Article contents
Coefficients of ergodicity for stochastically monotone Markov chains
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 July 2016
Abstract
In this paper we show that to each distance d defined on the finite state space S of a strongly ergodic Markov chain there corresponds a coefficient ρd of ergodicity based on the Wasserstein metric. For a class of stochastically monotone transition matrices P, the infimum over all such coefficients is given by the spectral radius of P – R, where R = limkPk and is attained. This result has a probabilistic interpretation of a control of the speed of convergence of 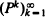 by the metric d and is linked to the second eigenvalue of P.
by the metric d and is linked to the second eigenvalue of P.
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Applied Probability Trust 1992
References
- 2
- Cited by


