Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 March 2009
In the first part of this work a higher-order solution of the anharmonic oscillator equation describing the nonlinear rippled equilibrium state of magnetically focused, partially neutralized electron beams is given. Thus, using the method of harmonic balance, we derive a ripple-&litude solution of the form
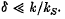
where ø=ω1t+β0,ω1 being the nonlinear proper frequency and β0 a phase shift depending on the initial conditions. In the second part of the work we carry out a stability analysis of the nonlinear equilibrium state found in the first part with respect to long- and short-wavelength surface space-charge perturbations. In the framework of a local approximation the wave equation for the rippled beam is found to be a Hill type of equation which contains harmonic terms up to cos 3kSz (ks is the wavenumber of the ripple). This equation is solved by a resonant-mode coupling method; coupling of fast-fast, slow-slow and slow-fast waves is considered. The growth rates and band widths for different possible wave couplings are derived and compared.