Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 August 2018
We study almost prime solutions of systems of Diophantine equations in the Birch setting. Previous work shows that there exist integer solutions of size 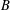 $B$ with each component having no prime divisors below
$B$ with each component having no prime divisors below 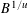 $B^{1/u}$, where
$B^{1/u}$, where  $u$ equals
$u$ equals 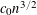 $c_{0}n^{3/2}$,
$c_{0}n^{3/2}$,  $n$ is the number of variables and
$n$ is the number of variables and 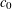 $c_{0}$ is a constant depending on the degree and the number of equations. We improve the polynomial growth
$c_{0}$ is a constant depending on the degree and the number of equations. We improve the polynomial growth 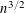 $n^{3/2}$ to the logarithmic
$n^{3/2}$ to the logarithmic 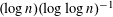 $(\log n)(\log \log n)^{-1}$. Our main new ingredients are the generalization of the Brüdern–Fouvry vector sieve in any dimension and the incorporation of smooth weights into the Davenport–Birch version of the circle method.
$(\log n)(\log \log n)^{-1}$. Our main new ingredients are the generalization of the Brüdern–Fouvry vector sieve in any dimension and the incorporation of smooth weights into the Davenport–Birch version of the circle method.