Article contents
Evidence of preferential sweeping during snow settling in atmospheric turbulence
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 October 2021
Abstract
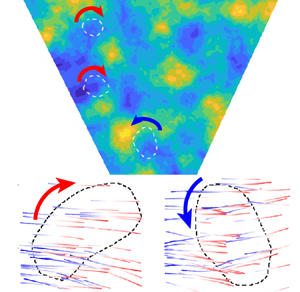
We present a field study of snow settling dynamics based on simultaneous measurements of the atmospheric flow field and snow particle trajectories. Specifically, a super-large-scale particle image velocimetry (SLPIV) system using natural snow particles as tracers is deployed to quantify the velocity field and identify vortex structures in a 22 m  $\times$ 39 m field of view centred 18 m above the ground. Simultaneously, we track individual snow particles in a 3 m
$\times$ 39 m field of view centred 18 m above the ground. Simultaneously, we track individual snow particles in a 3 m  $\times$ 5 m sample area within the SLPIV using particle tracking velocimetry. The results reveal the direct linkage among vortex structures in atmospheric turbulence, the spatial distribution of snow particle concentration and their settling dynamics. In particular, with snow turbulence interaction at near-critical Stokes number, the settling velocity enhancement of snow particles is multifold, and larger than what has been observed in previous field studies. Super-large-scale particle image velocimetry measurements show a higher concentration of snow particles preferentially located on the downward side of the vortices identified in the atmospheric flow field. Particle tracking velocimetry, performed on high resolution images around the reconstructed vortices, confirms the latter trend and provides statistical evidence of the acceleration of snow particles, as they move toward the downward side of vortices. Overall, the simultaneous multi-scale particle imaging presented here enables us to directly quantify the salient features of preferential sweeping, supporting it as an underlying mechanism of snow settling enhancement in the atmospheric surface layer.
$\times$ 5 m sample area within the SLPIV using particle tracking velocimetry. The results reveal the direct linkage among vortex structures in atmospheric turbulence, the spatial distribution of snow particle concentration and their settling dynamics. In particular, with snow turbulence interaction at near-critical Stokes number, the settling velocity enhancement of snow particles is multifold, and larger than what has been observed in previous field studies. Super-large-scale particle image velocimetry measurements show a higher concentration of snow particles preferentially located on the downward side of the vortices identified in the atmospheric flow field. Particle tracking velocimetry, performed on high resolution images around the reconstructed vortices, confirms the latter trend and provides statistical evidence of the acceleration of snow particles, as they move toward the downward side of vortices. Overall, the simultaneous multi-scale particle imaging presented here enables us to directly quantify the salient features of preferential sweeping, supporting it as an underlying mechanism of snow settling enhancement in the atmospheric surface layer.
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
REFERENCES
- 17
- Cited by



