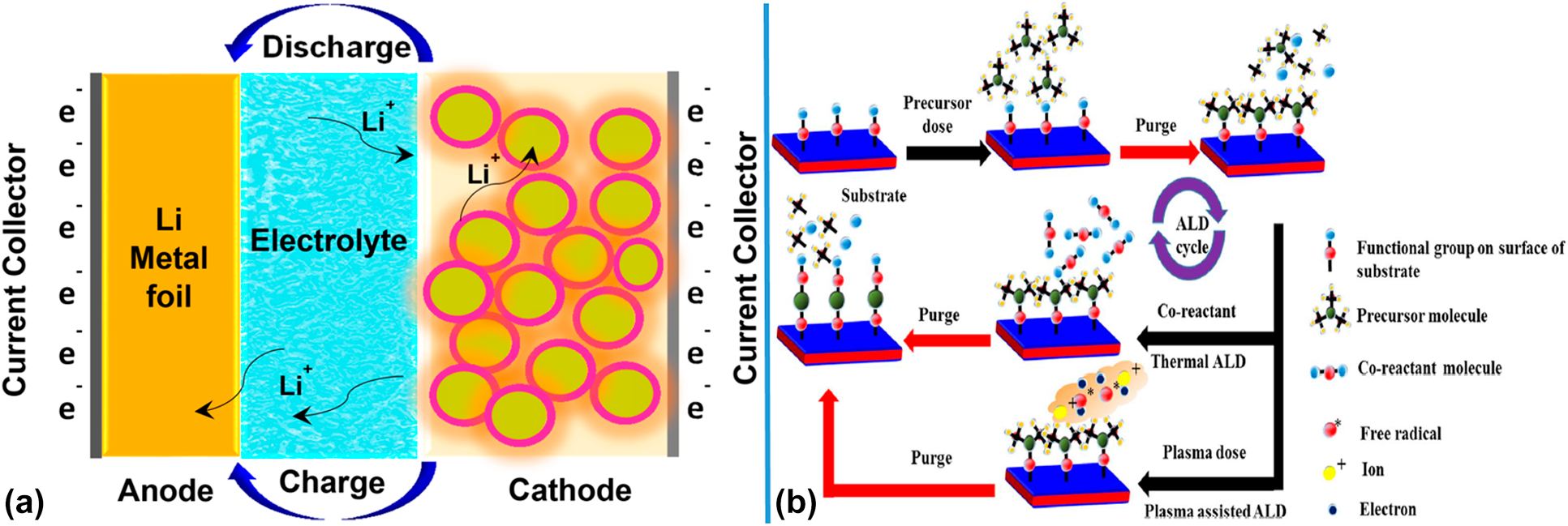
Introduction
In the last few decades, electrochemical energy storage has witnessed tremendous progress [Reference Ding, Cano, Yu, Lu and Chen1], where the high energy batteries have drawn the most attention, owing to their ever-growing operation in a wide range of applications, for instance, portable electronic devices, electrical vehicles (EVs), and stationary energy storage [Reference Reinhardt2]. Development of the cathode materials has a very important impact on lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) for achieving high energy density to fulfill EVs requirements. LIBs are regarded as the new generation of green high-energy batteries with excellent performance, and have become one of the elements of the high-tech development [Reference Y, Zhang and Chen3]. Benefitting from its numerous advantages, that is, high voltage, high capacity, low consumption, no memory effect, no pollution, small volume, small internal resistance, less self-discharge, and satisfactory life cycles, LIBs have been applied to many fields such as mobile phones, motorbikes, light bulbs, laptops, clocks, and other digital electronics [Reference Maleki Kheimeh Sari and Li4]. Nevertheless, application of LIBs in EVs, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) undergoes many obstacles due to the requirement of high energy density [Reference Shobana5, Reference Pinegar and Smith6, Reference Li7]. The diagram of LIBs work principle is shown in Fig. 1(a). As an important component, cathode electrode plays a key role in LIBs because of its large proportion (the mass ratio of cathode to anode electrode usually varies from 3:1 to 4:1), which determines the cost of LIBs and achievement of high energy density to fulfill electric vehicle requirements [Reference Wu8]. One of the most promising cathode materials is LiMnxCoyNi1−x−yO2 (LMCNO) cathodes materials, which includes LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2, Li1.2Mn0.54Co0.13Ni0.13O2, LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2, LiCoO2, LiMn2O4, LiNi0.5Mn0.3Co0.2O2, and LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4, among others [Reference Zhang9]. These LMCNO cathodes can potentially meet the sustainability, environmentally friendliness and high energy density required for the next-generation LIBS. However, there are several pitfalls associated with LMCNO cathodes, such as side reactions with electrolyte, structure degradation, phase transitions, and impedance increase during charge and discharge processes [Reference Zhang10]. Many researchers have done decent efforts to solve these problems. Coating and doping strategies have been widely employed to modify LMCNO cathodes. Coating approach contributes to suppressing the occurrence of side reactions and accelerating the transport of lithium ions [Reference Becker11, Reference Guo12, Reference Ding13, Reference Wu14, Reference Billaud15], whereas