No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 February 2011
The temperature dependence of the in-plane C11 C22. C12 and C66 modes between 80 and 260 K of superconducting crystals of Bi2Sr2Ca1Cu208 have been obtained via the measurements of ultrasonic-velocities. The anisotropic elasticity in the a-b plane of single crystal Bi2 Sr2Ca1Cu2O8 is manifest. The shear modulus of sound propagation along the [110] with the 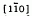 polarization has been also calculated and shows an overall trend of softening over a wide temperature range above Tc. The shear modulus C6 6 shows three obvious softening minima around 240–250 K, 150 K and 100 K.
polarization has been also calculated and shows an overall trend of softening over a wide temperature range above Tc. The shear modulus C6 6 shows three obvious softening minima around 240–250 K, 150 K and 100 K.