Research Article
Reproductive, genetic and ecological evidence that Actinia equina var. mesembryanthemum and var. fragacea are not conspecific
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 79-93
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Energy budget for a population of the limpet Patella vulgata
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 627-646
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Startle Response in Herring: The Effect of Sound Stimulus Frequency, Size of Fish and Selective Interference With The Acoustico-Lateralis System
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 871-879
-
- Article
- Export citation
Long-term trends in the distribution, abundance and seasonal occurrence of larvae of mackerel (Scomber scombrus L.) around the British Isles, 1948–1978
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 343-358
-
- Article
- Export citation
Epithelial sensory structures of trochids
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 95-106
-
- Article
- Export citation
The morphology of Patella spp. juveniles in Britain, and some phylogenetic inferences
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 647-666
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Age And Growth of Callista Chione
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 881-883
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the distribution of the intertidal barnacles Chthamalus stellatus, Chthamalus montagui and Euraphia depressa
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 359-380
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ammonia excretion by Nassarius reticulatus and Buccinum undatum (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia) during starvation and after feeding
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 381-390
-
- Article
- Export citation
Underwater television observations on the intertidal movements of shore crabs, Carcinus maenas, across a mudflat
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 107-116
-
- Article
- Export citation
Patterns of Variation in The Prosome Length of Overwintering Stage V Copepodites of Calanus Finmarchicus in The Firth of Clyde
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 885-899
-
- Article
- Export citation
The opening response of mussels (Mytilus edulis) exposed to rising sea-water concentrations
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 667-678
-
- Article
- Export citation
A re-examination of mucus feeding by the sea cucumber Leptopentacta ( = Cucumaria) elongata
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 679-683
-
- Article
- Export citation
The provision of oxygen to developing eggs by female shore crabs (Carcinus maenas)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 117-128
-
- Article
- Export citation
Visual predation by a marine cyclopoid copepod, Corycaeus anglicus
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 391-399
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Light Organs of Sepiola Atlantica and Spirula Spirula (Mollusca: Cephalopoda): Bacterial and Intrinsic Systems in The Order Sepioidea
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 901-916
-
- Article
- Export citation
Body cooling as a supplement to anaesthesia for fishes
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 129-131
-
- Article
- Export citation
Observations on the rate of production of external ridges on the shell of Pecten maximus in the laboratory
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 401-411
-
- Article
- Export citation
The effects of lowered salinity upon Branchiostoma lanceolatum from the English Channel
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 685-689
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fish in Salps: the Association of Squaretails (Tetragonurus Spp.) With Pelagic Tunicates1
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2009, pp. 917-927
-
- Article
- Export citation

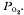 . The bubbling of air during the emersion response is sufficient to raise the oxygen tension of the water surrounding the eggs and is thus an attempt by the parent animal to maintain the oxygen uptake of the developing young. If left in a standing body of hypoxic sea water release of larvae is deferred until well-aerated conditions next prevail. Thus if the berried female is trapped in a rock pool the encroaching tide may act as a releasing stimulus which is of adaptive significance to the dispersal and survival of the larvae. When female crabs submerged in warm water (25 °C) bubbled cool air past the egg mass this had no significant cooling effect. The thermal tolerance of the developing eggs was low, rate of oxygen uptake being limited by temperature rises above 25 °C.
. The bubbling of air during the emersion response is sufficient to raise the oxygen tension of the water surrounding the eggs and is thus an attempt by the parent animal to maintain the oxygen uptake of the developing young. If left in a standing body of hypoxic sea water release of larvae is deferred until well-aerated conditions next prevail. Thus if the berried female is trapped in a rock pool the encroaching tide may act as a releasing stimulus which is of adaptive significance to the dispersal and survival of the larvae. When female crabs submerged in warm water (25 °C) bubbled cool air past the egg mass this had no significant cooling effect. The thermal tolerance of the developing eggs was low, rate of oxygen uptake being limited by temperature rises above 25 °C.