doping approach contributes to stabilizing the crystal structure and improving the reaction kinetics [Reference Sim16, Reference Lv17, Reference Song18, Reference Do19, Reference Yao20]. To obtain an excellent coating structure, various preparation methods have been developed, including high temperature sintering [Reference Gu and Schuth21], sol–gel method [Reference Cheng22], chemical vapor deposition (CVD) [Reference Yang23], liquid phase [Reference Diao24], hydrothermal [Reference Liu25] and solvothermal method [Reference Jurng26], atomic layer deposition (ALD) [Reference Jiang27], and solution-based precipitation [Reference Sharifi Rad and Ghorbanzadeh28]. Indeed, a large number of coating materials have been used, including metals (e.g., Ag [Reference Liu29]), metal oxides (e.g., Al2O3 [Reference Luo, Sun and Liu30], SnO2 [Reference Park31], ZrO2 [Reference Jin32], MnO2 [Reference Şahan33], Fe2O3 [Reference Xiao, Wang, Zhang, He, Yang, Tang, An and zheng34], MgO [Reference Deng35], and ZnO [Reference Shobana5]), fluorides (BiOF [Reference Zheng, Xu, Gu, Xiao, Browning, Yan, Wang and Zhang36] and AlF3 [Reference Sun, Zan and Zhang37]), metal phosphates (Li3PO4 [Reference Qing38], FePO4 [Reference Song39], AlPO4 [Reference Hu40], and Li4P2O7 [Reference Shen41]), and carbon, among others [Reference Ku42, Reference Liu43, Reference Hu44]. Notably, the coating layers obtained by traditional methods are generally thick, which is not suitable for yielding superior electrochemical performances [Reference Berdova45]. As an emerging coating technology, ALD displays a noticeable improvement in deposition of ultrathin coating materials due to its atomic-level precision, and has been widely applied in construction of the coating layers on LMCNO substrate materials [Reference Jiang27]. Currently, as an important technology, ALD has emerged for depositing thin films and powders in many fields, such as microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) [Reference Kan46], optoelectronic materials and devices [Reference Park47], DRAM and MRAM dielectric layers [Reference Oviroh48], films [Reference Kim49], and electrodes [Reference Switzer50]. ALD has a broad potential application in micro-nanoelectronics and nanomaterials because of its highly controllable deposition parameters (thickness, composition, and structure), excellent deposition uniformity, and consistency [Reference Puurunen51]. In the ALD technique, the coating materials are deposited on the substrate surface by a series of repetitive, distinct, irreversible, and self-limiting chemical reactions, where an atomic-level precision can be obtained.

Figure 1. (a) Schematic illustration of transfer of ions inside LIBs. Reprinted with permission from Sarkar et al. 2017. Copyright (2017) American Chemical Society. (b) Schematic diagram of ALD reaction mechanism. Reprinted with permission from Mallick et al. 2019. Copyright (2017) The Electrochemical Society.
