Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Taylor, J. R.
and
Zhou, Q.
2017.
A multi-parameter criterion for layer formation in a stratified shear flow using sorted buoyancy coordinates.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 823,
Issue. ,
Lucas, Dan
Caulfield, C. P.
and
Kerswell, Rich R.
2017.
Layer formation in horizontally forced stratified turbulence: connecting exact coherent structures to linear instabilities.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 832,
Issue. ,
p.
409.
Deguchi, Kengo
2017.
Scaling of small vortices in stably stratified shear flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 821,
Issue. ,
p.
582.
Watanabe, Tomoaki
Riley, James J.
Nagata, Koji
Onishi, Ryo
and
Matsuda, Keigo
2018.
A localized turbulent mixing layer in a uniformly stratified environment.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 849,
Issue. ,
p.
245.
Lefauve, Adrien
Partridge, J. L.
Zhou, Qi
Dalziel, S. B.
Caulfield, C. P.
and
Linden, P. F.
2018.
The structure and origin of confined Holmboe waves.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 848,
Issue. ,
p.
508.
Pouquet, A.
Rosenberg, D.
and
Marino, R.
2019.
Linking dissipation, anisotropy, and intermittency in rotating stratified turbulence at the threshold of linear shear instabilities.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 10,
de Bruyn Kops, Stephen M.
and
Riley, James J.
2019.
The effects of stable stratification on the decay of initially isotropic homogeneous turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 860,
Issue. ,
p.
787.
Salehipour, Hesam
and
Peltier, W. R.
2019.
Deep learning of mixing by two ‘atoms’ of stratified turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 861,
Issue. ,
Portwood, G. D.
de Bruyn Kops, S. M.
and
Caulfield, C. P.
2019.
Asymptotic Dynamics of High Dynamic Range Stratified Turbulence.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 122,
Issue. 19,
Haghshenas, Armin
and
Mellado, Juan Pedro
2019.
Characterization of wind-shear effects on entrainment in a convective boundary layer.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 858,
Issue. ,
p.
145.
Taylor, J. R.
de Bruyn Kops, S. M.
Caulfield, C. P.
and
Linden, P. F.
2019.
Testing the Assumptions Underlying Ocean Mixing Methodologies Using Direct Numerical Simulations.
Journal of Physical Oceanography,
Vol. 49,
Issue. 11,
p.
2761.
Shete, Kedar Prashant
and
de Bruyn Kops, Stephen M.
2020.
Area of scalar isosurfaces in homogeneous isotropic turbulence as a function of Reynolds and Schmidt numbers.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 883,
Issue. ,
Caulfield, Colm-cille P.
2020.
Open questions in turbulent stratified mixing: Do we even know what we do not know?.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 11,
Howland, Christopher J.
Taylor, John R.
and
Caulfield, C. P.
2020.
Mixing in forced stratified turbulence and its dependence on large-scale forcing.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 898,
Issue. ,
Cope, Laura
Garaud, P.
and
Caulfield, C. P.
2020.
The dynamics of stratified horizontal shear flows at low Péclet number.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 903,
Issue. ,
Halawa, B.
Merhi, S.
Tang, C.
and
Zhou, Q.
2020.
Three-dimensional visualization of stratified turbulent wakes at varying Reynolds number.
Journal of Visualization,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 3,
p.
437.
Lefauve, Adrien
and
Linden, P. F.
2020.
Buoyancy-driven exchange flows in inclined ducts.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 893,
Issue. ,
Lewin, S.F.
and
Caulfield, C.P.
2021.
The influence of far field stratification on shear-induced turbulent mixing.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 928,
Issue. ,
Howland, Christopher J.
Taylor, John R.
and
Caulfield, C.P.
2021.
Quantifying mixing and available potential energy in vertically periodic simulations of stratified flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 914,
Issue. ,
Katagiri, T.
Watanabe, T.
and
Nagata, K.
2021.
Statistical properties of a model of a turbulent patch arising from a breaking internal wave.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 5,
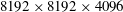 $8192\times 8192\times 4096$ grid points. In addition to classifying regions consistently with contour plots of potential enstrophy, our method identifies quiescent regions as regions where
$8192\times 8192\times 4096$ grid points. In addition to classifying regions consistently with contour plots of potential enstrophy, our method identifies quiescent regions as regions where 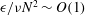 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D716}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}N^{2}\sim O(1)$, layers as regions where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D716}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}N^{2}\sim O(1)$, layers as regions where 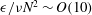 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D716}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}N^{2}\sim O(10)$ and patches as regions where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D716}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}N^{2}\sim O(10)$ and patches as regions where 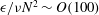 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D716}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}N^{2}\sim O(100)$. Here,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D716}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}N^{2}\sim O(100)$. Here,  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D716}$ is the dissipation rate of turbulence kinetic energy,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D716}$ is the dissipation rate of turbulence kinetic energy,  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}$ is the kinematic viscosity and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}$ is the kinematic viscosity and 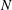 $N$ is the (overall) buoyancy frequency. By far the highest local dissipation and mixing rates, and the majority of dissipation and mixing, occur in patch regions, even when patch regions occupy only 5 % of the flow volume. We conjecture that treating stratified turbulence as an instantaneous assemblage of these different regions in varying proportions may explain some of the apparently highly scattered flow dynamics and statistics previously reported in the literature.
$N$ is the (overall) buoyancy frequency. By far the highest local dissipation and mixing rates, and the majority of dissipation and mixing, occur in patch regions, even when patch regions occupy only 5 % of the flow volume. We conjecture that treating stratified turbulence as an instantaneous assemblage of these different regions in varying proportions may explain some of the apparently highly scattered flow dynamics and statistics previously reported in the literature.