Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 October 2013
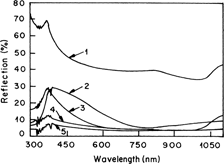
Sol–gel-derived aluminum (Al)-doped zinc oxide thin films have been deposited on silicon (Si) wafers and microslide glass substrates using the spin coating technique. The atomic ratio of Al:Zn in the films is 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3. The films have been characterized using different techniques, i.e., x-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, UV-visible-near infrared spectrophotometry, spectroscopic ellipsometry, and the four-probe method. The films have exhibited excellent optical transmittance (∼90%). The refractive indices of the films are in the range between 1.47 and 1.53. The thickness of the films is in the range of 103–115 nm. The films have demonstrated reflectivity of about 3% at a wave length of 600 nm. The reflectivity, transmittance, refractive index, and thickness values of the films show that the films are promising candidates for utility as antireflection coatings in silicon solar cells.