD}$ can be thought of as a benchmark for evaluating timely service. Although stochastic clearing theory has a long history, the existing literature on the analysis of 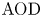 $\textrm {AOD}$ as a service measure has several limitations. Hence, we extend the previous analysis by proposing a more general method for a generic analytical derivation of
$\textrm {AOD}$ as a service measure has several limitations. Hence, we extend the previous analysis by proposing a more general method for a generic analytical derivation of 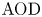 $\textrm {AOD}$ for any renewal-type clearing policy, including but not limited to alternative shipment consolidation policies in the previous literature. Our proposed method utilizes a new martingale point of view and lends itself for a generic analytical characterization of
$\textrm {AOD}$ for any renewal-type clearing policy, including but not limited to alternative shipment consolidation policies in the previous literature. Our proposed method utilizes a new martingale point of view and lends itself for a generic analytical characterization of 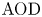 $\textrm {AOD}$, leading to a complete comparative analysis of alternative renewal-type clearing policies. Hence, we also close the gaps in the literature on shipment consolidation via a complete set of analytically provable results regarding
$\textrm {AOD}$, leading to a complete comparative analysis of alternative renewal-type clearing policies. Hence, we also close the gaps in the literature on shipment consolidation via a complete set of analytically provable results regarding 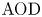 $\textrm {AOD}$ which were only illustrated through numerical tests previously.
$\textrm {AOD}$ which were only illustrated through numerical tests previously.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences , Volume 36 , Issue 2 , April 2022 , pp. 217 - 236
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2020. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 2
- Cited by


