Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 April 2022
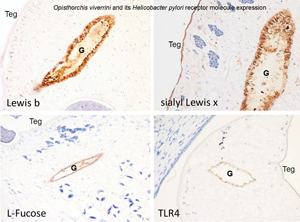
Recent reports implicate both the liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini as a reservoir of Helicobacter pylori within the human gastrointestinal tract and H. pylori in the pathogenesis of opisthorchiasis-associated cholangiocarcinoma. We postulated that adherence of bacterial ligands to host receptors initiates colonization of the live fluke by H. pylori and here we aimed to assess the molecular interaction between O. viverrini and H. pylori by investigating host receptors for H. pylori in the fluke. Several known receptors of H. pylori including Lewis B, sialyl-Lewis X, Toll-like receptor 4 and L-fucose were detected immunohistochemically and histochemically by focusing analysis on the gut epithelium and tegument of the adult stage of the fluke. The frequency of detection of Lewis B, sialyl-Lewis X, TLR4 and L-fucose in 100 individual worms was 3, 3, 19 and 70%, respectively. Detection of H. pylori by a diagnostic ureA gene-based PCR assay revealed the presence of H. pylori in individual O. viverrini worms in 41 of 49 (79%) worms examined. In addition, numbers of bacteria decreased in a dose- and time-dependent fashion following exposure to fucosidase. These findings suggested that L-fucose represents a tractable receptor for H. pylori that can mediate bacterial colonization of the gut of O. viverrini.