Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Pirozzoli, Sergio
Bernardini, Matteo
Verzicco, Roberto
and
Orlandi, Paolo
2017.
Mixed convection in turbulent channels with unstable stratification.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 821,
Issue. ,
p.
482.
McColl, Kaighin A.
van Heerwaarden, Chiel C.
Katul, Gabriel G.
Gentine, Pierre
and
Entekhabi, Dara
2017.
Role of large eddies in the breakdown of the Reynolds analogy in an idealized mildly unstable atmospheric surface layer.
Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society,
Vol. 143,
Issue. 706,
p.
2182.
Li, Dong
Luo, Kun
and
Fan, Jianren
2017.
Buoyancy effects in an unstably stratified turbulent boundary layer flow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 1,
Blass, A.
Pirozzoli, S.
and
Verzicco, R.
2019.
Progress in Turbulence VIII.
Vol. 226,
Issue. ,
p.
47.
Deng, Bing-Qing
Yang, Zixuan
Xuan, Anqing
and
Shen, Lian
2019.
Influence of Langmuir circulations on turbulence in the bottom boundary layer of shallow water.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 861,
Issue. ,
p.
275.
Shvab, A. V.
and
Turubaev, R. R.
2019.
Simulation of Swirling Turbulent Flow Aerodynamics in a Centrifugal Machine.
Theoretical Foundations of Chemical Engineering,
Vol. 53,
Issue. 2,
p.
242.
Yang, Xiang I. A.
Pirozzoli, Sergio
and
Abkar, Mahdi
2020.
Scaling of velocity fluctuations in statistically unstable boundary-layer flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 886,
Issue. ,
Blass, Alexander
Zhu, Xiaojue
Verzicco, Roberto
Lohse, Detlef
and
Stevens, Richard J. A. M.
2020.
Flow organization and heat transfer in turbulent wall sheared thermal convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 897,
Issue. ,
Serra, Sylvain
Franquet, Erwin
Boutrouche, Valentin
and
Manceau, Rémi
2021.
Asymmetric reverse transition phenomenon in internal turbulent channel flows due to temperature gradients.
International Journal of Thermal Sciences,
Vol. 159,
Issue. ,
p.
106463.
Blass, Alexander
Tabak, Pier
Verzicco, Roberto
Stevens, Richard J.A.M.
and
Lohse, Detlef
2021.
The effect of Prandtl number on turbulent sheared thermal convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 910,
Issue. ,
Lallemand, Pierre
Luo, Li-Shi
Krafczyk, Manfred
and
Yong, Wen-An
2021.
The lattice Boltzmann method for nearly incompressible flows.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 431,
Issue. ,
p.
109713.
Cheng, Yu
Li, Qi
Li, Dan
and
Gentine, Pierre
2021.
Logarithmic profile of temperature in sheared and unstably stratified atmospheric boundary layers.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 3,
Deng, Bing‐Qing
Zhao, Ming‐Xiang
Wang, Qing
and
Shen, Lian
2021.
Numerical Study of Near‐Surface Jet in the Atmospheric Surface Layer Over an Oceanic Temperature Front.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres,
Vol. 126,
Issue. 5,
Yerragolam, Guru Sreevanshu
Verzicco, Roberto
Lohse, Detlef
and
Stevens, Richard J.A.M.
2022.
How small-scale flow structures affect the heat transport in sheared thermal convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 944,
Issue. ,
Madhusudanan, Anagha
Illingworth, Simon J.
Marusic, Ivan
and
Chung, Daniel
2022.
Navier-Stokes–based linear model for unstably stratified turbulent channel flows.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 4,
Jin, Tian-Cheng
Wu, Jian-Zhao
Zhang, Yi-Zhao
Liu, Yu-Lu
and
Zhou, Quan
2022.
Shear-induced modulation on thermal convection over rough plates.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 936,
Issue. ,
Ma, Yuan
Mohebbi, Rasul
and
Sheremet, Mikhail
2023.
Heat transfer and fluid flow around starfish-inspired cylinder by immersed boundary-simplified thermal lattice Boltzmann method.
Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements,
Vol. 146,
Issue. ,
p.
656.
Xu, Ao
Xu, Ben-Rui
and
Xi, Heng-Dong
2023.
Wall-sheared thermal convection: heat transfer enhancement and turbulence relaminarization.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 960,
Issue. ,
Yerragolam, Guru Sreevanshu
Howland, Christopher J.
Stevens, Richard J.A.M.
Verzicco, Roberto
Shishkina, Olga
and
Lohse, Detlef
2024.
Scaling relations for heat and momentum transport in sheared Rayleigh–Bénard convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 1000,
Issue. ,
Howland, Christopher J.
Yerragolam, Guru Sreevanshu
Verzicco, Roberto
and
Lohse, Detlef
2024.
Turbulent mixed convection in vertical and horizontal channels.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 998,
Issue. ,
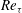 $\mathit{Re}_{{\it\tau}}$) and Rayleigh number (
$\mathit{Re}_{{\it\tau}}$) and Rayleigh number (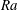 $\mathit{Ra}$). Our focus is on deviations from the logarithmic law of the wall due to buoyant motion. The effects of convection in the relevant ranges are discussed, providing measurements of mean profiles of velocity, temperature and Reynolds stresses as well as of the friction coefficient. A phenomenological model is proposed and shown to capture the observed deviations of the velocity profile in the log-law region from the non-convective case.
$\mathit{Ra}$). Our focus is on deviations from the logarithmic law of the wall due to buoyant motion. The effects of convection in the relevant ranges are discussed, providing measurements of mean profiles of velocity, temperature and Reynolds stresses as well as of the friction coefficient. A phenomenological model is proposed and shown to capture the observed deviations of the velocity profile in the log-law region from the non-convective case.