Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 February 2020
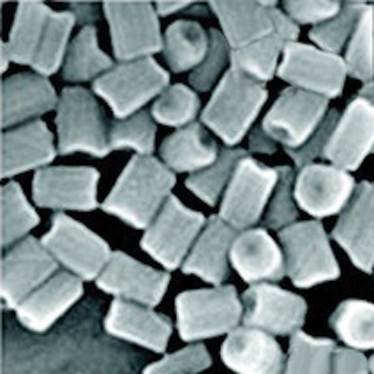
Self-assembly techniques are powerful and efficient methods for the synthesis of nanoscale materials. Using these techniques and their combination with other bottom-up fabrication processes, materials with hierarchical features can be produced with form and function in multiple length scales. We synthesize multifunctional nanoparticles through surfactant-assisted noncovalent interactions using nanoparticle building blocks. Self-assembly of these nano-building blocks results in functional materials that exhibit well-defined morphologies and hierarchical architectures for a wide range of applications. Hierarchically structured porphyrin nanocrystals can be synthesized through surfactant micelle-confined noncovalent interactions of photoactive porphyrins. We can amplify the intrinsic advantages of individual photoactive porphyrins by engineering them into well-defined active nanostructures. Through kinetic control, these nanocrystals exhibit precisely defined size, shape, and spatial arrangement of the individual porphyrins, which facilitates intermolecular mass and energy transfer. These self-assembly techniques provide remarkable flexibility to design morphologies and architectures that produce desirable properties for practical applications including photocatalysis, photodegradation, and phototherapy.
This article is based on the MRS Mid-Career Researcher Award presentation given by Hongyou Fan, Sandia National Laboratories and The University of New Mexico, at the 2019 MRS Spring Meeting in Phoenix, Ariz.