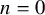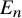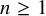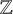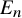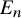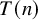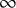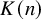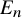1 Introduction
Background & overview
The classical m-dimensional Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) is a linear isomorphism
associated to a primitive m-th root of unity
![]() $\omega \in \mathbb {C}$
, whose characteristic property is transforming the convolution product on the source to the pointwise product on the target. More generally, one can associate to every commutative ring R with an m-th root of unity
$\omega \in \mathbb {C}$
, whose characteristic property is transforming the convolution product on the source to the pointwise product on the target. More generally, one can associate to every commutative ring R with an m-th root of unity
![]() $\omega \colon \mathbb {Z}/m \to R^\times $
, a natural transformation of R-algebras,
$\omega \colon \mathbb {Z}/m \to R^\times $
, a natural transformation of R-algebras,
from the group R-algebra of an m-torsion abelian group M to the algebra of R-valued functions on its Pontryagin dual
![]() $M^* = \hom (M, \mathbb {Q}/\mathbb {Z})$
. Furthermore,
$M^* = \hom (M, \mathbb {Q}/\mathbb {Z})$
. Furthermore,
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
is an isomorphism if and only if the image of
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
is an isomorphism if and only if the image of
![]() $\omega $
is primitive in every residue field of R. The classical case is recovered by taking
$\omega $
is primitive in every residue field of R. The classical case is recovered by taking
![]() $R=\mathbb {C}$
and
$R=\mathbb {C}$
and
![]() $M = \mathbb {Z}/m$
.
$M = \mathbb {Z}/m$
.
The passage from the ordinary category of abelian groups to the
![]() $\infty $
-category of spectra (i.e., from classical commutative algebra to stable homotopy theory) introduces new ‘characteristics’. The Morava K-theory ring spectra of heights
$\infty $
-category of spectra (i.e., from classical commutative algebra to stable homotopy theory) introduces new ‘characteristics’. The Morava K-theory ring spectra of heights
![]() $n=0,\dots ,\infty $
at an (implicit) prime p,
$n=0,\dots ,\infty $
at an (implicit) prime p,
are in a precise sense the prime fields in the world of spectra and can be thought of as providing an interpolation between the classical characteristics
![]() $0$
and p; see [Reference Hopkins and SmithHS98]. A central tool in the study of these intermediate characteristics is Lubin–Tate spectra. For each
$0$
and p; see [Reference Hopkins and SmithHS98]. A central tool in the study of these intermediate characteristics is Lubin–Tate spectra. For each
![]() $0<n<\infty $
, this is a
$0<n<\infty $
, this is a
![]() $K(n)$
-local commutative algebra
$K(n)$
-local commutative algebra
![]() $E_n$
that can be realized as the algebraic closure of the
$E_n$
that can be realized as the algebraic closure of the
![]() $K(n)$
-local sphere, and which has deep connections to the algebraic geometry of formal groups making it amenable to computations. For example, in [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13], Hopkins and Lurie prove the following theorem, which resembles the discrete Fourier transform only in higher chromatic heights:
$K(n)$
-local sphere, and which has deep connections to the algebraic geometry of formal groups making it amenable to computations. For example, in [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13], Hopkins and Lurie prove the following theorem, which resembles the discrete Fourier transform only in higher chromatic heights:
Theorem 1.1 [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Corollary 5.3.26].
For all integers
![]() $n\ge 1$
, there is a natural isomorphism of
$n\ge 1$
, there is a natural isomorphism of
![]() $K(n)$
-local commutative
$K(n)$
-local commutative
![]() $E_n$
-algebras
$E_n$
-algebras
where M is a connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite (i.e., having only finitely many nonvanishing homotopy groups, all of which are finite) p-local
$\pi $
-finite (i.e., having only finitely many nonvanishing homotopy groups, all of which are finite) p-local
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-module and
$\mathbb {Z}$
-module and
![]() $M^*$
is its Pontryagin dual.
$M^*$
is its Pontryagin dual.
Furthermore, they deduce from this result several fundamental structural properties of local systems of
![]() $K(n)$
-local algebras on
$K(n)$
-local algebras on
![]() $\pi $
-finite spaces, reproving among other things the convergence of the
$\pi $
-finite spaces, reproving among other things the convergence of the
![]() $K(n)$
-based Eilenberg–Moore spectral sequence from [Reference BauerBau08].
$K(n)$
-based Eilenberg–Moore spectral sequence from [Reference BauerBau08].
In this paper, we develop a general theory that formalizes and substantiates the analogy between Theorem 1.1 and the classical Fourier transform. In particular, we reinterpret both in terms of a unified notion of a chromatic Fourier transform isomorphism for all finite chromatic heights and show that it shares many of the formal properties of the classical Fourier transform. We then apply this theory to generalize Theorem 1.1 in three different directions:
-
(1) We lift it to the telescopic world by replacing
 $E_n$
with certain faithful Galois extensions of the
$E_n$
with certain faithful Galois extensions of the
 $T(n)$
-local sphere (Theorem A). By analogy with the
$T(n)$
-local sphere (Theorem A). By analogy with the
 $K(n)$
-local case, we deduce several structural results for local systems of
$K(n)$
-local case, we deduce several structural results for local systems of
 $T(n)$
-local algebras over
$T(n)$
-local algebras over
 $\pi $
-finite spaces (Theorem B). We also obtain an analogue of Kummer theory at heights
$\pi $
-finite spaces (Theorem B). We also obtain an analogue of Kummer theory at heights
 $n\ge 1$
(Theorem C).
$n\ge 1$
(Theorem C). -
(2) We extend it over
 $E_n$
to all (i.e., not just
$E_n$
to all (i.e., not just
 $\mathbb {Z}$
-module) connective
$\mathbb {Z}$
-module) connective
 $\pi $
-finite p-local spectra (Theorem D) and deduce from this the conjectured description of the discrepancy spectrum of Ando–Hopkins–Rezk in terms of the Brown–Comenetz spectrum (Theorem E). As another application, we construct a certain
$\pi $
-finite p-local spectra (Theorem D) and deduce from this the conjectured description of the discrepancy spectrum of Ando–Hopkins–Rezk in terms of the Brown–Comenetz spectrum (Theorem E). As another application, we construct a certain
 $K(n)$
-local pro-
$K(n)$
-local pro-
 $\pi $
-finite Galois extension, which is a strong analogue of the classical p-typical cyclotomic extension (Theorem F).
$\pi $
-finite Galois extension, which is a strong analogue of the classical p-typical cyclotomic extension (Theorem F). -
(3) We categorify it into a symmetric monoidal equivalence between
 $\infty $
-categories of local systems of
$\infty $
-categories of local systems of
 $K(n)$
-local
$K(n)$
-local
 $E_n$
-modules on the underlying spaces of two dual
$E_n$
-modules on the underlying spaces of two dual
 $\pi $
-finite spectra. Among other things, this generalizes the weight space decomposition of representations of finite abelian groups in characteristic zero (Theorem G). We also explain how this categorification accords with semiadditive redshift phenomena.
$\pi $
-finite spectra. Among other things, this generalizes the weight space decomposition of representations of finite abelian groups in characteristic zero (Theorem G). We also explain how this categorification accords with semiadditive redshift phenomena.
We shall now discuss each of these sets of results in some more detail and outline along the way some of the key aspects of the general theory.
Telescopic lift
Recall that the telescopic localization
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is the Bousfield localization of
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is the Bousfield localization of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}$
with respect to
$\textrm {Sp}$
with respect to
![]() $T(n) = F(n)[v^{-1}]$
, where
$T(n) = F(n)[v^{-1}]$
, where
![]() $F(n)$
is (any) finite spectrum of type n with a
$F(n)$
is (any) finite spectrum of type n with a
![]() $v_n$
-self map of the form
$v_n$
-self map of the form
![]() $v\colon \Sigma ^d F(n) \to F(n)$
. It is a classical fact that
$v\colon \Sigma ^d F(n) \to F(n)$
. It is a classical fact that
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)} \subseteq \textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
, and a long standing conjecture of Ravenel, known as the telescope conjecture, states that the two localizations are, in fact, equal. While proven to be true in heights
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)} \subseteq \textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
, and a long standing conjecture of Ravenel, known as the telescope conjecture, states that the two localizations are, in fact, equal. While proven to be true in heights
![]() $n=0,1$
, the telescope conjecture is widely believed to be false for all
$n=0,1$
, the telescope conjecture is widely believed to be false for all
![]() $n\ge 2$
and all primes p. In recent years, the telescopic localizations gained new interest (independently of the status of the telescope conjecture) due to their pivotal role in several remarkable developments, of which we mention two: first, the work [Reference HeutsHeu21] of Heuts on unstable chromatic homotopy theory, which generalizes Quillen’s classical rational homotopy theory to higher chromatic heights, and second, the works [Reference Land, Mathew, Meier and TammeLMMT20, Reference Clausen, Mathew, Naumann and NoelCMNN20], which made major progress on establishing the conjectural chromatic redshift philosophy pioneered by Rognes (see, for example, [Reference RognesRog14]).
$n\ge 2$
and all primes p. In recent years, the telescopic localizations gained new interest (independently of the status of the telescope conjecture) due to their pivotal role in several remarkable developments, of which we mention two: first, the work [Reference HeutsHeu21] of Heuts on unstable chromatic homotopy theory, which generalizes Quillen’s classical rational homotopy theory to higher chromatic heights, and second, the works [Reference Land, Mathew, Meier and TammeLMMT20, Reference Clausen, Mathew, Naumann and NoelCMNN20], which made major progress on establishing the conjectural chromatic redshift philosophy pioneered by Rognes (see, for example, [Reference RognesRog14]).
The
![]() $T(n)$
-localizations are considerably less amenable to computations than the corresponding
$T(n)$
-localizations are considerably less amenable to computations than the corresponding
![]() $K(n)$
-localizations, largely due to the lack of a (faithful) telescopic lift of
$K(n)$
-localizations, largely due to the lack of a (faithful) telescopic lift of
![]() $E_n$
. Nevertheless, we show that the isomorphism of Theorem 1.1 descends from
$E_n$
. Nevertheless, we show that the isomorphism of Theorem 1.1 descends from
![]() $E_n$
to a deeper base, which does admit a faithful telescopic lift and over to which the chromatic Fourier transform lifts as well. To explain this in more detail, we first note that while the classical Fourier transform is not defined over
$E_n$
to a deeper base, which does admit a faithful telescopic lift and over to which the chromatic Fourier transform lifts as well. To explain this in more detail, we first note that while the classical Fourier transform is not defined over
![]() $\mathbb {Q}$
, one does not need to go all the way up to
$\mathbb {Q}$
, one does not need to go all the way up to
![]() $\mathbb {C}$
or even
$\mathbb {C}$
or even
![]() $\overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
. Instead, for
$\overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
. Instead, for
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/m$
-modules, it suffices to have a primitive m-th root of unity
$\mathbb {Z}/m$
-modules, it suffices to have a primitive m-th root of unity
![]() $\omega _m$
so one can construct the Fourier transform already over the cyclotomic field
$\omega _m$
so one can construct the Fourier transform already over the cyclotomic field
![]() $\mathbb {Q}(\omega _m)$
, which is a finite Galois extension of
$\mathbb {Q}(\omega _m)$
, which is a finite Galois extension of
![]() $\mathbb {Q}$
. In the same spirit, we observe that natural transformations as in Theorem 1.1 are in a canonical bijection with higher roots of unity
$\mathbb {Q}$
. In the same spirit, we observe that natural transformations as in Theorem 1.1 are in a canonical bijection with higher roots of unity
![]() $\Sigma ^n \mathbb {Z}/p^r \to E_n^\times $
of
$\Sigma ^n \mathbb {Z}/p^r \to E_n^\times $
of
![]() $E_n$
. Moreover, the natural isomorphisms are in a canonical bijection with those higher roots of unity that are primitive in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Definition 4.2].
$E_n$
. Moreover, the natural isomorphisms are in a canonical bijection with those higher roots of unity that are primitive in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Definition 4.2].
Remark 1.2. In [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13], the isomorphism of Theorem 1.1 is constructed from a normalization of the p-divisible group
![]() $\mathbb {G}$
associated with
$\mathbb {G}$
associated with
![]() $E_n$
– namely, an isomorphism of the top alternating power
$E_n$
– namely, an isomorphism of the top alternating power
![]() $\operatorname{{Alt}}_n (\mathbb {G})$
with the constant p-divisible group
$\operatorname{{Alt}}_n (\mathbb {G})$
with the constant p-divisible group
![]() $\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p$
. It can be verified directly, that such data are equivalent to compatible systems of primitive higher roots of unity of
$\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p$
. It can be verified directly, that such data are equivalent to compatible systems of primitive higher roots of unity of
![]() $E_n$
,
$E_n$
,
We then proceed to show that, as in the classical case, the chromatic Fourier isomorphism exists already over the higher cyclotomic extensions
![]() $R_{n,r}$
, which are certain faithful
$R_{n,r}$
, which are certain faithful
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^\times $
-Galois extensions of the
$(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^\times $
-Galois extensions of the
![]() $K(n)$
-local sphere classifying primitive higher roots of unity in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b]. The key point now is that, by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Theorem A], the extensions
$K(n)$
-local sphere classifying primitive higher roots of unity in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b]. The key point now is that, by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Theorem A], the extensions
![]() $R_{n,r}$
admit faithful
$R_{n,r}$
admit faithful
![]() $T(n)$
-local lifts
$T(n)$
-local lifts
![]() $R^f_{n,r}$
, the corresponding
$R^f_{n,r}$
, the corresponding
![]() $T(n)$
-local higher cyclotomic extensions. Consequently, the general theory developed in this paper, combined with the nilpotence theorem, allows us to lift the chromatic Fourier transform to the telescopic world.
$T(n)$
-local higher cyclotomic extensions. Consequently, the general theory developed in this paper, combined with the nilpotence theorem, allows us to lift the chromatic Fourier transform to the telescopic world.
Theorem A (7.33).
For every
![]() $n,r\ge 1$
, there exists a faithful
$n,r\ge 1$
, there exists a faithful
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^\times $
-Galois extension
$(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^\times $
-Galois extension
![]() $R^f_{n,r}$
of the
$R^f_{n,r}$
of the
![]() $T(n)$
-local sphere and a natural isomorphism of
$T(n)$
-local sphere and a natural isomorphism of
![]() $T(n)$
-local commutative
$T(n)$
-local commutative
![]() $R^f_{n,r}$
-algebras
$R^f_{n,r}$
-algebras
where M is a connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite
$\pi $
-finite
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-module and
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-module and
![]() $M^*$
is its Pontryagin dual.
$M^*$
is its Pontryagin dual.
Among other things, these natural isomorphisms provide a tool for studying group ring spectra. In particular, it is used by Nikolaus, Yuan and the second-named author in [Reference Carmeli, Nikolaus and YuanCNY] to show that finitely generated abelian groups embed fully faithfully, via the spherical group ring construction, in commutative ring spectra.
The natural isomorphisms of Theorem A are compatible with varying r. Thus, if we replace the individual extensions
![]() $R^f_{n,r}$
with the colimit
$R^f_{n,r}$
with the colimit
![]() $R_n^f := \underrightarrow {\operatorname {lim}}\, R_{n,r}^f$
, we obtain a telescopic Fourier transform for all connective
$R_n^f := \underrightarrow {\operatorname {lim}}\, R_{n,r}^f$
, we obtain a telescopic Fourier transform for all connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite
$\pi $
-finite
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-module (or equivalently, p-local
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-module (or equivalently, p-local
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-module) spectra as in Theorem 1.1. The commutative ring spectrum
$\mathbb {Z}$
-module) spectra as in Theorem 1.1. The commutative ring spectrum
![]() $R_n^f$
can be viewed as the infinite p-typical higher cyclotomic extension and is a telescopic lift of Westerland’s
$R_n^f$
can be viewed as the infinite p-typical higher cyclotomic extension and is a telescopic lift of Westerland’s
![]() $K(n)$
-local commutative ring spectrum
$K(n)$
-local commutative ring spectrum
![]() $R_n$
(see [Reference WesterlandWes17]). However, in contrast with
$R_n$
(see [Reference WesterlandWes17]). However, in contrast with
![]() $R_n$
, it is not known whether
$R_n$
, it is not known whether
![]() $R_n^f$
is faithful. This subtle point might also shed some new light on (the failure of) the telescope conjecture. Localizing
$R_n^f$
is faithful. This subtle point might also shed some new light on (the failure of) the telescope conjecture. Localizing
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
with respect to
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
with respect to
![]() $R_n^f$
forms an interesting intermediate localization between
$R_n^f$
forms an interesting intermediate localization between
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
and
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
and
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
. In particular, if one speculates that
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
. In particular, if one speculates that
![]() $R_n^f$
is, in fact,
$R_n^f$
is, in fact,
![]() $K(n)$
-local, the telescope conjecture becomes equivalent to the faithfulness of
$K(n)$
-local, the telescope conjecture becomes equivalent to the faithfulness of
![]() $R_n^f$
.
