Article contents
Synthesis and characterization of highly organized crystalline rutile nanoparticles by low-temperature dissolution-reprecipitation process
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 June 2015
Abstract
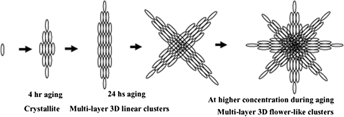
Rutile nanoparticles have been synthesized by acid hydrolysis of titanium isopropoxide by low-temperature dissolution-reprecipitation process. High-resolution transmission electron micrographs of the rutile colloidal solution show needle-shaped rutile nanoparticles with the dimensions of 10–30 nm in diameter and 100–150 nm in length. X-ray diffraction (XRD) data show the existence of only the rutile polymorph in TiO2 powder with a crystallite size of 11.3 nm. The dielectric constant of rutile nanoparticles has been found to be 57 at 10 MHz AC frequency and DC conductance as 2.3 × 10−6 S/cm. Transmission electron micrographs and XRD data analysis imply that the rutile crystallites are self-organized in a regular fashion to produce multilayer three-dimensional linear clusters. The clusters have been found to be microporous (average porosity 1.4 nm) with high specific surface area (132.2 m2/g). At higher concentration, the clusters aggregate to produce interconnected network of star- or flower-like structures. This organized crystalline microporous metal-oxide semiconductor might find various practical applications.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2015
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by


