Article contents
Optical properties of Si nanowires: Dependence on substrate crystallographic orientation and light polarization
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 March 2015
Abstract
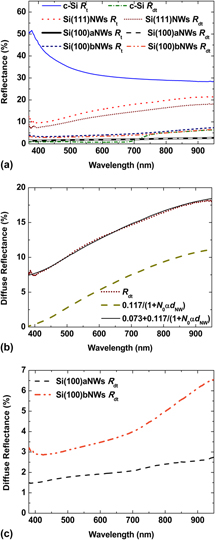
Optical properties of Si nanowire (SiNW) arrays prepared on p-doped Si(111) and Si(100) substrates were studied. SiNWs were synthesized by self-assembly electroless metal deposition nanoelectrochemistry in an ionic silver HF solution through selective etching. Total reflectance (Rt) and total diffuse reflectance (Rdt) of SiNWs change drastically in comparison to polished Si. To understand these changes, diffuse reflectance (Rd) with polarized incident light was studied. For samples prepared on Si(111), the wave length integrated Rd (wIRd) shows maxima at certain angles of incidence θ, regardless of the incident light polarization. For samples prepared on Si(100), wIRd increases with θ and depends on incident light polarization. Also, Rd spectra show structures due to interference effects. Therefore, SiNWs prepared on Si(100) can be considered as thin films whose refractive index depends on light polarization. Moreover, Rdt of SiNWs prepared on Si(111) can be modeled as an ensemble of diffuse reflectors.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2015
References
REFERENCES
- 6
- Cited by