In this article, we summarize the application of ALD in the design and preparation of LMCNO coating structure, including coating layer thickness, coating material type, and crystal structure in detail. Particularly, the electrochemical performance enhancement intrinsic reasons for ALD coating in LMCNO substrate material are thoroughly discussed in this review. Finally, based on the as-reported ALD enhancement strategies, the development direction of ALD coating structure in LMCNO LIBs cathode materials is proposed.
ALD mechanism
The conception of ALD was firstly introduced by Prof. Aleskovskii in 1952 [Reference O'Neill52]. Later, he and Prof. Kolt'sov published the principle of ALD with the title of “Molecular Layering” (ML). Tuomo Suntola et al. firstly used ALD technology in 1970 to produce a high-quality large-area flat panel with electroluminescent thin film, that is, polycrystalline luminescent ZnS: Mn and amorphous alumina insulating films [Reference Kim49]. This method was originally used for growth of epitaxial films, so it is known as ALE (atomic layer epitaxy), which focused on the surface action, and the growth process of atomic layer films which were alternately deposited. Later, Suntola's group found that molecular precursors, named ZnCl2 and H2S, produced a more production-worthy process on account of operability under viscous flow criteria rather than requiring a fine vacuum environment. These early endeavors were guided toward electronic applications and concentrated primarily on micrometer-thickness films requesting several thousands of ALD cycles [Reference Parsons53]. Afterwards, ML was developed by Professors Aleskovskii and Koltsov from the USSR Academy of Sciences [Reference Aleskovsky and Koltcov54], where metal oxides were deposited using alternating exposure of metal chloride precursors and water. Several conference papers from the early 1960s described TiO2 and GeO2 ML, but these studies were overlooked by researchers from outside the Soviet Union because they were published only in Russian [Reference Mallick55]. In Japan, the ALD process was called molecular layer epitaxy. The term epitaxy refers to the growth of the crystal structure of the deposited film and the underlying substrate. ALD coatings are generally amorphous in nature. Therefore, “depositing” rather than “stretching” is more adaptable to describe all processes belonging to this category, and this is reflected in modern nomenclature, albeit with limited unequal examples. Additionally, molecular layer deposition (MLD) has been developed as an analogy to ALD, in which a thin film polymer layer is deposited using a preferred organic compound. The microchemical group has demonstrated that the coverage of the saturated surface of the metal oxygen species can be controlled by adjusting the spatial bulk of the precursor ligand or by preheating the substrate for partial surface dehydroxylation.
An increase in ALD research and development began in the late 1990s and early 2000s and continues to this day. The variety of ALD materials can be greatly expanded, including most of elements in the periodic table as well as oxides, nitrides, sulfides, and metals. Hitherto, the ALD technique has served as the most extensive coating technology for oxides. A schematic of ALD process is shown in Fig. 1(b) [Reference Johnson, Hultqvist and Bent56]. The ALD technique has several distinct advantages including (i) precise control on the film thickness, crystallinity, and composition compared with other techniques (e.g., CVD and electrochemical deposition) can often be controlled at the angstrom (Å) level [Reference Detavernier57]; (ii) excellent chemical selectivity: ALD is a deposition technique based on the chemisorption of species. Therefore, the ALD deposition occurs only in certain coordinates [Reference Wen58]; (iii) Excellent surface uniformity: ALD offers the capability of film deposition with ultra-high conformity [Reference Cherkashinin59].
In addition, ALD usually is thought as a bottom-up synthetic route. The desired ALD materials are synthesized via two or more steps with a variety of purge steps. As shown in Fig. 1(b), in the first step, the substrate is exposed to the precursor (precursor A). In this step, precursor A is chemisorbed on the surface of substrate to initiate surface reactions between the precursor A and the functional group of the substrate. These surface reactions continue to occur until all available substrate functional groups are consumed. Generally, single or several by-products could be released from the initial surface reactions. Therefore, the second step of ALD involves the removal of the by-products as well as unreacted precursor A by purging the inert gas. Then, in the third step, self-limited ALD reactions happen between the co-reactant on the surface of the substrate and the chemisorbed precursor A. This is the second purge step and produces new fresh active sites with functional groups on the surface of the substrate by releasing by-products and unreacted co-reactants which can initiate the next cycle. Each reaction step of ALD is carried out by self-limited surface reactions between the precursor and the substrate, each of which involves the creation of a new starting surface of the chemisorption process. Example of ALD Al2O3: the hydroxyl group on the surface of the substrate reacts with trimethylaluminum, and the methane and excess trimethylaluminum are removed in the “purge” stage. The complex formed by the reaction of the hydroxyl group on the surface of the substrate with trimethylaluminum reacts with water to form alumina and methane, and the methane and excess water are removed in the “purge” stage. ALD cycles can be repeated thousands of times to achieve any desired deposition [Reference Johnson, Hultqvist and Bent56].