$R_n^f$
.
As in [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13], we deduce from Theorem A several structural properties of local systems of
![]() $T(n)$
-local algebras over
$T(n)$
-local algebras over
![]() $\pi $
-finite spaces.
$\pi $
-finite spaces.
Theorem B. Let A be a
![]() $\pi $
-finite space such that
$\pi $
-finite space such that
![]() $\pi _1(A,a)$
is a p-group and
$\pi _1(A,a)$
is a p-group and
![]() $\pi _{n+1}(A,a)$
is of order prime to p, for all
$\pi _{n+1}(A,a)$
is of order prime to p, for all
![]() $a\in A$
.
$a\in A$
.
-
(1) (7.29) For every
 $R \in \operatorname{{Alg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})^A$
, the global sections functor
$R \in \operatorname{{Alg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})^A$
, the global sections functor
 $A_*(-) := \lim _A(-)$
induces a symmetric monoidal equivalence
$A_*(-) := \lim _A(-)$
induces a symmetric monoidal equivalence 
-
(2) (7.30) For every
 $R \in \operatorname{{Alg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})$
and spaces B and C mapping to A, such that B or C are
$R \in \operatorname{{Alg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})$
and spaces B and C mapping to A, such that B or C are
 $\pi $
-finite, the canonical Eilenberg–Moore map is an isomorphism:
$\pi $
-finite, the canonical Eilenberg–Moore map is an isomorphism: 
-
(3) (7.31) Assuming A is connected, every
 $R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})^A$
is
$R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})^A$
is
 $\Omega A$
-Galois, in the sense of Rognes, over
$\Omega A$
-Galois, in the sense of Rognes, over
 $A_*R$
.
$A_*R$
.
Remark 1.3. The assumptions on
![]() $\pi _1$
and
$\pi _1$
and
![]() $\pi _{n+1}$
are necessary. The spaces
$\pi _{n+1}$
are necessary. The spaces
![]() $B^{n+1}C_p$
and
$B^{n+1}C_p$
and
![]() $ BC_q$
for
$ BC_q$
for
![]() $q \neq p$
are counterexamples to all three claims. However, for
$q \neq p$
are counterexamples to all three claims. However, for
![]() $n\ge 1$
, Theorem B is interesting already for
$n\ge 1$
, Theorem B is interesting already for
![]() $A = BG$
, where G is a finite p-group.
$A = BG$
, where G is a finite p-group.
We think of the first claim as an affineness property (cf. [Reference Mathew and MeierMM15]) and study it in a general context by abstracting the
![]() $K(n)$
-local arguments of [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, §5.4]. In particular, in an ambidextrous setting, it both implies and is implied by (a very special case of) the second claim regarding the Eilenberg–Moore isomorphism. Roughly speaking, the affineness of A reduces the Eilenberg–Moore isomorphism to the Künneth isomorphism for the fibers of B and C over A, which in an ambidextrous setting is guaranteed by the
$K(n)$
-local arguments of [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, §5.4]. In particular, in an ambidextrous setting, it both implies and is implied by (a very special case of) the second claim regarding the Eilenberg–Moore isomorphism. Roughly speaking, the affineness of A reduces the Eilenberg–Moore isomorphism to the Künneth isomorphism for the fibers of B and C over A, which in an ambidextrous setting is guaranteed by the
![]() $\pi $
-finiteness assumptions. The suitable special case of the Eilenberg–Moore isomorphism is then deduced from the chromatic Fourier transform, replacing ‘cohomology’ with ‘homology’, for which the analogous claim holds for formal reasons.
$\pi $
-finiteness assumptions. The suitable special case of the Eilenberg–Moore isomorphism is then deduced from the chromatic Fourier transform, replacing ‘cohomology’ with ‘homology’, for which the analogous claim holds for formal reasons.
Generally, Eilenberg–Moore type isomorphisms play a vital role in relating stable and unstable homotopy theory. In particular, Gijs Heuts has been employing the second claim of Theorem B in the study of unstable telescopic chromatic homotopy theory [Reference HeutsHeu]. The third claim of Theorem B, which we learned from Dustin Clausen, that the Galois condition is automatically satisfied, is also a rather formal consequence of affineness and might have been known to other experts (in the
![]() $K(n)$
-local case), though we are not aware that it has appeared in the literature. This result is also important for the study of Galois descent in
$K(n)$
-local case), though we are not aware that it has appeared in the literature. This result is also important for the study of Galois descent in
![]() $T(n)$
-localized algebraic K-theory in an upcoming work of the last three authors.
$T(n)$
-localized algebraic K-theory in an upcoming work of the last three authors.
As a further corollary of the above, we obtain an analogue of Kummer theory at higher chromatic heights
![]() $n\ge 1$
. Here, a connective
$n\ge 1$
. Here, a connective
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-module spectrum M is called n-finite if it is
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-module spectrum M is called n-finite if it is
![]() $\pi $
-finite and n-truncated.
$\pi $
-finite and n-truncated.
Theorem C. (7.34)
Let R be a
![]() $T(n)$
-local commutative algebra admitting a primitive higher
$T(n)$
-local commutative algebra admitting a primitive higher
![]() $p^r$
-th root of unity, and let M be a connected n-finite
$p^r$
-th root of unity, and let M be a connected n-finite
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-module spectrum. Then,
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-module spectrum. Then,
That is, we obtain a classification of abelian Galois extensions of a commutative algebra in terms of its units, in the presence of enough primitive (higher) roots of unity.Footnote 1
Spherical orientations
Generalizing Theorem 1.1 in another direction, we show that when one works
![]() $K(n)$
-locally and over
$K(n)$
-locally and over
![]() $E_n$
, the chromatic Fourier transform extends to all connective
$E_n$
, the chromatic Fourier transform extends to all connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local spectra (i.e., not just
$\pi $
-finite p-local spectra (i.e., not just
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-modules), provided that we replace Pontryagin duality by Brown–Comenetz duality.
$\mathbb {Z}$
-modules), provided that we replace Pontryagin duality by Brown–Comenetz duality.
Theorem D (7.8).
There is a natural isomorphism of
![]() $K(n)$
-local commutative
$K(n)$
-local commutative
![]() $E_n$
-algebras
$E_n$
-algebras
where M is a connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local spectrum and
$\pi $
-finite p-local spectrum and
![]() $I M$
is its Brown–Comenetz dual.
$I M$
is its Brown–Comenetz dual.
Theorem D generalizes Theorem 1.1, as for
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-module spectra the Brown–Comenetz dual identifies canonically with the Pontryagin dual. Conversely, it can be obtained from Theorem 1.1 by a bootstrap procedure. To begin with, for a
$\mathbb {Z}$
-module spectra the Brown–Comenetz dual identifies canonically with the Pontryagin dual. Conversely, it can be obtained from Theorem 1.1 by a bootstrap procedure. To begin with, for a
![]() $K(n)$
-local commutative algebra R, a compatible system of primitive higher
$K(n)$
-local commutative algebra R, a compatible system of primitive higher
![]() $p^r$
-th roots of unity defines a map
$p^r$
-th roots of unity defines a map
Denoting by
![]() $I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
the Brown–Comenetz spectrum, we show that extensions of the chromatic Fourier transformation over R to non-
$I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
the Brown–Comenetz spectrum, we show that extensions of the chromatic Fourier transformation over R to non-
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-module spectra are in a natural bijection with solutions to the following extension problem:
$\mathbb {Z}$
-module spectra are in a natural bijection with solutions to the following extension problem:

We call such extensions spherical orientations of R and think of them as spherical analogues of (compatible systems of) primitive higher roots of unity of R. Using a devissage argument, we show that the Fourier transform associated to a spherical orientation is an isomorphism for all connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local spectra. By studying the obstructions for extending higher roots of unity to spherical orientations, we construct a universal R with a spherical orientation, the spherical cyclotomic extension, and prove that it is
$\pi $
-finite p-local spectra. By studying the obstructions for extending higher roots of unity to spherical orientations, we construct a universal R with a spherical orientation, the spherical cyclotomic extension, and prove that it is
![]() $K(n)$
-locally faithful. In fact, we even construct it
$K(n)$
-locally faithful. In fact, we even construct it
![]() $T(n)$
-locally and show that it is faithful over the intermediate localization,
$T(n)$
-locally and show that it is faithful over the intermediate localization,
We further introduce a natural higher connectedness property for commutative algebras, which guarantees the canonical vanishing of said obstructions, providing a practical criterion for extending the chromatic Fourier transform to non-
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-module spectra for specific choices of R. As a consequence of the ‘chromatic Nullstellensatz’ of the third author with Burklund and Yuan [Reference Burklund, Schlank and YuanBSY22], this criterion is satisfied for
$\mathbb {Z}$
-module spectra for specific choices of R. As a consequence of the ‘chromatic Nullstellensatz’ of the third author with Burklund and Yuan [Reference Burklund, Schlank and YuanBSY22], this criterion is satisfied for
![]() $R = E_n$
, thus yielding Theorem D.
$R = E_n$
, thus yielding Theorem D.
Remark 1.4. More specifically, the required ingredient is [Reference Burklund, Schlank and YuanBSY22, Proposition 8.14],
Looping this isomorphism once yields
which was conjectured, and subsequently proven, by Hopkins and Lurie (see [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Conjecture 5.4.14]), though we are not aware of a written account of their proof. We note that the second isomorphism suffices for establishing Theorem D for all connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local spectra whose n-truncation admits a module structure over the
$\pi $
-finite p-local spectra whose n-truncation admits a module structure over the
![]() $(n-1)$
-truncated sphere spectrum.
$(n-1)$
-truncated sphere spectrum.
As a further consequence of Theorem D, we deduce that a spherical orientation of
![]() $E_n$
identifies the connective cover of
$E_n$
identifies the connective cover of
![]() $\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
with the universal left approximation of
$\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
with the universal left approximation of
![]() $E_n^\times $
by an ind-
$E_n^\times $
by an ind-
![]() $\pi $
-finite connective p-local spectrum. We denote the latter by
$\pi $
-finite connective p-local spectrum. We denote the latter by
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(E_n)$
as a ‘spherical’ analogue of the spectrum of ordinary p-typical roots of unity of
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(E_n)$
as a ‘spherical’ analogue of the spectrum of ordinary p-typical roots of unity of
![]() $E_n$
. We then reinterpret
$E_n$
. We then reinterpret
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(E_n)$
as the p-local part of the connective cover of the so-called discrepancy spectrum of
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(E_n)$
as the p-local part of the connective cover of the so-called discrepancy spectrum of
![]() $E_n$
, which was defined by Ando, Hopkins and Rezk to be the fiber of the localization map
$E_n$
, which was defined by Ando, Hopkins and Rezk to be the fiber of the localization map
![]() $E_n^\times \to L_n E_n^\times $
. To summarize, we obtain the following result, originally announced by Hopkins and Lurie:
$E_n^\times \to L_n E_n^\times $
. To summarize, we obtain the following result, originally announced by Hopkins and Lurie:
Theorem E (7.23).
The p-localization of the connective cover of the discrepancy spectrum of
![]() $E_n$
is isomorphic to the connective cover of
$E_n$
is isomorphic to the connective cover of
![]() $\Sigma ^n I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
.
$\Sigma ^n I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
.
As the discrepancy spectrum is constructed from
![]() $K(n)$
-local ingredients, it is somewhat remarkable that one can read off of it the first n stable homotopy groups of spheres, which are a ‘global’ invariant. This relation also ties the chromatic filtration with the Postnikov filtration, which are, generally speaking, two quite ‘orthogonal’ filtrations in stable homotopy theory.
$K(n)$
-local ingredients, it is somewhat remarkable that one can read off of it the first n stable homotopy groups of spheres, which are a ‘global’ invariant. This relation also ties the chromatic filtration with the Postnikov filtration, which are, generally speaking, two quite ‘orthogonal’ filtrations in stable homotopy theory.
To systematize the study of the various flavours of the chromatic Fourier transform, and to facilitate dévissage arguments, we introduce a general notion of an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n for every connective p-local commutative ring spectrum
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n for every connective p-local commutative ring spectrum
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
. This is the type of data from which one can construct the chromatic Fourier transform for connective
$\mathfrak {R}$
. This is the type of data from which one can construct the chromatic Fourier transform for connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite
$\pi $
-finite
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module spectra. The case
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module spectra. The case
![]() $\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
recovers primitive height n roots of unity, while the case
$\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
recovers primitive height n roots of unity, while the case
![]() $\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
recovers spherical orientations. Furthermore, we show that if
$\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
recovers spherical orientations. Furthermore, we show that if
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
is itself n-truncated and
$\mathfrak {R}$
is itself n-truncated and
![]() $\pi $
-finite, then the associated
$\pi $
-finite, then the associated
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension, classifying
$\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension, classifying
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations, is
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations, is
![]() $\mathfrak {R}^\times $
-Galois. Note that, in general,
$\mathfrak {R}^\times $
-Galois. Note that, in general,
![]() $\mathfrak {R}^\times $
is not a finite discrete group, but a
$\mathfrak {R}^\times $
is not a finite discrete group, but a
![]() $\pi $
-finite group in the homotopical sense. We deduce from this that the spherical cyclotomic extension is a pro-
$\pi $
-finite group in the homotopical sense. We deduce from this that the spherical cyclotomic extension is a pro-
![]() $\pi $
-finite Galois extension.
$\pi $
-finite Galois extension.
Theorem F (7.7).
The
![]() $K(n)$
-local spherical cyclotomic extension is pro-G-Galois for
$K(n)$
-local spherical cyclotomic extension is pro-G-Galois for
![]() $G = \tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_p^\times $
, viewed as a pro-
$G = \tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_p^\times $
, viewed as a pro-
![]() $\pi $
-finite group.
$\pi $
-finite group.
The classical p-typical cyclotomic extension
![]() $\mathbb {Q}_p(\omega _{p^\infty })$
, and the corresponding p-typical cyclotomic character classifying it
$\mathbb {Q}_p(\omega _{p^\infty })$
, and the corresponding p-typical cyclotomic character classifying it
plays a fundamental role in number theory in the formulation of various arithmetic duality theorems, via the construction of Tate twists. In [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b], it is shown that Westerland’s ring spectrum
![]() $R_n$
, which is a
$R_n$
, which is a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_p^\times $
-Galois extension of
$\mathbb {Z}_p^\times $
-Galois extension of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
, can be similarly viewed as a p-typical higher cyclotomic extension. As the pro-finite Galois extensions of
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
, can be similarly viewed as a p-typical higher cyclotomic extension. As the pro-finite Galois extensions of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
are classified by the Morava stabilizer group
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
are classified by the Morava stabilizer group
![]() $\mathbb {G}_n$
, associated to
$\mathbb {G}_n$
, associated to
![]() $R_n$
is the higher cyclotomic character
$R_n$
is the higher cyclotomic character
which is essentially the determinant map. This higher cyclotomic character plays a similarly fundamental role in chromatic homotopy theory, via the construction of the determinant sphere featuring in Gross-Hopkins duality. Theorem F, together with the theory developed in this paper, suggests that the spherical cyclotomic extension should assume a similarly pivotal role in
![]() $K(n)$
-local higher Galois theory, which deals with pro-
$K(n)$
-local higher Galois theory, which deals with pro-
![]() $\pi $
-finite Galois extensions of
$\pi $
-finite Galois extensions of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
. A more systematic account of this circle of ideas and their applications is a subject for a future work.
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
. A more systematic account of this circle of ideas and their applications is a subject for a future work.
