Article contents
Effects of poly(para-dioxanone-co-L-lactide) on the in vitro hydrolytic degradation behaviors of poly(L-lactide)/poly(para-dioxanone) blends
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 February 2015
Abstract
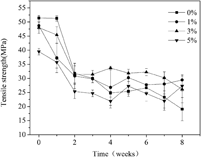
Poly(L-lactide)/poly(para-dioxanone) (PLLA/PPDO) (85/15 w/w) blends with 0, 1, 3, and 5 wt% poly(para-dioxanone-co-L-lactide) (PDOLLA) as a compatibilizer were prepared by solution coprecipitation. The in vitro hydrolytic degradation (HD) of blend bars with different contents of PDOLLA was studied by immersing the bars in a phosphate buffer solution (PBS) at pH 7.49. To estimate the degradation of blend bars, the weight loss, water absorption, thermal properties, surface morphology, and mechanical properties of blend bars, as well as the pH value changes of the PBS, were studied for 8 wk of HD. By adding 1 and 3 wt% PDOLLA, the weight loss of PLLA/PPDO (85/15 w/w) blends increased from 6.4 to 6.8 and 7.4% after 8 wk of HD, 6.2 and 15.6% increment, respectively, while, the average tensile strength of PLLA/PPDO (85/15 w/w) blends for 2–8 wk of HD increased from 25.8 to 29.0 MPa and 31.0 MPa, 12.4 and 20.2% increment, respectively. Considering their good mechanical properties and HD rate, the PLLA/PPDO (85/15 w/w) blends with 1 and 3 wt% PDOLLA are potential to be used as a medical implant material.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2015
References
REFERENCES
- 3
- Cited by