Improvement of LiMnxCoyNi1−x−yO2 via ALD
ALD technology has been widely used to construct LMCNO cathodes with a coating structure. In this regard, it is crucial to insure the coating uniformity on the surface of electrode particles so as to suppress the undesired appearance of phase transformation, particle cracking, oxygen gas release, and transition-metal (TM) ion dissolution on the oxide particles surface, which eventually spread toward the bulk during the later charge/discharge process. Thus, the ALD coating technique proposes a unique method to uniformly coat the oxide particles in order to alleviate these degradation phenomena. The electrochemical performance of LiMnxCoyNi1−x−yO2 LIB cathodes based on the ALD coating technology is mainly realized by forming the amorphous phases and the smooth electron transport channels, precise controlling of coating thickness, small amount of doping, separating electrolyte and active material, and stabilizing cathode structure. The previous articles of ALD coating on LMCNO cathodes are summarized in Table I, which clearly confirms the improvement of LMCNO cathode performance by ALD coating. By the ALD treatment, Al2O3 will form a dense oxide film which will decrease side reactions, but Al2O3 film will be corroded by the electrolyte that cannot provide long time protection. The ultrathin Al2O3 film will increase the capacity and cycle stability, but thick Al2O3 film will hinder the diffusion of lithium ions. TiO2 exists in the forms of islands on the surface of LMCNO particles. And TiO2 coating will increase obviously cycle’s stability. ZnO ALD coating layer will allow lithium ions to cross through. The fluoride and phosphate ALD coating will increase cycle capacity.
TABLE I: Nanostructured LMCNO cathode materials generated by ALD.

Remarks: σw: Li+ diffusion coefficient; OT: optimum thickness; CR: capacity retention after 100 cycles; C: current density; P: pristine LMCNO cathodes; @P: ALD-coated LMCNO cathodes; …: no data.
Decreasing side reactions
As it is known, the direct contact between the active materials and the electrolyte could cause side reactions, which decreases the capacity of the battery [Reference You60, Reference Kalyani and Kalaiselvi61]. Meanwhile, the trace water in battery could react with electrolyte to form HF, which corrodes the cathode surface and leads to battery breakdown [Reference Wu62]. Through ALD treatment, a coating layer can be formed on LIB cathode surface, which would protect active materials against erosion from the electrolyte. Similar with the purpose of other coatings [Reference Liu29, Reference Gao63], the main function of the ALD coating layer is to separate electrolyte and active materials, inhibiting the electrolyte corroding the active material, as shown in Fig. 2(c). The side reactions lead to the pristine sample structural degradation and the formation of a thick solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) film during charge/discharge cycles. The direct contacts of active materials with electrolyte results in TMs dissolution and structural phase transition. By ALD coating, the coating layer separates electrolyte and active materials, protects active materials from being eroded by electrolytes, and forms intact and robust SEI film. In addition, according to Gao's research [Reference Laskar64], Figs. 2(a)–2(e) further illustrate that the ALD coating sample can effectively scavenge HF to suppress side reactions with electrolyte and stabilize the structure of cathode particles.

