Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 October 2012
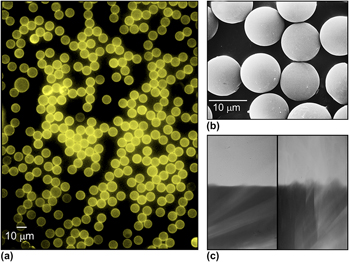
Semiconductor quantum dots (QDs)-doped polystyrene (PS) microspheres with high luminescence were prepared using a self-assembly approach. Hydrophobic CdSe/ZnS QDs were first carboxylized by ligand exchange using mercaptocarboxylic acid. PS microspheres were separately encapsulated with polyethyleneimine via electrostatic interactions and then adsorbed with the carboxyl QDs to form QDs-doped microspheres. We then characterized the combinations using optical, electrical, and mechanical approaches and obtained the following findings: (i) microspheres can be fully coated by QD nanoparticles with a coverage rate of 1.0 pmole/cm2, in which QDs were evenly distributed on the surfaces; (ii) the anchored QDs exhibited similar optical property as they performed in isolated suspension; and (iii) the fluorescence of QDs-doped microspheres remained intact after stressed by ultrasound-induced cavitation, demonstrating the robustness of interactions between QDs and microspheres. The self-assembly approach developed in this study offered a facile and controllable strategy for preparation of QDs-encoded microparticles with high luminescence and stability.