Categorification
Finally, we also extend Theorem 1.1 by way of categorification. The key feature of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
that allows the chromatic Fourier transform to be an isomorphism is higher semiadditivity in the sense of [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Definition 4.4.2]. Moreover, the chromatic height n, which appears as the ‘shift’ in the chromatic Fourier transform, can be interpreted as the semiadditive height of
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
that allows the chromatic Fourier transform to be an isomorphism is higher semiadditivity in the sense of [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Definition 4.4.2]. Moreover, the chromatic height n, which appears as the ‘shift’ in the chromatic Fourier transform, can be interpreted as the semiadditive height of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a]. Similarly, our telescopic lift of Theorem 1.1 relies on the higher semiadditivity of
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a]. Similarly, our telescopic lift of Theorem 1.1 relies on the higher semiadditivity of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
, which is the maximal higher semiadditive localization of
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
, which is the maximal higher semiadditive localization of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}$
of height n (see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22]). We therefore construct and study the higher Fourier natural transformation in the general setting of higher semiadditive symmetric monoidal
$\textrm {Sp}$
of height n (see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22]). We therefore construct and study the higher Fourier natural transformation in the general setting of higher semiadditive symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-categories of a given semiadditive height n (at an implicit prime p). However, it is not easy to determine, in this abstract setting, when the Fourier transform is an isomorphism, and a large portion of this paper is devoted to developing tools for answering this question.
$\infty $
-categories of a given semiadditive height n (at an implicit prime p). However, it is not easy to determine, in this abstract setting, when the Fourier transform is an isomorphism, and a large portion of this paper is devoted to developing tools for answering this question.
One interesting source of examples of higher semiadditive
![]() $\infty $
-categories, outside of the stable realm, is higher category theory itself. As already observed in [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13], the
$\infty $
-categories, outside of the stable realm, is higher category theory itself. As already observed in [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13], the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\textrm {Pr}}$
of presentable
${\textrm {Pr}}$
of presentable
![]() $\infty $
-categories is
$\infty $
-categories is
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditive. More generally, for any presentably symmetric monoidal
$\infty $
-semiadditive. More generally, for any presentably symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, the
${\mathscr {C}}$
, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{\mathscr {C}}}$
of
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{\mathscr {C}}}$
of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear presentable
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear presentable
![]() $\infty $
-categories is
$\infty $
-categories is
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditive.
$\infty $
-semiadditive.
Regarding roots of unity, a height n root of unity
![]() $\omega \colon \Sigma ^n {\mathbb {Z}}/m \to R^\times $
of a commutative algebra R in
$\omega \colon \Sigma ^n {\mathbb {Z}}/m \to R^\times $
of a commutative algebra R in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
deloops uniquely to a height
${\mathscr {C}}$
deloops uniquely to a height
![]() $n+1$
root of unity
$n+1$
root of unity
of
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
, viewed as a commutative algebra in
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
, viewed as a commutative algebra in
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{\mathscr {C}}}$
. Note that the ‘shift by one’ in the height is consistent with the semiadditive redshift phenomenon from [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a].
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{\mathscr {C}}}$
. Note that the ‘shift by one’ in the height is consistent with the semiadditive redshift phenomenon from [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a].
Namely, if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
happens to be itself
${\mathscr {C}}$
happens to be itself
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditive and R is of semiadditive height n in
$\infty $
-semiadditive and R is of semiadditive height n in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, then
${\mathscr {C}}$
, then
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
is of semiadditive height
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
is of semiadditive height
![]() $n+1$
in
$n+1$
in
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{\mathscr {C}}}$
. As the semiadditive height generalizes the chromatic height, this is strongly related to the chromatic redshift philosophy. Now, given
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{\mathscr {C}}}$
. As the semiadditive height generalizes the chromatic height, this is strongly related to the chromatic redshift philosophy. Now, given
![]() $\omega $
as above, our theory provides a Fourier transform of commutative R-algebras in
$\omega $
as above, our theory provides a Fourier transform of commutative R-algebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
${\mathscr {C}}$
and also a ‘categorified’ Fourier transform of symmetric monoidal
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
-linear presentable
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
-linear presentable
![]() $\infty $
-categories
$\infty $
-categories
Unpacking the definitions, the right-hand side is the
![]() $\infty $
-category of
$\infty $
-category of
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
-valued local systems on
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
-valued local systems on
![]() $\Omega ^{\infty -(n+1)}M^{*}$
with the pointwise symmetric monoidal structure, while the source is the
$\Omega ^{\infty -(n+1)}M^{*}$
with the pointwise symmetric monoidal structure, while the source is the
![]() $\infty $
-category of
$\infty $
-category of
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
-valued local systems on
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
-valued local systems on
![]() $\Omega ^\infty M$
with the Day convolution symmetric monoidal structure. Our main result regarding this situation is that
$\Omega ^\infty M$
with the Day convolution symmetric monoidal structure. Our main result regarding this situation is that
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{\overline {\omega }}$
is an isomorphism if and only if
${\mathfrak {F}}_{\overline {\omega }}$
is an isomorphism if and only if
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{\omega }$
is an isomorphism.
${\mathfrak {F}}_{\omega }$
is an isomorphism.
Categorification of spherical orientations is more subtle. In general, there can be an obstruction for delooping a height n spherical orientation
![]() $\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p} \to R^\times $
of R to a height
$\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p} \to R^\times $
of R to a height
![]() $n+1$
spherical orientation
$n+1$
spherical orientation
![]() $\Sigma ^{n+1}I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p} \to \textrm {pic}(R)$
of
$\Sigma ^{n+1}I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p} \to \textrm {pic}(R)$
of
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
. However, it does give an
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
. However, it does give an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation for the truncated p-local sphere spectrum
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation for the truncated p-local sphere spectrum
![]() ${\mathfrak {R}} = \tau _{\le n}{\mathbb {S}}_{(p)}$
. In the case of the
${\mathfrak {R}} = \tau _{\le n}{\mathbb {S}}_{(p)}$
. In the case of the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category ![]() of
of
![]() $K(n)$
-local
$K(n)$
-local
![]() $E_n$
-modules, this partial result reads as follows:
$E_n$
-modules, this partial result reads as follows:
Theorem G (7.9).
For every
![]() $n\ge 0$
, there is a natural equivalence of symmetric monoidal
$n\ge 0$
, there is a natural equivalence of symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-categories:
$\infty $
-categories:
for M a connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local spectrum, assuming the vanishing of the canonical map
$\pi $
-finite p-local spectrum, assuming the vanishing of the canonical map
Remark 1.5. For a connective M, the induced isomorphism on the endomorphism objects of the respective monoidal units in the equivalence of Theorem G recovers Theorem D.
The technical assumption on M is equivalent to the
![]() $(n+1)$
-truncation of M having a (necessarily unique) module structure over the n-truncated sphere spectrum. This happens, for example, if M admits a
$(n+1)$
-truncation of M having a (necessarily unique) module structure over the n-truncated sphere spectrum. This happens, for example, if M admits a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-module structure, as in the original statement of Theorem 1.1, in which case the equivalence exists already over
$\mathbb {Z}$
-module structure, as in the original statement of Theorem 1.1, in which case the equivalence exists already over
![]() $R_n$
(or even
$R_n$
(or even
![]() $R_n^f$
). We conjecture, however, that this hypothesis is unnecessary – namely, that the spherical orientation of
$R_n^f$
). We conjecture, however, that this hypothesis is unnecessary – namely, that the spherical orientation of
![]() $E_n$
can be delooped to a spherical orientation of
$E_n$
can be delooped to a spherical orientation of ![]() . This would happen if, for example,
. This would happen if, for example,
where
![]() $\textrm {br}$
stands for the Brauer spectrum (cf. Remark 1.4).
$\textrm {br}$
stands for the Brauer spectrum (cf. Remark 1.4).
The height
![]() $n=0$
case of Theorem G recovers a classical fact. For a finite abelian group A and
$n=0$
case of Theorem G recovers a classical fact. For a finite abelian group A and
![]() $M = A^*$
, we get
$M = A^*$
, we get
![]() $\Omega ^\infty M = A^*$
and
$\Omega ^\infty M = A^*$
and
![]() $\Omega ^{\infty - 1} IM = BA$
. We therefore obtain an equivalence between the symmetric monoidal (derived) categories of
$\Omega ^{\infty - 1} IM = BA$
. We therefore obtain an equivalence between the symmetric monoidal (derived) categories of
![]() $\overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
-representations of A and of
$\overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
-representations of A and of
![]() $A^*$
-graded
$A^*$
-graded
![]() $\overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
-vector spaces. This equivalence is provided, unsurprisingly, by decomposition into weight spaces. Assuming A is a p-group, for a general height n and
$\overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
-vector spaces. This equivalence is provided, unsurprisingly, by decomposition into weight spaces. Assuming A is a p-group, for a general height n and
![]() $M = A^*$
, we get a similar ‘weight space decomposition’ of the symmetric monoidal
$M = A^*$
, we get a similar ‘weight space decomposition’ of the symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category of
$\infty $
-category of ![]() -representations of the higher group
-representations of the higher group
![]() $G = B^nA$
,
$G = B^nA$
,

For an example of a different flavor, in height
![]() $n=1$
with
$n=1$
with
![]() $M = \Sigma A$
, we get an equivalence between
$M = \Sigma A$
, we get an equivalence between ![]() -representations of A and of
-representations of A and of
![]() $A^*$
, but with different symmetric monoidal structures. A similar (non-monoidal) equivalence was considered by Treumann in [Reference TreumannTre15].
$A^*$
, but with different symmetric monoidal structures. A similar (non-monoidal) equivalence was considered by Treumann in [Reference TreumannTre15].
Outline of chromatic applications
The bulk of this paper is devoted to the development of the formal theory of Fourier transforms and affineness in an abstract setting. The reader primarily concerned with the applications to chromatic homotopy theory might thus be interested in a compressed outline of the path leading to these applications indicating where and how exactly this formal theory is being used. We shall hence provide such an outline for a sample of the results involving the Lubin–Tate spectrum
![]() $E_n$
, culminating in the computation of the discrepancy spectrum.
$E_n$
, culminating in the computation of the discrepancy spectrum.
The first main result in this direction is the extension of the natural isomorphism constructed by Hopkins and Lurie,
from
![]() $\pi $
-finite
$\pi $
-finite
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-module spectra M to arbitrary
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-module spectra M to arbitrary
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local spectra (Theorem D). As already explained, this is equivalent to solving the extension problem for orientations:
$\pi $
-finite p-local spectra (Theorem D). As already explained, this is equivalent to solving the extension problem for orientations:

The approach we take is to break this problem up into two steps:
-
(1) Constructing some map
 $\overline {\omega }$
as above (i.e., an
$\overline {\omega }$
as above (i.e., an
 $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-pre-orientation) extending
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-pre-orientation) extending
 $\omega $
.
$\omega $
. -
(2) Showing that any such extension
 $\overline {\omega }$
is automatically an
$\overline {\omega }$
is automatically an
 $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation.
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation.
The proof of (2) proceeds by a dévissage argument. Let us say that a
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local spectrum M is oriented if the associated chromatic Fourier transform map
$\pi $
-finite p-local spectrum M is oriented if the associated chromatic Fourier transform map
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{\overline {\omega }}$
is an isomorphism at M. The base case consists of spectra M admitting a
${\mathfrak {F}}_{\overline {\omega }}$
is an isomorphism at M. The base case consists of spectra M admitting a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-module structure. These are shown to be oriented using the isomorphism of Hopkins and Lurie by constructing the Fourier transform sufficiently functorially to allow pushing forward (pre-)orientations along the map
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-module structure. These are shown to be oriented using the isomorphism of Hopkins and Lurie by constructing the Fourier transform sufficiently functorially to allow pushing forward (pre-)orientations along the map
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}\to \mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
. As every
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}\to \mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
. As every
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local spectrum M is an iterated extension of
$\pi $
-finite p-local spectrum M is an iterated extension of
![]() $\pi $
-finite
$\pi $
-finite
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-module spectra (via the Postnikov tower), it suffices to show that oriented modules are closed under extensions – namely, that given a cofiber sequence
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-module spectra (via the Postnikov tower), it suffices to show that oriented modules are closed under extensions – namely, that given a cofiber sequence
![]() $M' \to M \to M"$
of
$M' \to M \to M"$
of
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local spectra, if
$\pi $
-finite p-local spectra, if
![]() $M'$
and
$M'$
and
![]() $M"$
are oriented, then so is M (see Proposition 4.11 and Proposition 4.12).
$M"$
are oriented, then so is M (see Proposition 4.11 and Proposition 4.12).
To prove the closure of oriented modules under extensions, we first show that the source and target of the Fourier transform are cofiber-preserving functors. For the source, this is obvious, and for the target, it is deduced from the Eilenberg–Moore isomorphism, which follows from affineness and is itself established by a separate dévissage argument from the orientability of
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-modules. This implies that oriented modules are closed under cofibers. As the
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-modules. This implies that oriented modules are closed under cofibers. As the
![]() $\infty $
-category of commutative algebras is not stable, closure under cofibers does not automatically imply closure under extensions. To get that, we show that the chromatic Fourier transform canonically promotes to a morphism of Hopf algebras (see Corollary 3.31). Loosely speaking, we exploit the fact that we are dealing with an exact sequence of group objects. Finally, as one actually deals with (co)fibers in connective spectra, there is a fringe effect at
$\infty $
-category of commutative algebras is not stable, closure under cofibers does not automatically imply closure under extensions. To get that, we show that the chromatic Fourier transform canonically promotes to a morphism of Hopf algebras (see Corollary 3.31). Loosely speaking, we exploit the fact that we are dealing with an exact sequence of group objects. Finally, as one actually deals with (co)fibers in connective spectra, there is a fringe effect at
![]() $\pi _0(M)$
. Hence, to complete the proof, one also has to use the fact that the chromatic Fourier transform intertwines Brown–Comenetz duality with Spanier–Whitehead duality (see Proposition 3.25).
$\pi _0(M)$
. Hence, to complete the proof, one also has to use the fact that the chromatic Fourier transform intertwines Brown–Comenetz duality with Spanier–Whitehead duality (see Proposition 3.25).
The above outlined argument for (2) is quite general, as it only uses that
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)} \to \mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
is a map of local ring spectra that induces an isomorphism on residue fields. In particular, it even suffices that
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)} \to \mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
is a map of local ring spectra that induces an isomorphism on residue fields. In particular, it even suffices that
![]() $\overline {\omega }$
restricts to an
$\overline {\omega }$
restricts to an
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation (i.e., a height n primitive p-th root of unity). In contrast, the proof of (1) relies on some very special properties of
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation (i.e., a height n primitive p-th root of unity). In contrast, the proof of (1) relies on some very special properties of
![]() $E_n$
, which we recast and abstract in the theory of categorical connectedness, as we explain next.
$E_n$
, which we recast and abstract in the theory of categorical connectedness, as we explain next.
We say that a commutative algebra
![]() $R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is d-connected if the canonical map of spaces
$R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is d-connected if the canonical map of spaces
is an isomorphism for all d-finite p-spaces A. The relevance of this notion to our discussion is that it allows for inductively extending (pre-)orientations of R along the (double) tower
by showing that the respective obstructions vanish for formal reasons (see Proposition 6.44).
Moreover, when
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height n, a
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height n, a
![]() $\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation of R is already the same as an
$\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation of R is already the same as an
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation (see Remark 3.4).
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation (see Remark 3.4).
The fact that
![]() $E_n$
is n-connected was conjectured and subsequently proved (though not published) by Hopkins and Lurie. Using affineness, the condition of n-connectedness can be reduced from all n-finite p-spaces A to the single special case
$E_n$
is n-connected was conjectured and subsequently proved (though not published) by Hopkins and Lurie. Using affineness, the condition of n-connectedness can be reduced from all n-finite p-spaces A to the single special case
![]() $A = B^n C_p$
. Moreover, using the
$A = B^n C_p$
. Moreover, using the
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-linear Fourier transform of Hopkins and Lurie, this is equivalent to
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-linear Fourier transform of Hopkins and Lurie, this is equivalent to
In this form, it was also proven by a different method in the work of the third author with Burklund and Yuan on the chromatic nullstellensatz [Reference Burklund, Schlank and YuanBSY22]. Combined with the obstruction theory for orientation extensions mentioned above, this allows one to extend an arbitrary
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of
![]() $E_n$
to a
$E_n$
to a
![]() $\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation. This is, however, not completely satisfactory as it is still one step away from providing a full spherical orientation for
$\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation. This is, however, not completely satisfactory as it is still one step away from providing a full spherical orientation for
![]() $E_n$
.
$E_n$
.
