Article contents
Surface plasma waves induced electron acceleration in a static magnetic field
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 June 2016
Abstract
The acceleration of an electron beam by surface plasma waves (SPW), in the presence of external magnetic field parallel to surface and perpendicular to direction of propagation of SPW has been studied. This wave propagating along the 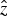 $\hat z$-axis is excited using Kretschmann geometry, having maximum amplitude at the metal–vacuum interface. Equations of motion have been solved for electron energy and trajectory. The electron gains and retains energy in the form of cyclotron oscillations due to the combined effect of the static magnetic field and SPW field. The energy gained by the beam increases with the strength of magnetic field and laser intensity. In the present scheme, electron beams can achieve ~15 KeV energy for the SPW amplitude A1 = 1.6 × 1011 V/m, plasma frequency ωp = 1.3 × 1016 rad/s and cyclotron frequency ωc/ωp = 0.003.
$\hat z$-axis is excited using Kretschmann geometry, having maximum amplitude at the metal–vacuum interface. Equations of motion have been solved for electron energy and trajectory. The electron gains and retains energy in the form of cyclotron oscillations due to the combined effect of the static magnetic field and SPW field. The energy gained by the beam increases with the strength of magnetic field and laser intensity. In the present scheme, electron beams can achieve ~15 KeV energy for the SPW amplitude A1 = 1.6 × 1011 V/m, plasma frequency ωp = 1.3 × 1016 rad/s and cyclotron frequency ωc/ωp = 0.003.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2016
References
REFERENCES
- 2
- Cited by


