Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 May 2019
We consider the asymmetry of the buoyancy field in the vertical direction in stratified turbulence. While this asymmetry is known, its causes are not well understood, and it has not been systematically quantified previously. Using theoretical arguments, it is shown that both stratified turbulence and isotropic turbulence in the presence of a mean scalar gradient will become positively skewed, as a direct consequence of the presence of stratification and mean scalar gradient, respectively. Assuming a rapid adjustment of isotropic turbulence to a stable stratification on a time scale 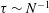 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}\sim N^{-1}$, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}\sim N^{-1}$, where 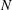 $N$ is the Brunt–Väisälä frequency, a scaling for the skewness of the vertical buoyancy gradient is obtained. Direct numerical simulations of stratified turbulence with forcing are performed and the positive skewness of
$N$ is the Brunt–Väisälä frequency, a scaling for the skewness of the vertical buoyancy gradient is obtained. Direct numerical simulations of stratified turbulence with forcing are performed and the positive skewness of 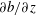 $\unicode[STIX]{x2202}b/\unicode[STIX]{x2202}z$ is confirmed (
$\unicode[STIX]{x2202}b/\unicode[STIX]{x2202}z$ is confirmed (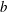 $b$ is the buoyancy). Both the volume-averaged dimensional skewness,
$b$ is the buoyancy). Both the volume-averaged dimensional skewness, 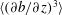 $\langle (\unicode[STIX]{x2202}b/\unicode[STIX]{x2202}z)^{3}\rangle$, and the non-dimensional skewness,
$\langle (\unicode[STIX]{x2202}b/\unicode[STIX]{x2202}z)^{3}\rangle$, and the non-dimensional skewness, 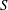 $S$, are computed and compared against the theoretical predictions. There is a good agreement for
$S$, are computed and compared against the theoretical predictions. There is a good agreement for 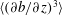 $\langle (\unicode[STIX]{x2202}b/\unicode[STIX]{x2202}z)^{3}\rangle$, while there is a discrepancy in the behaviour of
$\langle (\unicode[STIX]{x2202}b/\unicode[STIX]{x2202}z)^{3}\rangle$, while there is a discrepancy in the behaviour of 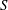 $S$. The theory predicts
$S$. The theory predicts 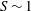 $S\sim 1$ and a constant skewness, while the direct numerical simulations confirm that the skewness is
$S\sim 1$ and a constant skewness, while the direct numerical simulations confirm that the skewness is 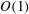 $O(1)$ but with a remaining dependence on the Froude number. The results are interpreted as being due to the concurrent action of linear and nonlinear processes in stratified turbulence leading to
$O(1)$ but with a remaining dependence on the Froude number. The results are interpreted as being due to the concurrent action of linear and nonlinear processes in stratified turbulence leading to 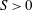 $S>0$ and to the formation of layers and interfaces in vertical profiles of buoyancy.
$S>0$ and to the formation of layers and interfaces in vertical profiles of buoyancy.