As a height n commutative algebra R is never
![]() $(n+1)$
-connected, the last extension step indeed requires an essential new ingredient. By the semiadditive redshift principle, categorification has the effect of rising the semiadditive height by 1, which in turn gives access to one additional homotopy group of
$(n+1)$
-connected, the last extension step indeed requires an essential new ingredient. By the semiadditive redshift principle, categorification has the effect of rising the semiadditive height by 1, which in turn gives access to one additional homotopy group of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
. More precisely, the symmetric monoidal
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
. More precisely, the symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category ![]() of
of
![]() $K(n)$
-local
$K(n)$
-local
![]() $E_n$
-modules is a commutative algebra in
$E_n$
-modules is a commutative algebra in
![]() ${\textrm {Pr}}$
, which is of semiadditive height
${\textrm {Pr}}$
, which is of semiadditive height
![]() $n+1$
. Thus, it can be and in fact is
$n+1$
. Thus, it can be and in fact is
![]() $(n+1)$
-connected. To establish this fact, one needs the following strengthening of the Hopkins–Lurie conjecture (also proved in [Reference Burklund, Schlank and YuanBSY22]):
$(n+1)$
-connected. To establish this fact, one needs the following strengthening of the Hopkins–Lurie conjecture (also proved in [Reference Burklund, Schlank and YuanBSY22]):
In addition, we need to show that an
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation (of height n) of
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation (of height n) of
![]() $E_n$
deloops to an
$E_n$
deloops to an
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation (of height
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation (of height
![]() $n + 1$
) of
$n + 1$
) of ![]() , and conversely, the extended
, and conversely, the extended
![]() $\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation of
$\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation of ![]() loops back to a
loops back to a
![]() $\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation of
$\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation of
![]() $E_n$
. To this end, we analyze the categorical Fourier transform and derive an explicit formula (see Proposition 5.13) for its evaluation at connected modules in terms of the Fourier transform over
$E_n$
. To this end, we analyze the categorical Fourier transform and derive an explicit formula (see Proposition 5.13) for its evaluation at connected modules in terms of the Fourier transform over
![]() $E_n$
. To analyze the categorical Fourier transform for arbitrary modules, we again employ the dévissage and reflection techniques discussed earlier.
$E_n$
. To analyze the categorical Fourier transform for arbitrary modules, we again employ the dévissage and reflection techniques discussed earlier.
We conclude this outline with an explanation of how all this relates to the discrepancy spectrum of
![]() $E_n$
. Given a
$E_n$
. Given a
![]() $T(n)$
-local commutative ring R, its connective spectrum of units
$T(n)$
-local commutative ring R, its connective spectrum of units
![]() $R^\times $
need not be
$R^\times $
need not be
![]() $T(n)$
- or even
$T(n)$
- or even
![]() $L_n^f$
-local. In general, its p-localization fits into a cofiber sequence
$L_n^f$
-local. In general, its p-localization fits into a cofiber sequence
The
![]() $L_n^f$
-acyclic part
$L_n^f$
-acyclic part
![]() $C_n^f R^\times $
, or some close variant thereof, is called the discrepancy spectrum of R. A result announced by Hopkins and Lurie states that the discrepancy spectrum of
$C_n^f R^\times $
, or some close variant thereof, is called the discrepancy spectrum of R. A result announced by Hopkins and Lurie states that the discrepancy spectrum of
![]() $E_n$
identifies with the shifted Brown–Comenetz dual
$E_n$
identifies with the shifted Brown–Comenetz dual
![]() $\Sigma ^n I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
on connective covers. This fact admits an interesting interpretation, and consequently a proof, from the perspective of our theory. First, it can be shown in general that
$\Sigma ^n I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
on connective covers. This fact admits an interesting interpretation, and consequently a proof, from the perspective of our theory. First, it can be shown in general that
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^f(R) \simeq \mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
(see Theorem 7.23), where the right-hand side is the co-reflection of
$\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^f(R) \simeq \mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
(see Theorem 7.23), where the right-hand side is the co-reflection of
![]() $R^\times $
onto the full subcategory of ind-
$R^\times $
onto the full subcategory of ind-
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local spectra. Less formally,
$\pi $
-finite p-local spectra. Less formally,
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
is a
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
is a
![]() $\pi $
-finite analogue of the spectrum of p-power roots of unity of R. By adjunction, a spherical pre-orientation on R is the same as a map
$\pi $
-finite analogue of the spectrum of p-power roots of unity of R. By adjunction, a spherical pre-orientation on R is the same as a map
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p} \to \mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
. Thus, given an isomorphism
$\tau _{\ge 0}\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p} \to \mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
. Thus, given an isomorphism
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R) \simeq \tau _{\ge 0}\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
(see Corollary 6.59), there is a canonical spherical pre-orientation on R, which can be easily seen to be an orientation. Conversely, and somewhat surprisingly, we show that if R admits a spherical orientation and is n-connected, then we must have
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R) \simeq \tau _{\ge 0}\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
(see Corollary 6.59), there is a canonical spherical pre-orientation on R, which can be easily seen to be an orientation. Conversely, and somewhat surprisingly, we show that if R admits a spherical orientation and is n-connected, then we must have
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R) \simeq \tau _{\ge 0}\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
. Given the above, this in particular implies that
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R) \simeq \tau _{\ge 0}\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
. Given the above, this in particular implies that
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(E_n) \simeq \tau _{\ge 0}\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
, reproducing the announced result of Hopkins and Lurie.
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(E_n) \simeq \tau _{\ge 0}\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
, reproducing the announced result of Hopkins and Lurie.
Remark 1.6. In [Reference Freed and HopkinsFH21], Hopkins and Freed suggested that a key feature of possible targets for topological quantum field theories is having as the categorical units spectra closely related to
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
, as this implies that invertible field theories with that target are determined by the partition function. The aforementioned relationship between categorical connectedness and
$\tau _{\ge 0}\Sigma ^nI_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
, as this implies that invertible field theories with that target are determined by the partition function. The aforementioned relationship between categorical connectedness and
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(-)$
suggests an additional possible principle: targets for topological quantum field theories should be maximally connected in the categorical sense.
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(-)$
suggests an additional possible principle: targets for topological quantum field theories should be maximally connected in the categorical sense.
Organization
In Section 2, we study the notion of affineness. We begin in 2.1 by introducing it in the general setting of monoidal functors. We establish equivalent characterizations for affine functors and certain closure and monoidal properties thereof. Then, in 2.2, we specialize to functors arising as pullbacks for local systems and relate the property of affineness to the behavior of Eilenberg–Moore maps and Galois extensions. We end this section, in 2.3, by studying the interaction of affineness with ambidexterity and semiadditive height, establishing among other things the mutual implications of affineness and the Eilenberg–Moore isomorphism.
In Section 3, we lay down the foundations of the abstract theory of Fourier transforms. In 3.1, we define
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations of height n for a connective p-local commutative ring spectrum
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations of height n for a connective p-local commutative ring spectrum
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
and the corresponding notion of Brown–Comenetz duality for
$\mathfrak {R}$
and the corresponding notion of Brown–Comenetz duality for
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules. In 3.2, we proceed to construct the Fourier (not necessarily invertible) transformation associated to an
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules. In 3.2, we proceed to construct the Fourier (not necessarily invertible) transformation associated to an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation and discuss its functoriality and duality invariance. We conclude, in 3.3, by promoting the Fourier transform to a map of Hopf algebras and deducing an analogue of the classical translation invariance property.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation and discuss its functoriality and duality invariance. We conclude, in 3.3, by promoting the Fourier transform to a map of Hopf algebras and deducing an analogue of the classical translation invariance property.
In Section 4, we study
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations, which are
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations, which are
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations such that the associated Fourier transform is an isomorphism for all suitably finite
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations such that the associated Fourier transform is an isomorphism for all suitably finite
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules. In 4.1, after presenting the relevant definitions and functorialities, we establish for a given
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules. In 4.1, after presenting the relevant definitions and functorialities, we establish for a given
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation various closure properties of the class of oriented modules (those for which the Fourier transform is an isomorphism). Next, in 4.2, we introduce the universal
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation various closure properties of the class of oriented modules (those for which the Fourier transform is an isomorphism). Next, in 4.2, we introduce the universal
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-oriented algebras, the
$\mathfrak {R}$
-oriented algebras, the
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extensions, and show that they are
$\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extensions, and show that they are
![]() $\mathfrak {R}^\times $
-Galois under certain finiteness hypotheses. Then, in 4.3, we discuss virtual orientability, which is the property of admitting an
$\mathfrak {R}^\times $
-Galois under certain finiteness hypotheses. Then, in 4.3, we discuss virtual orientability, which is the property of admitting an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation after a faithful extension of scalars, or equivalently, that the
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation after a faithful extension of scalars, or equivalently, that the
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension is faithful. We show that under the assumption of virtual
$\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension is faithful. We show that under the assumption of virtual
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientability, the underlying space of a suitably finite
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientability, the underlying space of a suitably finite
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module is affine and deduce a general form of higher Kummer theory. Finally, in 4.4, we focus on local rings
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module is affine and deduce a general form of higher Kummer theory. Finally, in 4.4, we focus on local rings
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
and show that an
$\mathfrak {R}$
and show that an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation can be checked to be an orientation after pushforward to the residue field of
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation can be checked to be an orientation after pushforward to the residue field of
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
. This result is essential in lifting primitive (higher) p-th roots of unity to spherical orientations.
$\mathfrak {R}$
. This result is essential in lifting primitive (higher) p-th roots of unity to spherical orientations.
In Section 5, we investigate the interaction of the Fourier transform with categorification. In the preliminary subsection 5.1, we review the categorification-decategorification adjunction taking, in one direction, an
![]() $\mathbb {E}_n$
-algebra to its
$\mathbb {E}_n$
-algebra to its
![]() $\mathbb {E}_{n-1}$
-monoidal category of modules, and in the other, an
$\mathbb {E}_{n-1}$
-monoidal category of modules, and in the other, an
![]() $\mathbb {E}_{n-1}$
-monoidal
$\mathbb {E}_{n-1}$
-monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category to the
$\infty $
-category to the
![]() $\mathbb {E}_n$
-algebra of (enriched) endomorphisms of the unit. We reinterpret the property of affineness in terms of this adjunction and address certain set-theoretical issues related to
$\mathbb {E}_n$
-algebra of (enriched) endomorphisms of the unit. We reinterpret the property of affineness in terms of this adjunction and address certain set-theoretical issues related to
![]() ${\textrm {Pr}}$
not being itself presentable. In 5.2, we initiate the study of the ‘categorified’ Fourier transform, by describing its source and target in explicit terms and explaining how the ‘decategorified’ Fourier transform can be recovered from it. We continue, in 5.3, to show that orientations categorify to orientations and that the categorical
${\textrm {Pr}}$
not being itself presentable. In 5.2, we initiate the study of the ‘categorified’ Fourier transform, by describing its source and target in explicit terms and explaining how the ‘decategorified’ Fourier transform can be recovered from it. We continue, in 5.3, to show that orientations categorify to orientations and that the categorical
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension is the categorification of the usual
$\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension is the categorification of the usual
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension.
In Section 6, we concentrate on
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-(pre)-orientations for local ring spectra
$\mathfrak {R}$
-(pre)-orientations for local ring spectra
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field
$\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
, paying special attention to the following tower of rings:
$\mathbb {F}_p$
, paying special attention to the following tower of rings:
In 6.1, we study the consequences of virtual
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientability (at height n). In particular, we show that it implies affineness for all
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientability (at height n). In particular, we show that it implies affineness for all
![]() $\pi $
-finite spaces as in Theorem B. We also show that it implies virtual
$\pi $
-finite spaces as in Theorem B. We also show that it implies virtual
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientability for all connective
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientability for all connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite commutative ring spectra with residue field
$\pi $
-finite commutative ring spectra with residue field
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
, such as
$\mathbb {F}_p$
, such as
![]() $\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
. In 6.2, we relate
$\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
. In 6.2, we relate
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-orientations in the stable setting to primitive higher
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-orientations in the stable setting to primitive higher
![]() $p^r$
-th roots of unity in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b] and deduce that virtual
$p^r$
-th roots of unity in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b] and deduce that virtual
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientability is detected by nil-conservative functors. We also characterize virtual
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientability is detected by nil-conservative functors. We also characterize virtual
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientability in terms of the affineness of certain spaces and the Galois condition for the higher cyclotomic extensions. We proceed, in 6.3, to study the consequences of virtual
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientability in terms of the affineness of certain spaces and the Galois condition for the higher cyclotomic extensions. We proceed, in 6.3, to study the consequences of virtual
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientability. First, we show that it implies virtual
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientability. First, we show that it implies virtual
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientability for all local ring spectra
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientability for all local ring spectra
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field
$\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
, and so, in particular, that the spherical cyclotomic extension is faithful (the case
$\mathbb {F}_p$
, and so, in particular, that the spherical cyclotomic extension is faithful (the case
![]() $\mathfrak {R}=\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
). Second, we show that in the stable setting, it implies that the localization with respect to the infinite p-typical higher cyclotomic extension (or equivalently, the spherical cyclotomic extension) is a smashing localization and provide a formula for its unit. Finally, in 6.4, we study truncated spherical orientations (i.e.,
$\mathfrak {R}=\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
). Second, we show that in the stable setting, it implies that the localization with respect to the infinite p-typical higher cyclotomic extension (or equivalently, the spherical cyclotomic extension) is a smashing localization and provide a formula for its unit. Finally, in 6.4, we study truncated spherical orientations (i.e.,
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations for
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations for
![]() $\mathfrak {R} = \tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
). Observing that the case
$\mathfrak {R} = \tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
). Observing that the case
![]() $d = n$
is already equivalent to an
$d = n$
is already equivalent to an
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation, we study the obstructions for lifting a
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation, we study the obstructions for lifting a
![]() $\tau _{\le d-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation to a
$\tau _{\le d-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation to a
![]() $\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation for
$\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation for
![]() $d = 1,\dots ,n$
. To this end, we introduce the notion of d-connectedness, which ensures that the said obstructions vanish up to d, and relate this property to the connectedness of the (ordinary) roots of unity
$d = 1,\dots ,n$
. To this end, we introduce the notion of d-connectedness, which ensures that the said obstructions vanish up to d, and relate this property to the connectedness of the (ordinary) roots of unity
![]() $\mu _p$
and ‘spherical’ roots of unity
$\mu _p$
and ‘spherical’ roots of unity
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}$
spectra. The last step
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}$
spectra. The last step
![]() $d = n$
requires a categorification argument from Section 5 and, accordingly, involves the Picard spectrum. We conclude with a discussion of the spherical cyclotomic extension, showing it is pro-Galois.
$d = n$
requires a categorification argument from Section 5 and, accordingly, involves the Picard spectrum. We conclude with a discussion of the spherical cyclotomic extension, showing it is pro-Galois.
In Section 7, we apply the abstract theory developed in the previous sections to chromatic homotopy theory. In the preliminary subsection 7.1, we briefly recall some material on the monochromatic
![]() $\infty $
-categories
$\infty $
-categories
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
and
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
and
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
, the Lubin–Tate spectra
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
, the Lubin–Tate spectra
![]() $E_n$
, and the higher cyclotomic extensions
$E_n$
, and the higher cyclotomic extensions
![]() $R_{n,r}$
and
$R_{n,r}$
and
![]() $R_{n,r}^f$
. In 7.2, we study the Fourier theory over
$R_{n,r}^f$
. In 7.2, we study the Fourier theory over
![]() $E_n$
. First, we interpret Theorem 1.1 as the existence of a
$E_n$
. First, we interpret Theorem 1.1 as the existence of a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientation on
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientation on
![]() $E_n$
and bootstrap it to an
$E_n$
and bootstrap it to an
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation, proving Theorem D. By the general theory, this readily implies Theorem F on the
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation, proving Theorem D. By the general theory, this readily implies Theorem F on the
![]() $K(n)$
-local spherical cyclotomic extension, and Theorem G on the categorified spherical Fourier transform. We conclude with the study of the discrepancy spectrum, proving Theorem E. Finally, in 7.3, we apply the theory of orientations and the Fourier transform to the telescopic setting. We first prove that
$K(n)$
-local spherical cyclotomic extension, and Theorem G on the categorified spherical Fourier transform. We conclude with the study of the discrepancy spectrum, proving Theorem E. Finally, in 7.3, we apply the theory of orientations and the Fourier transform to the telescopic setting. We first prove that
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is virtually
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is virtually
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-orientable and deduce Theorem A. From the general theory, we immediately deduce all the properties of local systems of
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-orientable and deduce Theorem A. From the general theory, we immediately deduce all the properties of local systems of
![]() $K(n)$
-local algebras on
$K(n)$
-local algebras on
![]() $\pi $
-finite spaces stated in Theorem B and the higher Kummer theory as formulated in Theorem C. We conclude with a short discussion about the universal
$\pi $
-finite spaces stated in Theorem B and the higher Kummer theory as formulated in Theorem C. We conclude with a short discussion about the universal
![]() $T(n)$
-local virtually spherically oriented localization and its relation to the properties of
$T(n)$
-local virtually spherically oriented localization and its relation to the properties of
![]() $R_n^f$
and the telescope conjecture.
