Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 May 2009
Recent published work on the origin of the South Wales coals has shown that the “original deposition theory” is invalid; the pronounced devolatilization of the coals is due to a cause which operated after the formation of all of the seams and the rate of change of the volatiles is governed by a function which can be expressed as an empirical equation. Nevertheless minor variations in coal seam volatiles arising from differences in original composition of vegetation are recognized, and of several examples one is given from the Northumbrian geo-syncline where the highest volatiles are in the lowest Carboniferous Limestone coals and where the extreme variation throughout a sequence of 7,000 feet of coal-bearing strata is 11%. The minor variations lessen progressively if the coal seams become devolatilized. As illustrated by examples from American and European fields, a most important factor in coal seam devolatilization is orogenic pressure with incidental frictional heat.
The present basis of comparison of essential coal-substances (fixed carbon and volatiles) is shown to be empirical; a mathematical comparison should be based on the original composition of the coal (not peat) substance. it is shown that 50% fixed carbon and 50% volatiles (d.a.f.) constitute good average figures for the original composition of the coal substance of Carboniferous coals. Loss of weight in devolatilized coals is suffered only by the volatiles so that the best basis of mathematical comparison is the 50% fixed carbon (d.a.f.). The volatile percentages of the South Wales seams when calculated on this basis all show a pronounced drop in values, and on the 50% fixed carbon basis it is necessary to find a new controlling function for the rate of change of volatiles in coal seams lying in vertical sequence. It is found that this is best expressed by the following exponential equation:
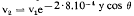
where v2 and v1 represent the volatiles of the lower and upper seams respectively, y is the vertical distance in feet of v2 below v1; and θ is the angle of dip of the zero plane previously determined in South Wales as 5°.