Figure 2. (a, b) Schematic illustration of the pristine LiNi1.5Mn1.5O4 and @LiNi1.5Mn1.5O4 after 350 charge and discharge cycles. Reprinted with permission from Xiao et al. (2017). Copyright (2017) WILEY-VCH. (c) ALD coating separating the active materials from the electrolyte. SEM images of (d) pristine and (e) ALD coated cathodes after cycles. Reprinted with permission from Gao et al. (2018). Copyright (2018) American Chemical Society. (f–k) TEM of LMCNO cathodes after ALD treatment. Reprinted with permission from Laskar et al. (2016), Mohanty et al. (2016), Kong et al. (2014), Zhao et al. (2013), Zhu et al. (2019), Shi et al. (2016). Copyright (2018) American Chemical Society, (2016) Springer Nature, (2014) Elsevier BV, (2013) Elsevier Ltd., (2019) Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, (2016) Elsevier Ltd., respectively.
A uniform and consequent coating layer can be formed by ALD technology on the surface of cathodes, as it is evidently shown in Figs. 2(f)–2(k) from other researches [Reference Zhao and Wang65, Reference Patel, Palaparty and Liang66, Reference Mohanty67, Reference Kong68, Reference Yu, Lin and Huang69, Reference Yu, Gao and Liang70]. These coating layers applied on LMCNO cathodes can effectively suppress side reactions and stabilize the structure, resulting in the enhancement of electrochemical performance. It is believed that there are two primary theories which explain how an ALD coating layer protects the cathode materials. The first theory is that the coated materials replace the active substances which react with HF (such as Al2O3, TiO2), but do not provide protection when the coated material is heavily eroded by HF. The second theory states that the coated material does not react with HF and acts only as a physical barrier (such as AlF3), which provides a longer protection of the active material eroded by HF, with possible sacrificing capacity. According to Yu's research [Reference Song71], using Al2O3 and AlF3 composite ALD coating can create a stable solid permeable interphase layer without sacrificing capacity.
Generally, there are two processes for ALD coating: cathode particle surface coating and pole piece surface coating. Most of the researches use the method of particle surface coating, which is helpful to study the mechanism of the coating layer to protect the cathode material. The pole piece surface ALD coating can separate active materials and electrolyte, but cannot inhibit volume expansion of cathode particles due to Li+ insertion/deinsertion during charge and discharge.
Accelerating lithium diffusion
During charge and discharge, the electrochemical impedance of the pristine LMCNO cathodes increases because of the blockage of lithium diffusion channels, which deteriorates discharge capacity and rate performance. The lithium diffusion can be accelerated by selecting appropriate types of coating materials and coating method. ALD coating can suppress the increase of impendence and accelerate lithium intercalation/deintercalation through the ultrathin coating film and the nature of ALD coating layer.
A flexible structure like a liquid in a disorderly manner with the amorphous phase can benefit the diffusion of lithium [Reference Hayashi, Konishi, Tadanaga, Minami and Tatsumisago72]. Many solid electrolytes are amorphous phase because the flexible structure of the amorphous phase can promote the diffusion of ions [Reference Sakurai73, Reference Xiao74]. According to the previous studies [Reference Switzer50, Reference Song71, Reference Jackson75, Reference Kong76], an amorphous phase forms after ALD treatment on the surface of LMCNO cathodes, which may be owing to ALD deposition temperature, that is, between 100 and 200 °C, which is not hot enough to obtain crystalline phase. These amorphous phases can be clearly observed with uniform and consistent coating layer on the cathode surface in transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) images displayed in Figs. 3(a)–3(e). In addition, X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern further proves that the coating is amorphous in Figs. 3(f)–3(g). The arrangement of atoms or molecules of the amorphous phase is not periodic, resulting in zero diffraction effects on X-rays. It was proved by Kong's research [Reference Chen, Gerdes and Song77] that ALDs deposited ultrathin layers at low temperature and have a slight influence on the structure of host materials. Ultrathin amorphous phase obtained by ALD technology (as shown in Table I) could enhance the electrochemical performance through favoring the lithium diffusion. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) results could attest that the amorphous phase can accelerate lithium ions diffusion and suppress the increase of impedance [Figs. 3(h) and 3(i)].

