Article contents
Three species of Exorchis Kobayashi, 1921 (Digenea: Cryptogonimidae) in the East-Asian region: morphological and molecular data
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 July 2021
Abstract
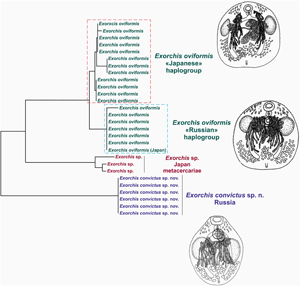
New data have been obtained for three representatives of Exorchis; Exorchis convictus sp. n., Exorchis oviformis and Exorchis sp., from fish in the East-Asian region. For the first time, based on combined sequences of the ITS2 rDNA region and the 28S rRNA gene, Exorchis is confirmed to belong Cryptogonimidae. Based on analysis of a mitochondrial marker (cox1), the ‘Japanese’ and ‘Russian’ haplogroups are identified for E. oviformis isolated from Silurus asotus. One specimen of E. oviformis obtained in Japan is identical to the ‘Russian’ haplotype. Haplotype patterns are also observed for metacercariae of Exorchis sp. from Tanakia lanceolata and Carassius sp. fish in Kyushu Island (Japan).
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 3
- Cited by