$R_n^f$
and the telescope conjecture.
Notation and conventions
Throughout the paper, we work in the framework of
![]() $\infty $
-categories (a.k.a. quasi-categories) as developed in [Reference LurieLur09] and [Reference LurieLur]. We generally follow the terminology and notation therein. For all concepts related to semiadditivity, semiadditive height and higher cyclotomic extensions, we refer the reader to [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a] and [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b]; precise references are given in the main body of the text.
$\infty $
-categories (a.k.a. quasi-categories) as developed in [Reference LurieLur09] and [Reference LurieLur]. We generally follow the terminology and notation therein. For all concepts related to semiadditivity, semiadditive height and higher cyclotomic extensions, we refer the reader to [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a] and [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b]; precise references are given in the main body of the text.
In addition, we employ the following notation:
-
(1) The underlying space of a spectrum X will be denoted by
 $\lfloor {X}\rfloor := \Omega ^{\infty }X$
. More generally, for an object X in a monoidal
$\lfloor {X}\rfloor := \Omega ^{\infty }X$
. More generally, for an object X in a monoidal
 $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
, we write
${\mathscr {C}}$
, we write  .
. -
(2) A square in an
 $\infty $
-category is called exact if it is both a pullback and a pushout square.
$\infty $
-category is called exact if it is both a pullback and a pushout square. -
(3) In our applications, we usually fix a prime p and work p-locally. We usually indicate the prime through a subscript; for instance, we write
 $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
for the category of p-local spectra.
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
for the category of p-local spectra. -
(4) A p-local spectrum X is said to be
 $\pi $
-finite if it is connective and
$\pi $
-finite if it is connective and
 $\bigoplus _n\pi _nX$
is a finite abelian group. We write
$\bigoplus _n\pi _nX$
is a finite abelian group. We write
 $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
for the category of p-local
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
for the category of p-local
 $\pi $
-torsion spectra (Definition 6.52) (i.e., those connective spectra which can be written as filtered colimits of p-local
$\pi $
-torsion spectra (Definition 6.52) (i.e., those connective spectra which can be written as filtered colimits of p-local
 $\pi $
-finite spectra). The p-local
$\pi $
-finite spectra). The p-local
 $\pi $
-torsion torsion part of a p-local spectrum X is denoted by
$\pi $
-torsion torsion part of a p-local spectrum X is denoted by
 $(X)_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
.
$(X)_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
.
2 Affineness and Eilenberg–Moore
In algebraic geometry, affine schemes are those which can be canonically recovered from their algebra of global regular functions. In this section, we study an analogous notion in homotopy theory and its interaction with Eilenberg–Moore type properties, Galois extensions and ambidexterity. Much of the material in this section is inspired by, and is an abstraction of, the results and arguments in [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, §5.4] for
![]() $K(n)$
-local spectra.
$K(n)$
-local spectra.
2.1 Affine functors
We begin the study of affineness in the abstract generality of presentably monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-categories. For
$\infty $
-categories. For
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
(i.e., a monoidal, colimit-preserving functor between presentably monoidal
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
(i.e., a monoidal, colimit-preserving functor between presentably monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-categories), write
$\infty $
-categories), write
![]() $f_*\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
for the right adjoint to
$f_*\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
for the right adjoint to
![]() $f^*$
, which exists by the adjoint functor theorem. By [Reference LurieLur, Corollary 7.3.2.7],
$f^*$
, which exists by the adjoint functor theorem. By [Reference LurieLur, Corollary 7.3.2.7],
![]() $f_*$
has a canonical structure of a lax monoidal functor. Hence, for every
$f_*$
has a canonical structure of a lax monoidal functor. Hence, for every
![]() $R \in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we have
$R \in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we have
![]() $f_*R \in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {D}})$
and an induced functor
$f_*R \in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {D}})$
and an induced functor
taking
![]() $X\in \operatorname{ {LMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
to
$X\in \operatorname{ {LMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
to
![]() $f_*X$
, endowed with its canonical
$f_*X$
, endowed with its canonical
![]() $f_*R$
-module structure. This functor admits a left adjoint
$f_*R$
-module structure. This functor admits a left adjoint
taking
![]() $Y \in \operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*R}({\mathscr {D}})$
to
$Y \in \operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*R}({\mathscr {D}})$
to
using the algebra map
![]() $f^*f_* R \to R$
provided by the counit of the adjunction
$f^*f_* R \to R$
provided by the counit of the adjunction
![]() $f^* \dashv f_*$
(as in the proof of [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Theorem 5.4.3]).
$f^* \dashv f_*$
(as in the proof of [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Theorem 5.4.3]).
Definition 2.1. A functor
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}}\to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}}\to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
is called affine if the functor
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
is called affine if the functor
is an equivalence.
This definition generalizes the usual notion of affineness from algebraic geometry in the following sense:
Example 2.2. Consider a morphism of commutative rings
![]() $g\colon R \to S$
, write
$g\colon R \to S$
, write
![]() $g^*\colon {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R \to {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_S$
for the extension of scalars functor between the associated module categories, and let
$g^*\colon {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R \to {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_S$
for the extension of scalars functor between the associated module categories, and let
![]() $g_*$
be its forgetful right adjoint. Then
$g_*$
be its forgetful right adjoint. Then
![]() $g^*$
is affine. More generally, let
$g^*$
is affine. More generally, let
![]() $f\colon X\to Y$
be a morphism of schemes and
$f\colon X\to Y$
be a morphism of schemes and
![]() $f^*\colon \operatorname{{QCoh}}(Y)\to \operatorname{{QCoh}}(X)$
the functor of pullback of (ordinary) quasi-coherent sheaves along f. Then,
$f^*\colon \operatorname{{QCoh}}(Y)\to \operatorname{{QCoh}}(X)$
the functor of pullback of (ordinary) quasi-coherent sheaves along f. Then,
![]() $f^*$
is affine if and only if f is an affine morphism of schemes.
$f^*$
is affine if and only if f is an affine morphism of schemes.
Characterization
Our first goal is to characterize affineness in terms of the intrinsic properties of
![]() $f^*$
, or rather its right adjoint
$f^*$
, or rather its right adjoint
![]() $f_*$
. A functor
$f_*$
. A functor
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
endows
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
endows
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
with a
${\mathscr {C}}$
with a
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear structure, by which we mean a structure of a right
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear structure, by which we mean a structure of a right
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-module in the symmetric monoidal
${\mathscr {D}}$
-module in the symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\textrm {Pr}}$
, and
${\textrm {Pr}}$
, and
![]() $f^*$
becomes canonically a
$f^*$
becomes canonically a
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear functor. Furthermore, we get a projection formula map
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear functor. Furthermore, we get a projection formula map
which for every
![]() $X\in {\mathscr {C}}$
and
$X\in {\mathscr {C}}$
and
![]() $Y\in {\mathscr {D}}$
is given by the composition
$Y\in {\mathscr {D}}$
is given by the composition
with u and c the unit and counit maps respectively of the adjunction
![]() $f^*\dashv f_*$
. If
$f^*\dashv f_*$
. If
![]() $\varphi $
happens to be a natural isomorphism, then
$\varphi $
happens to be a natural isomorphism, then
![]() $f_*$
is
$f_*$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear as well, and the whole adjunction
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear as well, and the whole adjunction
![]() $f^* \dashv f_*$
promotes to the world of
$f^* \dashv f_*$
promotes to the world of
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear categories (see [Reference LurieLur, Remark 7.3.2.9]).
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear categories (see [Reference LurieLur, Remark 7.3.2.9]).
Lemma 2.3. Let
![]() $f^* \colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
$f^* \colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. If
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. If
![]() $f^*$
is affine, then
$f^*$
is affine, then
![]() $f_*$
is
$f_*$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear, colimit-preserving and conservative.
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear, colimit-preserving and conservative.
Proof. If
![]() $f^*$
is affine, then up to isomorphism, the functor
$f^*$
is affine, then up to isomorphism, the functor
![]() $f_*$
identifies with the forgetful functor
$f_*$
identifies with the forgetful functor ![]() . Such functors are
. Such functors are
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear, colimit-preserving and conservative by [Reference LurieLur, Remark 4.8.4.11, Corollary 4.2.3.7, and Corollary 4.2.3.2].
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear, colimit-preserving and conservative by [Reference LurieLur, Remark 4.8.4.11, Corollary 4.2.3.7, and Corollary 4.2.3.2].
We shall show that the converse of Lemma 2.3 holds as well, giving a characterization of affine functors in terms of the properties of their right adjoint. We begin with the following more general fact:
Proposition 2.4. Let
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}}\to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}}\to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. If
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. If
![]() $f_*$
is
$f_*$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear and colimit-preserving, then for every algebra
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear and colimit-preserving, then for every algebra
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the functor
$R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the functor
![]() $f^\sharp \colon \operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*R}({\mathscr {D}}) \to \operatorname{ {LMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
is fully faithful.
$f^\sharp \colon \operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*R}({\mathscr {D}}) \to \operatorname{ {LMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
is fully faithful.
Proof. To prove that
![]() $f^\sharp $
is fully faithful, we have to show that the unit morphism
$f^\sharp $
is fully faithful, we have to show that the unit morphism
![]() $ u\colon X\to f_\sharp f^\sharp X $
is an isomorphism for every
$ u\colon X\to f_\sharp f^\sharp X $
is an isomorphism for every
![]() $X\in \operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*S}({\mathscr {D}})$
. First, note that
$X\in \operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*S}({\mathscr {D}})$
. First, note that
![]() $f_\sharp $
is colimit-preserving. Indeed, we have a commutative diagram
$f_\sharp $
is colimit-preserving. Indeed, we have a commutative diagram

where the vertical maps are the conservative and colimit-preserving forgetful functors, and the lower horizontal functor is colimit-preserving by assumption. Therefore, the upper horizontal functor is colimit-preserving as well. We get that the source and the target of
![]() $u\colon \textrm {Id} \to f_\sharp f^\sharp $
are colimit-preserving functors. Since
$u\colon \textrm {Id} \to f_\sharp f^\sharp $
are colimit-preserving functors. Since
![]() $\operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*R}({\mathscr {D}})$
is generated under colimits by the modules of the form
$\operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*R}({\mathscr {D}})$
is generated under colimits by the modules of the form
![]() $f_*R \otimes Y$
for
$f_*R \otimes Y$
for
![]() $Y\in {\mathscr {D}}$
, it suffices to show that u is an isomorphism at such modules. The image of
$Y\in {\mathscr {D}}$
, it suffices to show that u is an isomorphism at such modules. The image of
![]() $f_\sharp f^\sharp (f_*R\otimes Y)$
under the forgetful functor
$f_\sharp f^\sharp (f_*R\otimes Y)$
under the forgetful functor
![]() $\operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*R}({\mathscr {D}}) \to {\mathscr {D}}$
is given by
$\operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*R}({\mathscr {D}}) \to {\mathscr {D}}$
is given by
Via this identification, the map
![]() $u\colon f_*R \otimes Y \to f_\sharp f^\sharp (f_*R \otimes Y)$
corresponds to the projection morphism
$u\colon f_*R \otimes Y \to f_\sharp f^\sharp (f_*R \otimes Y)$
corresponds to the projection morphism
which is an isomorphism by our assumption that
![]() $f_*$
is
$f_*$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear. Since the forgetful functor is conservative, we deduce that u is an isomorphism at
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear. Since the forgetful functor is conservative, we deduce that u is an isomorphism at
![]() $f_*R\otimes Y$
, and the result follows.
$f_*R\otimes Y$
, and the result follows.
We deduce the following characterization and consequence of affineness (cf. [Reference Mathew and MeierMM15, Corollary 3.7]):
Proposition 2.5. Let
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}}\to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}}\to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. The functor
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. The functor
![]() $f^*$
is affine if and only if its right adjoint
$f^*$
is affine if and only if its right adjoint
![]() $f_*\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
is
$f_*\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear, colimit-preserving and conservative. Moreover, in such a case, for every
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear, colimit-preserving and conservative. Moreover, in such a case, for every
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the functor
$R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the functor
is an equivalence.
Proof. The ‘only if’ part is given by Lemma 2.3. Now, if
![]() $f_*$
is
$f_*$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear, colimit-preserving and conservative, then by Proposition 2.4, the functor
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear, colimit-preserving and conservative, then by Proposition 2.4, the functor
![]() $ f_\sharp \colon \operatorname{ {LMod}}_{R}({\mathscr {C}})\to \operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*R}({\mathscr {D}}) $
admits a fully faithful left adjoint. To show that
$ f_\sharp \colon \operatorname{ {LMod}}_{R}({\mathscr {C}})\to \operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*R}({\mathscr {D}}) $
admits a fully faithful left adjoint. To show that
![]() $f_\sharp $
is an equivalence, it therefore suffices to show that it is conservative. Note that the composition of
$f_\sharp $
is an equivalence, it therefore suffices to show that it is conservative. Note that the composition of
![]() $f_\sharp $
with the forgetful functor
$f_\sharp $
with the forgetful functor
![]() $\operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*R}({\mathscr {D}}) \to {\mathscr {D}}$
is the functor
$\operatorname{ {LMod}}_{f_*R}({\mathscr {D}}) \to {\mathscr {D}}$
is the functor
![]() $f_*$
, which is conservative by assumption. Thus,
$f_*$
, which is conservative by assumption. Thus,
![]() $f_\sharp $
is conservative as well, and hence an equivalence. In particular, the ‘if’ part follows by taking
$f_\sharp $
is conservative as well, and hence an equivalence. In particular, the ‘if’ part follows by taking ![]() .
.
Remark 2.6. Proposition 2.5 above is closely related to the Barr–Beck–Lurie monadicity theorem [Reference LurieLur, Theorem 4.7.3.5] and could have been proved using it. Namely, the fact that
![]() $f_*$
is colimit-preserving and conservative implies that the adjunction
$f_*$
is colimit-preserving and conservative implies that the adjunction
![]() $f^*\dashv f_*$
is monadic. The condition that it is also
$f^*\dashv f_*$
is monadic. The condition that it is also
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear identifies the monad
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear identifies the monad
![]() $f_*f^*$
on
$f_*f^*$
on
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
with the monad of tensoring with
${\mathscr {D}}$
with the monad of tensoring with ![]() , so that we can identify
, so that we can identify
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
with the category of left modules over
${\mathscr {C}}$
with the category of left modules over ![]() in
in
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
.
${\mathscr {D}}$
.
In view of Proposition 2.5, we adopt the following definition:
Definition 2.7. Let
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. We say that
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. We say that
![]() $f^*$
is semi-affine
Footnote
2
if
$f^*$
is semi-affine
Footnote
2
if
![]() $f_*$
is colimit-preserving and
$f_*$
is colimit-preserving and
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear.
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear.
As an immediate consequence of Proposition 2.5,
![]() $f^*$
is affine if and only if it is semi-affine and
$f^*$
is affine if and only if it is semi-affine and
![]() $f_*$
is conservative.
$f_*$
is conservative.
Closure properties
We now describe some of the closure properties enjoyed by the collection of affine functors. First, affine functors are closed under composition and satisfy cancellation from the left.
Proposition 2.8. Let
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
and
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
and
![]() $g^*\colon \mathscr {E} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
be morphisms in
$g^*\colon \mathscr {E} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
be morphisms in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. If
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. If
![]() $g^*$
is affine, then
$g^*$
is affine, then
![]() $f^*$
is affine if and only if
$f^*$
is affine if and only if
![]() $f^*g^*$
is affine.
$f^*g^*$
is affine.