Figure 3. (a–e) TEM micrograph of @LMCNO cathodes particles, which illustrates the formation of ultrathin coating layer; (f–g) XRD patterns of the pristine and the @LMCNO cathode particles, illustrating the amorphous phase of ALD coating layer; (h, i) EIS spectra and (j–m) Cycle performance of @LMCNO cathodes, illustrating the decrease and effect of thickness on lithium ions transport after ALD treatment; (n) Diagram of smooth electron transport after ALD coating; and (o) Rct of the pristine and ALD coated LMCNO cathodes before and after cycling. Reprinted with permission from Kong et al. (2015), Qin et al. (2016), Deng et al. (2017), Shi et al. (2016), Kong et al. (2016), Zhao et al. (2013), Patel et al. (2016), Gao et al. (2018). Copyright (2015) Elsevier BV, (2016) Royal Society of Chemistry, (2017) Elsevier Ltd., (2016) Elsevier Ltd., (2016) Elsevier BV, (2013) Elsevier Ltd., (2016) American Chemical Society, (2018) American Chemical Society, respectively.
On the other hand, for obtaining an improved electrochemical performance, the thickness of ALD coating needs to be optimized. It can be shown in Figs. 3(j)–3(m) that a thin coating layer cannot effectively protect the active materials from being attacked by the electrolyte, and a thick coating layer causes increased mass transfer resistance and produces more stresses during Li+ intercalation and deintercalation, leading to the discharge capacity decrease. By contrast, an appropriate coating thickness boosts the discharge capacity through speeding up Li+ transportation. ALD operates cyclically in a layer-by-layer manner. The thickness of a single layer deposit is in angstroms level because of its self-limited nature, which can be controlled precisely. Up to now, there have been many studies about ALD coating on the cathodes in LIBs. In previous studies, it was found that the thickness of a single layer coating is not stabilized to a certain number [Reference Jiang27, Reference Laskar64, Reference Patel, Palaparty and Liang66, Reference Mohanty67, Reference Yu, Gao and Liang70, Reference Kong76, Reference Chen, Gerdes and Song77, Reference Laskar78, Reference Ahn79, Reference Deng80, Reference Kong81, Reference Zhu82, Reference Sarkar83, Reference Qin84, Reference Guan and Wang85, Reference Ritala, Kukli, Rahtu, Leskela, Sajavaara and Keinonen86]. However, because of its self-limiting nature, the thickness does not increase when the single layer deposition is saturated. Hence, the thickness of a single deposited layer after saturation stabilizes to a certain value. Speculatively, disparate deposition temperatures [Reference Ma87] and unequal degrees of vacuum in different instruments obtain different thickness. The hypothermia may cause insufficient deposition, and a low vacuum increases the thickness due to the effect of CVD. According to Yu's research [Reference Song71], the formation of Li–M–O (M means metal, e.g., Al) film facilitates the diffusion of lithium during charge and discharge, and consequently increases the discharge capacity.
As summarized in Table I, the values of Li+ diffusion coefficient (σw) obtained from different studies increase after ALD coating. ALD coating can accelerate lithium diffusion through the formation of amorphous phase, and Li–M–O film, with appropriate thickness. Lithium diffusion rate directly affects electrochemical performance. The principle of LIBs charge and discharge is the insertion and extraction of lithium ions from the cathode and anode. Hence, a smooth lithium ion diffusion channel can effectively improve the electrochemical properties of LMCNO cathodes.
Improving electron transport
Generally, the rate performance of a battery can be improved by promoting (i) electronic conduction and (ii) ion diffusion. More conductive agents help to improve the electrochemical performance of LIBs. Some studies have shown that surface electronic conduction is tightly linked to the performance and capacity of LIBs. In previous works, it has been proved that some coating materials, such as graphene oxide (GO) [Reference Huang88], SnO2 [Reference Huang88], and TiOx [Reference Wang89] can either enhance or deteriorate the electron transport depending on their thickness and uniformity. According to Wang's study [Reference Zhao and Wang65], an ultrathin uniform ALD TiO2 coating layer leads to a smoother electron transport compared with the bare sample because of the self-limited ALD process, which allows a controllable and precise deposition of ultrathin films with an excellent uniformity with complicated nanostructures. A schematic of smooth electron transport after ALD TiO2 coating is shown in Fig. 3(n).
