Article contents
On the in situ study of Li ion transport in transmission electron microscope
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 November 2014
Abstract
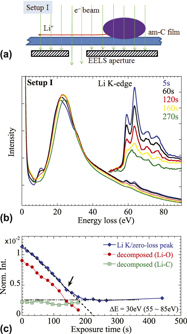
For understanding the atomic processes involved, in situ observation at near-atomic spatial resolution is needed in the studies of lithium ion battery materials. We show that the Li transport and the lithiation of carbon atoms may be triggered by the electron beam in an electron microscope, together with simultaneous real-time monitoring of electron energy-loss spectroscopy to reveal the chemical state of the species. The local electric field induced in an electrolyte particle by an electron beam acts on Li ions, resulting in Li transport and reaction with carbons. This process closely mimics the charging process of an electrochemical battery charge cycle, without an external power supply. We find that the lithium transport occurs in the form of Li+.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 30 , Issue 3: Focus Issue: In-situ and Operando Characterization of Materials , 14 February 2015 , pp. 424 - 428
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2014
References
REFERENCES
- 10
- Cited by