Proof. Let
![]() $h^*= f^*g^*$
. The functor
$h^*= f^*g^*$
. The functor ![]() can be identified with the composition
can be identified with the composition
The first functor
![]() $f_\sharp $
is an equivalence if and only if
$f_\sharp $
is an equivalence if and only if
![]() $f_*$
is affine by definition, and the second functor
$f_*$
is affine by definition, and the second functor
![]() $g_\sharp $
is an equivalence if
$g_\sharp $
is an equivalence if
![]() $g_*$
is affine by Proposition 2.5. Hence, the result follows by 2-out-of-3.
$g_*$
is affine by Proposition 2.5. Hence, the result follows by 2-out-of-3.
Our next goal is to study the closure properties of affine functors under limits in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. Let I be a small
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. Let I be a small
![]() $\infty $
-category, and let
$\infty $
-category, and let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_{(-)}$
and
${\mathscr {C}}_{(-)}$
and
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}_{(-)}$
be two functors from I to
${\mathscr {D}}_{(-)}$
be two functors from I to
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. Given a natural transformation
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. Given a natural transformation
![]() $f_{(-)}^*\colon {\mathscr {D}}_{(-)}\to {\mathscr {C}}_{(-)}$
which is level-wise affine, we would like to know when the induced map on the limits over I is affine as well. While we do not expect this to always be the case, we can show this under the assumption that
$f_{(-)}^*\colon {\mathscr {D}}_{(-)}\to {\mathscr {C}}_{(-)}$
which is level-wise affine, we would like to know when the induced map on the limits over I is affine as well. While we do not expect this to always be the case, we can show this under the assumption that
![]() $f_{(-)}^*$
is right adjointable, in the sense of [Reference LurieLur, Definition 4.7.4.16]. Namely, we need the lax natural transformation
$f_{(-)}^*$
is right adjointable, in the sense of [Reference LurieLur, Definition 4.7.4.16]. Namely, we need the lax natural transformation
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_{(-)}\to {\mathscr {D}}_{(-)}$
assembled from the right adjoints of the functors
${\mathscr {C}}_{(-)}\to {\mathscr {D}}_{(-)}$
assembled from the right adjoints of the functors
![]() $f_a^*$
to be a (strict) natural transformation.
$f_a^*$
to be a (strict) natural transformation.
Proposition 2.9. Let
![]() $f^*_{(-)}\colon {\mathscr {D}}_{(-)}\to {\mathscr {C}}_{(-)}$
be a natural transformation of I-shaped diagrams in
$f^*_{(-)}\colon {\mathscr {D}}_{(-)}\to {\mathscr {C}}_{(-)}$
be a natural transformation of I-shaped diagrams in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. Assume the following:
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. Assume the following:
-
1. For every
 $a\in I$
, the functor
$a\in I$
, the functor
 $f_a^*\colon {\mathscr {D}}_a \to {\mathscr {C}}_a$
is affine.
$f_a^*\colon {\mathscr {D}}_a \to {\mathscr {C}}_a$
is affine. -
2.
 $f^*_{(-)}$
is right adjointable.
$f^*_{(-)}$
is right adjointable.
Then, the induced functor on the limits
is affine.
Proof. Since
![]() $f_{(-)}^*$
is right adjointable, the right adjoint of
$f_{(-)}^*$
is right adjointable, the right adjoint of
![]() $f^*$
is given by the limit of the right adjoints
$f^*$
is given by the limit of the right adjoints
(see, for example, [Reference Arad, Carmeli and SchlankACS19, Proposition 2.1.7]). By Proposition 2.5, it suffices to show that
![]() $f_*$
is conservative, colimit-preserving and
$f_*$
is conservative, colimit-preserving and
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear. For the conservativity, since the projections
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear. For the conservativity, since the projections
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}\to {\mathscr {D}}_a$
are jointly conservative, it suffices to show that the compositions
${\mathscr {D}}\to {\mathscr {D}}_a$
are jointly conservative, it suffices to show that the compositions
are jointly conservative. But this follows from the facts that these composites identify with
and that the functors
![]() $(f_a)_*$
are all conservative. To see that
$(f_a)_*$
are all conservative. To see that
![]() $f_*$
is colimit-preserving, note that, since all the transition functors in the diagrams
$f_*$
is colimit-preserving, note that, since all the transition functors in the diagrams
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_{(-)}$
and
${\mathscr {C}}_{(-)}$
and
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}_{(-)}$
are colimit-preserving functors, the projections
${\mathscr {D}}_{(-)}$
are colimit-preserving functors, the projections
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}_a$
and
${\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}_a$
and
![]() ${\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {D}}_a$
jointly detect (and preserve) colimits in
${\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {D}}_a$
jointly detect (and preserve) colimits in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
and
${\mathscr {C}}$
and
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
, respectively. Hence, the result follows once again from the assumption that
${\mathscr {D}}$
, respectively. Hence, the result follows once again from the assumption that
![]() $(f_a)_*$
is colimit-preserving.
$(f_a)_*$
is colimit-preserving.
It remains to show that
![]() $f_*$
is
$f_*$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear. Let
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear. Let
![]() $X= \{X_a\}_{a\in I} \in {\mathscr {C}}$
and
$X= \{X_a\}_{a\in I} \in {\mathscr {C}}$
and
![]() $Y = \{Y_a\}_{a\in I} \in {\mathscr {D}}$
. Then, the a-th component of the projection morphism
$Y = \{Y_a\}_{a\in I} \in {\mathscr {D}}$
. Then, the a-th component of the projection morphism
is the projection morphism
which is an isomorphism by the assumption that all the functors
![]() $f_a^*$
are affine. We deduce that
$f_a^*$
are affine. We deduce that
![]() $f_*$
is
$f_*$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear and hence that
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear and hence that
![]() $f^*$
is affine.
$f^*$
is affine.
Corollary 2.10. Affine functors are closed under limits over spaces in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
.
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
.
Proof. For a space A, since all morphisms in A are invertible, all natural transformations of A-shaped diagrams in
![]() ${\textrm {Pr}}$
are right-adjointable. Hence, the result follows from Proposition 2.9.
${\textrm {Pr}}$
are right-adjointable. Hence, the result follows from Proposition 2.9.
Monoidal structure
By Proposition 2.5, for an algebra
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
and an affine functor
$R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
and an affine functor
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
, we can identify R-modules in
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
, we can identify R-modules in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
with
${\mathscr {C}}$
with
![]() $f_*R$
-modules in
$f_*R$
-modules in
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
. We shall show that this identification is compatible with the formation of relative tensor products of (left and right) modules. We first observe that for all
${\mathscr {D}}$
. We shall show that this identification is compatible with the formation of relative tensor products of (left and right) modules. We first observe that for all
![]() $N\in \operatorname{ {RMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
and
$N\in \operatorname{ {RMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
and
![]() $M\in \operatorname{ {LMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
, the lax monoidal structure on
$M\in \operatorname{ {LMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
, the lax monoidal structure on
![]() $f_*$
provides a canonical comparison map
$f_*$
provides a canonical comparison map
given by the composition
where the last map is the one induced on the relative tensor product from the counit
![]() $f^*f_* \to \textrm {Id}$
.
$f^*f_* \to \textrm {Id}$
.
Proposition 2.11. Let
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}}\to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}}\to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. If
$R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. If
![]() $f^*$
is affine, then for every
$f^*$
is affine, then for every
![]() $M \in \operatorname{ {LMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
and
$M \in \operatorname{ {LMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
and
![]() $N\in \operatorname{ {RMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
, the map
$N\in \operatorname{ {RMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
, the map
is an isomorphism.
Proof. Since
![]() $f_*$
is colimit-preserving, the source and target of
$f_*$
is colimit-preserving, the source and target of
![]() $\nu $
preserve colimits in the M-variable. The
$\nu $
preserve colimits in the M-variable. The
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\operatorname{ {LMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
is generated under colimits by modules of the from
$\operatorname{ {LMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
is generated under colimits by modules of the from
![]() $R\otimes X$
for
$R\otimes X$
for
![]() $X\in {\mathscr {C}}$
. Also, since
$X\in {\mathscr {C}}$
. Also, since
![]() $f_*$
is conservative,
$f_*$
is conservative,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is generated under colimits from the essential image of
${\mathscr {C}}$
is generated under colimits from the essential image of
![]() $f^*$
. Consequently, it suffices to show that
$f^*$
. Consequently, it suffices to show that
![]() $\nu $
is an isomorphism at modules of the form
$\nu $
is an isomorphism at modules of the form
![]() $N=R\otimes f^*Y$
for
$N=R\otimes f^*Y$
for
![]() $Y\in {\mathscr {D}}$
. Hence, it suffices to show that the natural transformation
$Y\in {\mathscr {D}}$
. Hence, it suffices to show that the natural transformation
obtained from
![]() $\nu $
via composing with the functor
$\nu $
via composing with the functor
![]() $R\otimes f^*(-)\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to \operatorname{ {LMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
in the Y-variable is a natural isomorphism. The assumption that
$R\otimes f^*(-)\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to \operatorname{ {LMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
in the Y-variable is a natural isomorphism. The assumption that
![]() $f_*$
is
$f_*$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear shows that the source and target of
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear shows that the source and target of
![]() $\overline {\nu }$
are
$\overline {\nu }$
are
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear functors, and
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear functors, and
![]() $\overline {\nu }$
is hence a natural transformation of
$\overline {\nu }$
is hence a natural transformation of
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear functors. Thus, we are reduced to the case
${\mathscr {D}}$
-linear functors. Thus, we are reduced to the case ![]() , where we get the canonical isomorphism
, where we get the canonical isomorphism
When dealing with symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-categories and commutative algebras, the above has a very clean interpretation.
$\infty $
-categories and commutative algebras, the above has a very clean interpretation.
Proposition 2.12. Let
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. If
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. If
![]() $f^*$
is affine, then for every
$f^*$
is affine, then for every
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we have a natural symmetric monoidal equivalence
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we have a natural symmetric monoidal equivalence
In particular, it induces an equivalence
Proof. Since the tensor product in the
![]() $\infty $
-category of modules over a commutative algebra is given by the relative tensor product, the first claim is a consequence of Proposition 2.11. The second claim follows by taking commutative algebra objects and using the natural identification
$\infty $
-category of modules over a commutative algebra is given by the relative tensor product, the first claim is a consequence of Proposition 2.11. The second claim follows by taking commutative algebra objects and using the natural identification
For
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, pushouts in
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, pushouts in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
are computed via the relative tensor product. Hence, for a symmetric monoidal functor
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
are computed via the relative tensor product. Hence, for a symmetric monoidal functor
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, Proposition 2.12 implies that if
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, Proposition 2.12 implies that if
![]() $f^*$
is affine, then the functor
$f^*$
is affine, then the functor
![]() $f_*\colon \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}}) \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {D}})$
preserves pushout squares. We shall now discuss a generalization of this property to the context of noncommutative algebras. Let
$f_*\colon \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}}) \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {D}})$
preserves pushout squares. We shall now discuss a generalization of this property to the context of noncommutative algebras. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let

be a commutative square in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. The right map
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. The right map
![]() $R_1\to S_1$
is a map of left
$R_1\to S_1$
is a map of left
![]() $R_0$
-modules. The
$R_0$
-modules. The
![]() $R_0$
-module structure of
$R_0$
-module structure of
![]() $S_1$
comes from restricting the
$S_1$
comes from restricting the
![]() $S_0$
-module structure along the left map. Hence, the restriction-extension of scalars adjunction along
$S_0$
-module structure along the left map. Hence, the restriction-extension of scalars adjunction along
![]() $R_0\to S_0$
induces a map of left
$R_0\to S_0$
induces a map of left
![]() $S_0$
-modules:
$S_0$
-modules:
Definition 2.13. We say that a square of algebras as above is a relative tensor square if the above map
![]() $S_0\otimes _{R_0}R_1\to S_1$
is an isomorphism.
$S_0\otimes _{R_0}R_1\to S_1$
is an isomorphism.
Every sifted colimit-preserving monoidal functor preserves relative tensor squares, as the relative tensor product can be realized via the geometric realization of a bar construction. For an affine functor, the same holds for its right adjoint.
Proposition 2.14. Let
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. If
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. If
![]() $f^*$
is affine, then a commutative square in
$f^*$
is affine, then a commutative square in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is a relative tensor square if and only if its image under
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is a relative tensor square if and only if its image under
![]() $f_* \colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
is a relative tensor square in
$f_* \colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
is a relative tensor square in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {D}})$
.
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {D}})$
.
Proof. Assume that
![]() $f^*$
is affine and let
$f^*$
is affine and let

be a commutative square in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. By Proposition 2.11, we have a canonical isomorphism
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. By Proposition 2.11, we have a canonical isomorphism
Via this isomorphism, we can identity the map
![]() $(f_*R_1) \otimes _{f_*R_0}(f_*S_0) \to f_*S_1$
with the image under
$(f_*R_1) \otimes _{f_*R_0}(f_*S_0) \to f_*S_1$
with the image under
![]() $f_*$
of the corresponding map
$f_*$
of the corresponding map
![]() $R_1 \otimes _{R_0} S_0 \to S_1$
. Hence, if the map
$R_1 \otimes _{R_0} S_0 \to S_1$
. Hence, if the map
![]() $R_1 \otimes _{R_0} S_0 \to S_1$
is an isomorphism, so is the map
$R_1 \otimes _{R_0} S_0 \to S_1$
is an isomorphism, so is the map
![]() $(f_*R_1) \otimes _{f_*R_0}(f_*S_0) \to f_*S_1$
. By Proposition 2.5, the functor
$(f_*R_1) \otimes _{f_*R_0}(f_*S_0) \to f_*S_1$
. By Proposition 2.5, the functor
![]() $f_*$
is conservative, so the converse of the above implication holds as well.
$f_*$
is conservative, so the converse of the above implication holds as well.
2.2 Affineness for local systems
We now specialize our discussion of affineness to the setting we are mostly interested in: that of local systems.
Definition 2.15. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. A map of spaces
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. A map of spaces
![]() $f\colon A\to B$
is said to be
$f\colon A\to B$
is said to be
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-(semi-)affine if the pullback functor
${\mathscr {C}}$
-(semi-)affine if the pullback functor
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^B\to {\mathscr {C}}^A$
is (semi-)affine in the sense of Definition 2.1 and Definition 2.7. A space A is called
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^B\to {\mathscr {C}}^A$
is (semi-)affine in the sense of Definition 2.1 and Definition 2.7. A space A is called
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-(semi-)affine if the canonical map
${\mathscr {C}}$
-(semi-)affine if the canonical map
![]() $f\colon A \to \textrm {pt}$
is so.
$f\colon A \to \textrm {pt}$
is so.
Basic properties
Given a map of spaces
![]() $f\colon A \to B$
and writing
$f\colon A \to B$
and writing
![]() $q\colon B \to \textrm {pt}$
for the terminal map, the unit of the adjunction
$q\colon B \to \textrm {pt}$
for the terminal map, the unit of the adjunction
![]() $f^* \dashv f_*$
induces a map
$f^* \dashv f_*$
induces a map
We now show that
![]() $f^* \colon {\mathscr {C}}^B \to {\mathscr {C}}^A$
is compatible with the functor
$f^* \colon {\mathscr {C}}^B \to {\mathscr {C}}^A$
is compatible with the functor ![]() given by extending scalars along the above map.
given by extending scalars along the above map.
Proposition 2.16. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $f\colon A\to B$
be a map of spaces with
$f\colon A\to B$
be a map of spaces with
![]() $q\colon B \to \textrm {pt}$
the terminal map. We have a commutative square of
$q\colon B \to \textrm {pt}$
the terminal map. We have a commutative square of
![]() $\infty $
-categories
$\infty $
-categories

In particular, when A and B are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, the top and bottom functors are isomorphic.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, the top and bottom functors are isomorphic.
Proof. It suffices to show that the square comprising from the right adjoints of all the functors commutes. As above, let
![]() $q\colon B \to \textrm {pt}$
be the terminal map. The composition
$q\colon B \to \textrm {pt}$
be the terminal map. The composition
is the functor that takes
![]() $X\in {\mathscr {C}}$
to
$X\in {\mathscr {C}}$
to
![]() $q_*f_*X \in {\mathscr {C}}$
with the induced
$q_*f_*X \in {\mathscr {C}}$
with the induced ![]() -module structure. This is evidently the same as restricting the
-module structure. This is evidently the same as restricting the ![]() -module structure on
-module structure on
![]() $q_*f_*X \in {\mathscr {C}}$
along the map
$q_*f_*X \in {\mathscr {C}}$
along the map
which is the second composition
The last claim follows from the fact that if A and B are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then the vertical functors are equivalences.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then the vertical functors are equivalences.