EIS measurements can prove the existence of a smoother electron transport after ALD treatment by decreasing Rct (charge transfer resistance) as depicted in Fig. 3(o). The P@ALD samples deliver lower Rct values at the 1st cycle and after cycling. Rct means the obstruction in transfer of charge in the battery; in other words, the resistance to electron and ion transmission inside a battery. It appears that these resistances are reduced after ALD deposition, confirming that electronic transfer at interface of surface film and active materials becomes easier. Moreover, the amorphous phase like a liquid in a disorderly manner not only accelerates lithium diffusion but also benefits the electron transport, owing to participation of both electron and lithium in charge and discharge on the surface of cathodes. The flexible structure of the amorphous phase and EIS measurements both illustrate that ALD coating can effectively reduce the impedance of lithium and electrons during transmission, enhancing the conduction of lithium and electrons.
Stabilizing cathode structure
Structural degradation is one of the main problems of the LMCNO cathodes. For these cathodes, especially layered ones, during Li+ intercalation and deintercalation, lithium ions leave the original site, which cause vacancies, and TM ions move into these vacancies, causing irreversible damage to the crystal structure, resulting in a decrease in LMCNO cycle stability. In addition, TM cations dissolved in electrolyte and volume expansion lead to structural degradation.
Mohanty [Reference Mohanty67] and Zhu [Reference Sarkar83] successfully stabilized the structure by inhibiting phase transition by ALD coating of titanium oxide and aluminum oxide on the surface of LiMO2 (M = Ni, Co, Mn) and NCM811, respectively. The evidence for suppressing phase transition is shown in the Figs. 4(a)–4(g). TEM, selective area electron diffraction (SAED), and dQ/dV curves can confirm that ALD coating can inhibit phase change and yield a stable structure. Furthermore, the oxide coating isolates LIBs layered cathode particles from electrolyte to mitigate the decomposition of electrolyte, and serves as a solid framework to restrict the unexpected phase transition of layers, providing better structural stability and cycle ability [Reference Dai90]. For the layered cathodes, one of the main reasons for phase transformation is charging to higher voltage (≥4.3 V), which induces oxygen loss from the surface that reduces the bonding interaction between the metal atoms and subsequently creates metal cations, which transfer from metal layer to lithium layer, rearranging the bulk structure and triggering structural transformation upon cycling. Additionally, although the structure is damaged during Li+ intercalation/deintercalation, the impedance will increase because the metal ions leave their original position and block the diffusion channel of lithium ions. Nonetheless, it is proved by EIS spectra in Figs. 4(h)–4(j) that the impedance and electrochemical polarity can be mitigated by ALD coating.

Figure 4. TEM and SAED images of the samples (a–c) before and (d–f) after TiO2 ALD coating samples after cycling; (g) dQ/dV profiles of pristine and Al2O3 ALD coated NCM811 in the first and 100th cycles; and (h–j) EIS spectra of uncoated and ALD coated cathodes. Reprinted with permission from Mohanty et al. (2016), Zhu et al. (2019), Patel et al. (2016), Gao et al. (2018). Copyright (2016) Springer Nature, (2019) Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, (2016) American Chemical Society, (2018) American Chemical Society, respectively.
