Research Article
Time of Sowing and the Yield of Winter Barley
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 405-411
-
- Article
- Export citation
Interactions between Rhizobium strains and lentil (Lens culinaris Linn.) genotypes under salt stress
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 199-205
-
- Article
- Export citation
Studies on thiaminase I activity in ruminant faeces and rumen bacteria
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 637-642
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vegetative growth of winter barley in relation to environmental conditions and grain yield
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 413-419
-
- Article
- Export citation
Short Notes
Response of maize to magnesium in tropical rainforest and savannah region
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 643-646
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Article
Studies on associative nitrogen fixation by antibiotic-resistant mutants of Azospirillum brasilense with genotypes of lentil (Lens culinaris) Rhizobium strains in calcareous soil
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 207-215
-
- Article
- Export citation
Intercropping of upland rice with blackgram [Vigna mungo (L.)]
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 217-221
-
- Article
- Export citation
Use of cluster analysis for classification of Benchmark soil samples from India in different micronutrient availability groups
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 421-424
-
- Article
- Export citation
Indox of Authors
Indox of Authors
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 647-650
-
- Article
- Export citation
Indox of Subjects
Indox of Subjects
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 651-657
-
- Article
- Export citation
Short Notes
Effect of airdrying, γ-irradiation and chloroform fumigation of soil on extractability of trace elements
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 223-226
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Article
Studies on the nitrification inhibitor, dicyandiamide (DCD), for increasing the efficiency of nitrogen applied to rice
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 425-428
-
- Article
- Export citation
Relationship of stalk morphology and chemical composition to lodging resistance in maize (Zea mays L.) in a rainforest zone
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 429-433
-
- Article
- Export citation
Short Notes
Nutritional characteristics of kura clover (Trifolium ambiguum Bieb.) compared with other forage legumes
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 227-229
-
- Article
- Export citation
Front matter
AGS volume 104 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Back matter
AGS volume 104 issue 3 Cover, Back matter and Corrigendum
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. b1-b10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Short Notes
Seasonal influences in milk production in Friesian-Bunaji crosses in northern Nigeria
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 231-233
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Article
Carbohydrase activity in the pancreatic tissue and small intestine mucosa of sheep fed dried-grass or ground maize-based diets
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 435-443
-
- Article
- Export citation
Short Notes
Time of sowing and the yield of winter wheat
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 235-238
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research Article
Hydrodynamics and the germination of oil-seed rape pollen
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2009, pp. 445-451
-
- Article
- Export citation

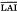 ) and net assimilation rate (NAR), were partially obscured by ontogenetic drift. In addition, a highly significant relationship was demonstrated between CDW (when the LAI reaches its maximum value) and grain yield. This suggests that the pre-anthesis period has a great influence in the determination of grain yield variation in hot, dry areas, where photosynthesis is very limited after ear emergence.
) and net assimilation rate (NAR), were partially obscured by ontogenetic drift. In addition, a highly significant relationship was demonstrated between CDW (when the LAI reaches its maximum value) and grain yield. This suggests that the pre-anthesis period has a great influence in the determination of grain yield variation in hot, dry areas, where photosynthesis is very limited after ear emergence.