For every point
![]() $b\in B$
, let
$b\in B$
, let ![]() be the
be the ![]() algebra structure on
algebra structure on ![]() given by evaluation at b.
given by evaluation at b.
Corollary 2.17. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and let B be a space with
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and let B be a space with
![]() $q\colon B \to \textrm {pt}$
the terminal map. For every
$q\colon B \to \textrm {pt}$
the terminal map. For every
![]() $b\in B$
, we have a commutative diagram,
$b\in B$
, we have a commutative diagram,

Proof. This is a special case of Proposition 2.16, with
![]() $A=\textrm {pt}$
and f the inclusion
$A=\textrm {pt}$
and f the inclusion
![]() $\textrm {pt} \xrightarrow {\:b\:} B$
.
$\textrm {pt} \xrightarrow {\:b\:} B$
.
We next observe that the closure properties of affine functors imply corresponding closure properties for
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine maps of spaces.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine maps of spaces.
Proposition 2.18. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and let
![]() $f\colon A\to B$
,
$f\colon A\to B$
,
![]() $f'\colon A' \to B'$
and
$f'\colon A' \to B'$
and
![]() $g\colon B\to C$
be maps of spaces.
$g\colon B\to C$
be maps of spaces.
-
(1) If f is an isomorphism, then it is
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. -
(2) If g is
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then f is
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then f is
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine if and only if
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine if and only if
 $g\circ f$
is
$g\circ f$
is
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. -
(3) If all the fibers of f are
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then f is
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then f is
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. -
(4) If f and
 $f'$
are
$f'$
are
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then
 $f\sqcup f^{\prime } \colon A\sqcup A^{\prime } \to B\sqcup B^{\prime }$
is
$f\sqcup f^{\prime } \colon A\sqcup A^{\prime } \to B\sqcup B^{\prime }$
is
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
Proof. (1) is clear, and (2) is an immediate consequence of Proposition 2.8. For (3), we observe that the functor
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^B\to {\mathscr {C}}^A$
can be written as a limit over
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^B\to {\mathscr {C}}^A$
can be written as a limit over
![]() $b\in B$
of the functors
$b\in B$
of the functors
![]() $f_b^*\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}^{f^{-1}(b)},$
where
$f_b^*\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}^{f^{-1}(b)},$
where
![]() $f_b \colon f^{-1}(b) \to \textrm {pt}$
is the terminal map. By assumption, each
$f_b \colon f^{-1}(b) \to \textrm {pt}$
is the terminal map. By assumption, each
![]() $f_b^*$
is affine, and by Corollary 2.10, affine functors are closed under limits over spaces, so the result follows. The proof of (4) is similar to that of (3). It follows from the isomorphism
$f_b^*$
is affine, and by Corollary 2.10, affine functors are closed under limits over spaces, so the result follows. The proof of (4) is similar to that of (3). It follows from the isomorphism
![]() $(f\sqcup f^{\prime })^* \simeq f^* \times f^{\prime *}$
and Corollary 2.10.
$(f\sqcup f^{\prime })^* \simeq f^* \times f^{\prime *}$
and Corollary 2.10.
Warning 2.19. Claim (3) cannot be promoted to an ‘if and only if’ statement. Namely, a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine map of spaces need not have
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine map of spaces need not have
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine fibers. Indeed, if A is a
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine fibers. Indeed, if A is a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine space, then the projection
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine space, then the projection
![]() $\pi _1 \colon A\times A \to A$
is
$\pi _1 \colon A\times A \to A$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine by (3). Since the composition
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine by (3). Since the composition
![]() $A \xrightarrow {\Delta } A\times A \xrightarrow {\pi _1} A$
is the identity, we deduce by (2) and (1) that the diagonal
$A \xrightarrow {\Delta } A\times A \xrightarrow {\pi _1} A$
is the identity, we deduce by (2) and (1) that the diagonal
![]() $\Delta \colon A \to A\times A$
is
$\Delta \colon A \to A\times A$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine as well. As the fibers of
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine as well. As the fibers of
![]() $\Delta $
are the loop-spaces
$\Delta $
are the loop-spaces
![]() $\Omega A$
, if the converse of (3) were to be true, it would have implied that if A is
$\Omega A$
, if the converse of (3) were to be true, it would have implied that if A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then
![]() $\Omega A$
is
$\Omega A$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine as well. However, for all
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine as well. However, for all
![]() $n\ge 0$
, we have that
$n\ge 0$
, we have that
![]() $B^{n+2} C_p$
is
$B^{n+2} C_p$
is
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
-affine while
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
-affine while
![]() $B^{n+1} C_p= \Omega B^{n+2} C_p$
is not (Proposition 2.40).
$B^{n+1} C_p= \Omega B^{n+2} C_p$
is not (Proposition 2.40).
Eilenberg–Moore
Our next goal is to show that affineness is strongly related to Eilenberg–Moore type formulas for the cohomology of pullbacks of spaces. Given a pullback square of spaces

and a ring
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we can form the square in
$R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we can form the square in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
,
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
,

In some cases, this square turns out to be a relative tensor square. For
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}=\textrm {Sp}$
, this implies the existence of a spectral sequence computing the R-cohomology of
${\mathscr {C}}=\textrm {Sp}$
, this implies the existence of a spectral sequence computing the R-cohomology of
![]() $ B'\times _B A$
from the R-cohomologies of
$ B'\times _B A$
from the R-cohomologies of
![]() $B,B'$
and A, known as the Eilenberg–Moore spectral sequence. This motivates the following definition:
$B,B'$
and A, known as the Eilenberg–Moore spectral sequence. This motivates the following definition:
Definition 2.20. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. A map of spaces
$R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. A map of spaces
![]() $f\colon A\to B$
is said to be Eilenberg–Moore with respect to
$f\colon A\to B$
is said to be Eilenberg–Moore with respect to
![]() $R \in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
if for every map
$R \in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
if for every map
![]() $g\colon B'\to B$
, the canonical morphism
$g\colon B'\to B$
, the canonical morphism
is an isomorphism.
In the special case where
![]() $B= \textrm {pt}$
, the Eilenberg–Moore property degenerates to the Künneth isomorphism, for which the following is a useful criterion.
$B= \textrm {pt}$
, the Eilenberg–Moore property degenerates to the Künneth isomorphism, for which the following is a useful criterion.
Proposition 2.21. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, and let A be a space. If
$R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, and let A be a space. If
![]() $R[A] \in \operatorname{ {LMod}}(R)$
is left dualizable, then A has the Eilenberg–Moore property with respect to R. That is, for every space B, we have a Künneth isomorphism
$R[A] \in \operatorname{ {LMod}}(R)$
is left dualizable, then A has the Eilenberg–Moore property with respect to R. That is, for every space B, we have a Künneth isomorphism
In particular, if ![]() is left dualizable, the above holds for every
is left dualizable, the above holds for every
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
$R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
Proof. Under the assumption that
![]() $R[A] \in \operatorname{ {LMod}}(R)$
is left dualizable, the module
$R[A] \in \operatorname{ {LMod}}(R)$
is left dualizable, the module
![]() $R^A \in \operatorname{ {RMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
is its left dual. Unwinding the definitions, the canonical comparison map
$R^A \in \operatorname{ {RMod}}_R({\mathscr {C}})$
is its left dual. Unwinding the definitions, the canonical comparison map
identifies with the assembly map for the functor
and the constant B-shaped limit. Now, by [Reference LurieLur, Proposition 4.6.2.1], the functor G is a right adjoint and hence preserves limits, so the claim follows. The last part follows from the fact that if ![]() is left dualizable, then
is left dualizable, then ![]() is left dualizable, by [Reference LurieLur, Example 4.6.2.5].
is left dualizable, by [Reference LurieLur, Example 4.6.2.5].
Example 2.22. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}= \textrm {Sp}$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}}= \textrm {Sp}$
, and let
![]() $R=\mathbb {F}$
be an ordinary field considered as a ring spectrum. Proposition 2.21 then recovers the classical fact that if a space A has finite-dimensional homology with coefficients in
$R=\mathbb {F}$
be an ordinary field considered as a ring spectrum. Proposition 2.21 then recovers the classical fact that if a space A has finite-dimensional homology with coefficients in
![]() $\mathbb {F}$
, then for every space B, we have a Künneth isomorphism for the cohomology of
$\mathbb {F}$
, then for every space B, we have a Künneth isomorphism for the cohomology of
![]() $A\times B$
with coefficients in
$A\times B$
with coefficients in
![]() $\mathbb {F}$
.
$\mathbb {F}$
.
Using affineness, we can reduce the general case of the Eilenberg–Moore property to the existence of Künneth isomorphisms for the fibers.
Proposition 2.23. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
and let
$R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
and let
![]() $f\colon A \to B$
be a map of spaces. If B is
$f\colon A \to B$
be a map of spaces. If B is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, and all the fibers of f are Eilenberg–Moore with respect to R, then f is Eilenberg–Moore with respect to R.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, and all the fibers of f are Eilenberg–Moore with respect to R, then f is Eilenberg–Moore with respect to R.
Proof. Let
![]() $q\colon B\to \textrm {pt}$
denote the projection, so that by our assumption q is
$q\colon B\to \textrm {pt}$
denote the projection, so that by our assumption q is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. For a map
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. For a map
![]() $g\colon B' \to B$
, the square
$g\colon B' \to B$
, the square

in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is obtained from the square
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is obtained from the square

in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}}^B)$
by applying the functor
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}}^B)$
by applying the functor
![]() $q_*$
. Since
$q_*$
. Since
![]() $q^*$
is affine, by Proposition 2.14, it would suffice to show that the latter square is a relative tensor square. We can verify this after applying the functors
$q^*$
is affine, by Proposition 2.14, it would suffice to show that the latter square is a relative tensor square. We can verify this after applying the functors
![]() $b^*$
for all
$b^*$
for all
![]() $b\colon \textrm {pt} \to B$
. Using the Beck–Chevalley isomorphism for local systems, this reduces the claim to the case
$b\colon \textrm {pt} \to B$
. Using the Beck–Chevalley isomorphism for local systems, this reduces the claim to the case
![]() $B= \textrm {pt}$
, and
$B= \textrm {pt}$
, and
![]() $A =f^{-1}(b)$
, which holds by assumption.
$A =f^{-1}(b)$
, which holds by assumption.
Remark 2.24. We can informally summarize Proposition 2.23 by the slogan:
Galois extensions
We shall now discuss the implications of affineness to Galois theory in the sense of Rognes. Our main result is that if the classifying space
![]() $BG$
of a group G is affine, then every commutative algebra with a G-action is faithful Galois over its G-fixed points. We refer the reader to [Reference RognesRog08] and [Reference MathewMat16] for a discussion of Galois extensions in the context of stable homotopy theory.
$BG$
of a group G is affine, then every commutative algebra with a G-action is faithful Galois over its G-fixed points. We refer the reader to [Reference RognesRog08] and [Reference MathewMat16] for a discussion of Galois extensions in the context of stable homotopy theory.
To make the connection with affineness more transparent, we shall rephrase Rognes’s notion of a Galois extension in terms of the space
![]() $BG$
rather than the group G. For a space A and a presentably symmetric monoidal
$BG$
rather than the group G. For a space A and a presentably symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, we denote by
${\mathscr {C}}$
, we denote by
the diagonal and terminal maps of A, respectively. For an A-local system of commutative algebras
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^A$
, the unit map
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^A$
, the unit map ![]() has a mate
has a mate ![]() with respect to the
with respect to the
![]() $q^* \dashv q_*$
adjunction. Considering the external product
$q^* \dashv q_*$
adjunction. Considering the external product
![]() $R\boxtimes R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^{A\times A}$
, the multiplication map
$R\boxtimes R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^{A\times A}$
, the multiplication map
has a mate
with respect to the adjunction
![]() $\Delta ^* \dashv \Delta _*$
.
$\Delta ^* \dashv \Delta _*$
.
Definition 2.25. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let A be a space. A local system
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let A be a space. A local system
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^A$
is called an A-Galois extension (of the unit object
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^A$
is called an A-Galois extension (of the unit object ![]() ) if it satisfies the following two properties:
) if it satisfies the following two properties:
-
(G1) The mate
 of the unit map is an isomorphism in
of the unit map is an isomorphism in
 $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. -
(G2) The mate
 $ R\boxtimes R \to \Delta _*R $
of the multiplication map is an isomorphism in
$ R\boxtimes R \to \Delta _*R $
of the multiplication map is an isomorphism in
 $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^{A\times A}$
.
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^{A\times A}$
.
We say that a Galois extension is faithful if the functor
![]() $R \otimes (-)\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}^A$
is conservative.
$R \otimes (-)\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}^A$
is conservative.
When A is connected, by choosing a basepoint for A, we get a grouplike
![]() $\mathbb {E}_1$
-space
$\mathbb {E}_1$
-space
![]() $G=\Omega A$
. Then, by definition, an A-local system of commutative algebras in
$G=\Omega A$
. Then, by definition, an A-local system of commutative algebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is a commutative algebra endowed with a G-action. Via this identification,
${\mathscr {C}}$
is a commutative algebra endowed with a G-action. Via this identification,
![]() $q_*R$
, which is the limit of R over A, identifies with the fixed points
$q_*R$
, which is the limit of R over A, identifies with the fixed points
![]() $R^{hG}$
of the G-action on R. Similarly,
$R^{hG}$
of the G-action on R. Similarly,
![]() $\Delta _*R$
identifies with the algebra of functions
$\Delta _*R$
identifies with the algebra of functions
![]() $R^G$
, with a suitable
$R^G$
, with a suitable
![]() $G\times G$
-action. Under these identifications, the maps appearing in conditions (G1) and (G2) are easily seen to correspond to the maps
$G\times G$
-action. Under these identifications, the maps appearing in conditions (G1) and (G2) are easily seen to correspond to the maps ![]() and
and
![]() $ R\otimes R \to R^G $
appearing in Rognes’s definition of a Galois extension; see, for example, [Reference MathewMat16, Definition 6.12]. Thus, Definition 2.25 is a base-point free reformulation of Rognes’s notion of a Galois extension. Furthermore, allowing nonconnected spaces A provides a natural extension of this Galois theory ‘downwards’.
$ R\otimes R \to R^G $
appearing in Rognes’s definition of a Galois extension; see, for example, [Reference MathewMat16, Definition 6.12]. Thus, Definition 2.25 is a base-point free reformulation of Rognes’s notion of a Galois extension. Furthermore, allowing nonconnected spaces A provides a natural extension of this Galois theory ‘downwards’.
Example 2.26. For
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and a finite discrete space A, it is easy to check that an A-Galois extension is a collection of idempotent rings
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and a finite discrete space A, it is easy to check that an A-Galois extension is a collection of idempotent rings
![]() $\{R_a \mid a \in A\}$
in
$\{R_a \mid a \in A\}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, such that
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, such that ![]() and
and
![]() $R_a \otimes R_b \simeq \textrm {pt}$
for all
$R_a \otimes R_b \simeq \textrm {pt}$
for all
![]() $a\neq b$
. In particular, if we denote by
$a\neq b$
. In particular, if we denote by
![]() $\pi _0({\mathscr {C}})$
the pro-finite set of connected components of
$\pi _0({\mathscr {C}})$
the pro-finite set of connected components of ![]() , then A-Galois extensions of
, then A-Galois extensions of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
are classified by continuous maps
${\mathscr {C}}$
are classified by continuous maps
![]() $\pi _0({\mathscr {C}}) \to A$
. In the stable case, this fits naturally into Mathew’s Galois theory developed in [Reference MathewMat16].
$\pi _0({\mathscr {C}}) \to A$
. In the stable case, this fits naturally into Mathew’s Galois theory developed in [Reference MathewMat16].
The somewhat surprising observation is that if A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then it suffices to check only the condition (G1) to ensure that we have a faithful A-Galois extension.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then it suffices to check only the condition (G1) to ensure that we have a faithful A-Galois extension.
Proposition 2.27. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let A be a
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let A be a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine space. A local system
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine space. A local system
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^A$
is a faithful Galois extension if and only if the map
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^A$
is a faithful Galois extension if and only if the map ![]() is an isomorphism.
is an isomorphism.