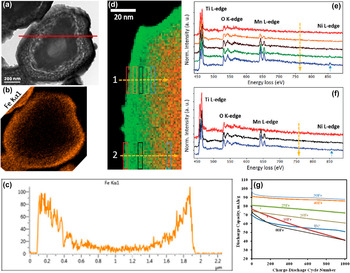
Doping is an effective approach to stabilize structure and improve cycle performance. Bulk doping during materials production aim for suppressing the phase transition [Reference Xiao91, Reference Ye92] on cathodes, but the excessive and unbridled doping will hinder the lithium ions diffusion channels in the bulk structure, resulting in active capacity loss [Reference Song39] at first cycle [Reference Patel93]. Considering the fact that the side reactions primarily happen on the surface of cathodes due to the imbalanced lithium ions movability on the boundary particularly at high current densities [Reference Berdova45], restricting the controllable doping modification within only the surface turns out to be a feasible and promising approach. The presence of defects on the surface of cathode particles is inevitable. According to Patel [Reference Zhang94] and Xiao [Reference Ye92]'s research, the deposited particles can be doped into the lattice structure during the ALD deposition process when the diameter of the pulsed particles is smaller than the defect size. In this regard, verifies that deposited metal ions enter into the structure of cathode particles through SEM, TEM, EDS, and EELS, respectively, as is shown in Figs. 5(a)–5(f). ALD deposition may begin at the structural defects; the ions start taking part in formation of ultrathin oxide films on the surface of cathode particles after the structural defects were saturated [Reference Zhang94]. During the Li+ insertion/deinsertion, formation of Li+ vacancies at deep charging states destabilizes the structure of cathodes. Doping elements can enter the interior of the cathode particles through doping to obtain a stable lattice structure. The occurrence of slight doping by applying ALD, without excessive and unbridled doping materials, can efficiently impede the blockage of Li+ diffusion channels, and consequently enhance the LIBs cathode cycle stability without sacrificing the capacity [e.g., shown in Fig. 5(g)], unlike the other doping methods [Reference Lv17, Reference Song18, Reference Do19, Reference Yao20].

Figure 5. (a) Cross sectional TEM image of an iron oxide ALD coated LiNi1.5Mn1.5O4 particle after 160 cycles; (b) Cross sectional EDS elemental mapping of Fe, and (c) Fe element EDS line scanning with the red line as shown in (a); (d) EELS map for the @TiO2 LiNi1.5Mn1.5O4 particle (Ti: green; Mn: red). (e, f) EELS spectra integrated with the corresponding areas as shown in (d). (g) Discharge capacity of cells made of LiNi1.5Mn1.5O4 particles coated with different thickness of iron oxide at 1C rate. Reprinted with permission from Patel et al. (2016) and Xiao et al. (2017). Copyright (2016) Springer Nature and (2017) Wiley Vch.
ALD coating can stabilize the structure by separating the active materials from electrolyte, because a direct contact between the active materials and the electrolyte will lead to TM ions dissolution into the electrolyte and structural degradation of cathode. With Li+ intercalation and deintercalation, cathode particles suffer from volume expansion, leading to structure damage, but after ALD coating, the coating layer acts like a solid shell encasing the active materials and inhibits the volume expansion. As shown in Table I, in @P samples, the capacity retention increases after ALD treatment on the pristine cathodes. It further proves that ALD coating can stabilize the LMCNO structure during Li+ intercalation and deintercalation.
Conclusion and outlook
In this review, the development and mechanism of ALD technology are broadly outlined. In ALD coating, the self-limited surface reactions between the precursor and the substrate are essential for obtaining a well-defined coating structure. Up to now, ALD has been successfully applied to the LiMnxCoyNi1−x−yO2 cathodes in LIBs, owing to its numerous advantages, such as simplicity of the process, excellent uniformity and consistency, precise control on the coating thickness, and formation of amorphous coating, which satisfy the requirements of LIB cathodes. ALD coating of oxides, fluorides, nitrides, and other metal salts can effectively boost the electrochemical performance of LiMnxCoyNi1−x−yO2 cathodes through suppressing side reactions, stabilizing the structure and accelerating the transport of lithium ions and electrons during charge and discharge process. To further optimize the ALD coating structure and enhance the Li+ storage properties, we made several recommendations for the development of ALD on LiMnxCoyNi1−x−yO2 cathodes as follows: (i) depositing new kinds of substances, such as single inert metals which hardly react with electrolyte and possess an excellent electrical conductivity; (ii) performing other modification treatments after ALD, such as annealing, to achieve a more stable coating structure; and (iii) depositing organic matter, which turns into carbon after annealing to obtain ultrathin and uniform carbon coating layers with excellent electrical conductivities.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support by Doctoral Scientific Research Startup Foundation of Xi’an University of Technology (101-451119016), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (51801153, 51672189 and 21975200), Natural science basic research plan in Shaanxi province of China (2019JLP-04) and Xi’an Science and Technology Project of China (201805037YD15CG21(20)).