Proof. If R is Galois, then by condition (G1), the unit map ![]() is an isomorphism. To prove the converse, we have to show that
is an isomorphism. To prove the converse, we have to show that
-
(1) The functor
 $R\otimes (-)\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}^A$
is conservative.
$R\otimes (-)\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}^A$
is conservative. -
(2) The map
 $\varphi \colon R\boxtimes R \to \Delta _*R$
, which is the mate of the multiplication, is an isomorphism.
$\varphi \colon R\boxtimes R \to \Delta _*R$
, which is the mate of the multiplication, is an isomorphism.
For
![]() $(1)$
, by Proposition 2.5, the functor
$(1)$
, by Proposition 2.5, the functor
![]() $q_*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^A \to {\mathscr {C}}$
is
$q_*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^A \to {\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear. Consequently, the composition
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear. Consequently, the composition
is a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear functor from
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear functor from
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
to
${\mathscr {C}}$
to
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, which is therefore given by tensoring with
${\mathscr {C}}$
, which is therefore given by tensoring with ![]() . By our assumption, this is the identity functor, so that
. By our assumption, this is the identity functor, so that
![]() $R\otimes (-)$
is left-invertible and, in particular, conservative.
$R\otimes (-)$
is left-invertible and, in particular, conservative.
For
![]() $(2)$
, let
$(2)$
, let
![]() $\pi _1,\pi _2 \colon A\times A \to A$
be the projections on the two factors. By Proposition 2.18, the map
$\pi _1,\pi _2 \colon A\times A \to A$
be the projections on the two factors. By Proposition 2.18, the map
![]() $\pi _1$
is
$\pi _1$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, and hence, by Proposition 2.5, the functor
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, and hence, by Proposition 2.5, the functor
![]() $(\pi _1)_*$
is
$(\pi _1)_*$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear and conservative. Using the conservativity, it suffices to show that the map
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear and conservative. Using the conservativity, it suffices to show that the map
is an isomorphism. By the projection formula for
![]() $(\pi _1)_*$
and the Beck–Chevalley isomorphism, we have
$(\pi _1)_*$
and the Beck–Chevalley isomorphism, we have
Unwinding the definition of
![]() $\varphi $
, the map
$\varphi $
, the map
![]() $(\pi _1)_*\varphi $
corresponds via this identification to the composition
$(\pi _1)_*\varphi $
corresponds via this identification to the composition
where c is the counit of the adjunction
![]() $q^*\dashv q_*$
and m is the multiplication map. By the assumption that
$q^*\dashv q_*$
and m is the multiplication map. By the assumption that ![]() , we have an isomorphism
, we have an isomorphism ![]() , so that this composite is an isomorphism and the result follows.
, so that this composite is an isomorphism and the result follows.
More generally, we define an A-Galois extension of any
![]() $S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
to be an A-Galois extension in the
$S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
to be an A-Galois extension in the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_S({\mathscr {C}})$
– that is, an object
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_S({\mathscr {C}})$
– that is, an object
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}_S({\mathscr {C}})^A$
satisfying the analogues of (G1) and (G2) relative to S. From Proposition 2.27, we deduce the following:
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}_S({\mathscr {C}})^A$
satisfying the analogues of (G1) and (G2) relative to S. From Proposition 2.27, we deduce the following:
Corollary 2.28. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let A be a
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let A be a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine space. Every
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine space. Every
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^A$
is a faithful Galois extension of
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^A$
is a faithful Galois extension of
![]() $q_*R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
for
$q_*R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
for
![]() $q\colon A \to \textrm {pt}$
the terminal map.
$q\colon A \to \textrm {pt}$
the terminal map.
Proof. Let
![]() $S= q_* R$
. By construction, the map
$S= q_* R$
. By construction, the map
![]() $S \to q_*R$
is an isomorphism, and hence, the claim follows from Proposition 2.27.
$S \to q_*R$
is an isomorphism, and hence, the claim follows from Proposition 2.27.
Example 2.29. The constant A-local system on ![]() (i.e.,
(i.e., ![]() ) is Galois over
) is Galois over ![]() .
.
In fact, the above example is universal. Let
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}_S^{A-\textrm {gal}}({\mathscr {C}}) \subseteq \operatorname{{CAlg}}_S({\mathscr {C}})^A$
denote the space of faithful A-Galois extensions of
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}_S^{A-\textrm {gal}}({\mathscr {C}}) \subseteq \operatorname{{CAlg}}_S({\mathscr {C}})^A$
denote the space of faithful A-Galois extensions of
![]() $S \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
$S \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
Proposition 2.30. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let A be a
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let A be a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine space. For every
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine space. For every
![]() $S \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, there is a natural isomorphism
$S \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, there is a natural isomorphism
In other words, the object ![]() co-represents A-Galois extensions of commutative algebras in
co-represents A-Galois extensions of commutative algebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
.
${\mathscr {C}}$
.
Proof. By Proposition 2.12, we have an equivalence of
![]() $\infty $
-categories
$\infty $
-categories ![]() under which the global sections functor
under which the global sections functor
![]() $q_* \colon \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}}^A) \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
corresponds to the forgetful functor
$q_* \colon \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}}^A) \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
corresponds to the forgetful functor ![]() . This is further isomorphic to the canonical projection functor
. This is further isomorphic to the canonical projection functor ![]() The latter is a left fibration whose fiber over
The latter is a left fibration whose fiber over
![]() $S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is the space
$S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is the space ![]() . Thus, this space is also isomorphic to the fiber of
. Thus, this space is also isomorphic to the fiber of
![]() $q_*$
– namely, the space of objects
$q_*$
– namely, the space of objects
![]() $R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}}^A)$
with an isomorphism of commutative algebras
$R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}}^A)$
with an isomorphism of commutative algebras
![]() $q_* R \simeq S$
. By Proposition 2.27, it is isomorphic to
$q_* R \simeq S$
. By Proposition 2.27, it is isomorphic to
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}_S^{A-\textrm {gal}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}_S^{A-\textrm {gal}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
Remark 2.31. Rognes develops the theory of A-Galois extensions under the additional assumption that
![]() $G= \Omega A$
is dualizable in
$G= \Omega A$
is dualizable in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. This occurs, for example, when A is weakly
${\mathscr {C}}$
. This occurs, for example, when A is weakly
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous (see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.3.10]).
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous (see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.3.10]).
2.3 Affineness and ambidexterity
Semi-affineness and ambidexterity
For truncated maps of spaces, (semi-)affineness turns out to be closely related to ambidexterity.
Proposition 2.32. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. A truncated map of spaces
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. A truncated map of spaces
![]() $f\colon A\to B$
is
$f\colon A\to B$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous if and only if f and all of its iterated diagonals are
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous if and only if f and all of its iterated diagonals are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affine.
Proof. We prove the claim by induction on the truncatedness level of f. For
![]() $m=-2$
, the map f is an isomorphism, and the claim holds trivially. For
$m=-2$
, the map f is an isomorphism, and the claim holds trivially. For
![]() $m\ge -1$
, the diagonal of f is
$m\ge -1$
, the diagonal of f is
![]() $(m-1)$
-truncated, so the claim holds for it by the inductive hypothesis. We are thus reduced to showing that if f is weakly ambidextrous, then it is ambidextrous if and only if it is semi-affine. Recall that f is
$(m-1)$
-truncated, so the claim holds for it by the inductive hypothesis. We are thus reduced to showing that if f is weakly ambidextrous, then it is ambidextrous if and only if it is semi-affine. Recall that f is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affine if and only if
${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affine if and only if
![]() $f_*$
is colimit-preserving and
$f_*$
is colimit-preserving and
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}^A$
-linear. By [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Proposition 4.3.9], since f is weakly ambidextrous, it is
${\mathscr {C}}^A$
-linear. By [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Proposition 4.3.9], since f is weakly ambidextrous, it is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous if and only if
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous if and only if
![]() $f_*$
is colimit-preserving. Hence, semi-affineness implies ambidexterity. Conversely, if f is ambidextrous, then by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Proposition 3.3.1], the functor
$f_*$
is colimit-preserving. Hence, semi-affineness implies ambidexterity. Conversely, if f is ambidextrous, then by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Proposition 3.3.1], the functor
![]() $f_* \simeq f_!$
is
$f_* \simeq f_!$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}^A$
-linear, and hence, f is semi-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}^A$
-linear, and hence, f is semi-affine.
Corollary 2.33. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
be semiadditive, and let p be a prime. The
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
be semiadditive, and let p be a prime. The
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is p-typically m-semiadditive if and only if the spaces
${\mathscr {C}}$
is p-typically m-semiadditive if and only if the spaces
![]() $BC_p,B^2C_p,\dots ,B^mC_p$
are all
$BC_p,B^2C_p,\dots ,B^mC_p$
are all
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affine.
Proof. By [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.1.2], it suffices to show that the spaces
![]() $ BC_p,B^2C_p,\dots ,B^mC_p$
are all
$ BC_p,B^2C_p,\dots ,B^mC_p$
are all
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous. This follows from Proposition 2.32 and Proposition 2.18, as the diagonal map
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous. This follows from Proposition 2.32 and Proposition 2.18, as the diagonal map
![]() $B^kC_p \to B^kC_p \times B^kC_p$
has fiber
$B^kC_p \to B^kC_p \times B^kC_p$
has fiber
![]() $B^{k-1}C_p$
.
$B^{k-1}C_p$
.
Under the assumption of ambidexterity, affineness reduces to the conservativity of the global sections functor.
Corollary 2.34. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $f\colon A\to B$
be a
$f\colon A\to B$
be a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous map of spaces. Then, f is
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous map of spaces. Then, f is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affine. Furthermore, f is
${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affine. Furthermore, f is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine if and only if
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine if and only if
![]() $f_*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^A\to {\mathscr {C}}^B$
is conservative.
$f_*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^A\to {\mathscr {C}}^B$
is conservative.
Proof. This follows from Proposition 2.32 and the characterization of affine functors given in Proposition 2.5.
Example 2.35. For
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
semiadditive, every map of spaces
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
semiadditive, every map of spaces
![]() $f\colon A\to B$
with finite discrete fibers is
$f\colon A\to B$
with finite discrete fibers is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Indeed, by Proposition 2.18, it suffices to show this when
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Indeed, by Proposition 2.18, it suffices to show this when
![]() $B=\textrm {pt}$
, and by the above Corollary 2.34, we only need to show that the functor
$B=\textrm {pt}$
, and by the above Corollary 2.34, we only need to show that the functor
![]() $f_*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^A\to {\mathscr {C}}$
is conservative. This functor takes an A-indexed collection of objects
$f_*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^A\to {\mathscr {C}}$
is conservative. This functor takes an A-indexed collection of objects
![]() $\left (X_a\right )_{a\in A}$
to their product
$\left (X_a\right )_{a\in A}$
to their product
![]() $\prod _{a\in A} X_a$
. The conservativity now follows from the fact that each projection
$\prod _{a\in A} X_a$
. The conservativity now follows from the fact that each projection
![]() $a^*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^A\to {\mathscr {C}}$
for
$a^*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^A\to {\mathscr {C}}$
for
![]() $a\in A$
is a retract of
$a\in A$
is a retract of
![]() $f_*$
.
$f_*$
.
Remark 2.36. For
![]() $f\colon A \to \textrm {pt}$
, the right adjoint
$f\colon A \to \textrm {pt}$
, the right adjoint
![]() $f_* \colon {\mathscr {C}}^A \to {\mathscr {C}}$
is conservative if and only if the image of the left adjoint
$f_* \colon {\mathscr {C}}^A \to {\mathscr {C}}$
is conservative if and only if the image of the left adjoint
![]() $f^*\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}^A$
generates
$f^*\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}^A$
generates
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}^A$
under colimits. That is if and only if every
${\mathscr {C}}^A$
under colimits. That is if and only if every
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-valued local system on A can be constructed from constant ones by colimits. By analogy with representation theory, one might call such local systems unipotent. Thus, we can rephrase the second part of Corollary 2.34, by saying that a
${\mathscr {C}}$
-valued local system on A can be constructed from constant ones by colimits. By analogy with representation theory, one might call such local systems unipotent. Thus, we can rephrase the second part of Corollary 2.34, by saying that a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous space A is
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous space A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine if and only if all
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine if and only if all
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-local systems on A are unipotent.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-local systems on A are unipotent.
Ambidexterity and Eilenberg–Moore
Under the assumption of ambidexterity, the relationship between affineness and the Eilenberg–Moore property can be further tightened. First, we have the following criterion for Künneth isomorphisms:
Proposition 2.37. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let A be a space. If A is
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let A be a space. If A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous, then A has the Eilenberg–Moore property with respect to every
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous, then A has the Eilenberg–Moore property with respect to every
![]() $R \in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. That is, for every space B, we have a Künneth isomorphism
$R \in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. That is, for every space B, we have a Künneth isomorphism
Proof. Since A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous,
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous, ![]() is dualizable by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.3.10]. Hence, the claim follows from Proposition 2.21.
is dualizable by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.3.10]. Hence, the claim follows from Proposition 2.21.
The combination of Proposition 2.37 and Proposition 2.23 shows that if B is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous, then the
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous, then the
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affineness of B implies the Eilenberg–Moore property for a large class of maps
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affineness of B implies the Eilenberg–Moore property for a large class of maps
![]() $A\to B$
. In fact, the ambidexterity assumption guarantees that affineness is also implied by a very special case of the Eilenberg–Moore property. The situation can be summarized as follows:
$A\to B$
. In fact, the ambidexterity assumption guarantees that affineness is also implied by a very special case of the Eilenberg–Moore property. The situation can be summarized as follows:
Theorem 2.38. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let B be a
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let B be a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous space. The following are equivalent:
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous space. The following are equivalent:
-
(1) The space B is
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. -
(2) Every
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous map
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous map
 $f\colon A\to B$
is Eilenberg–Moore with respect to every
$f\colon A\to B$
is Eilenberg–Moore with respect to every
 $R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
$R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. -
(3) For every pair of points
 $a,b\in B$
, the canonical map
$a,b\in B$
, the canonical map  is an isomorphism.
is an isomorphism.
Proof. We will show that (1)
![]() ${\implies }$
(2)
${\implies }$
(2)
![]() ${\implies }$
(3)
${\implies }$
(3)
![]() ${\implies }$
(1). For every
${\implies }$
(1). For every
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous map
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous map
![]() $f\colon A \to B$
, the fibers are Eilenberg–Moore with respect to every
$f\colon A \to B$
, the fibers are Eilenberg–Moore with respect to every
![]() $R{\in }{\operatorname{{Alg}}}({\mathscr {C}})$
by Proposition 2.37. Thus, if B is
$R{\in }{\operatorname{{Alg}}}({\mathscr {C}})$
by Proposition 2.37. Thus, if B is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then f is Eilenberg–Moore with respect to every
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then f is Eilenberg–Moore with respect to every
![]() $R\in {\operatorname{{Alg}}}({\mathscr {C}})$
by Proposition 2.23. That is, we have shown that (1) implies (2). Now, (3) follows from (2) by taking
$R\in {\operatorname{{Alg}}}({\mathscr {C}})$
by Proposition 2.23. That is, we have shown that (1) implies (2). Now, (3) follows from (2) by taking
![]() $f\colon \{a\}\to B$
and
$f\colon \{a\}\to B$
and
![]() $g\colon \{b\}\to B$
.
$g\colon \{b\}\to B$
.
It remains to show that (3) implies (1). To show that B is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, we need to show that the functor
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, we need to show that the functor
is an equivalence, where
![]() $q\colon B\to \textrm {pt}$
is the terminal map. By Corollary 2.34, the map q is
$q\colon B\to \textrm {pt}$
is the terminal map. By Corollary 2.34, the map q is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affine, and hence, by Proposition 2.4, the left adjoint
${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affine, and hence, by Proposition 2.4, the left adjoint
![]() $q^\sharp $
of
$q^\sharp $
of
![]() $q_\sharp $
is fully faithful. Hence, it remains to show that the counit map
$q_\sharp $
is fully faithful. Hence, it remains to show that the counit map
is an isomorphism for all
![]() $X\in {\mathscr {C}}^{B}$
. By [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Lemma 4.3.8], the category
$X\in {\mathscr {C}}^{B}$
. By [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Lemma 4.3.8], the category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}^{B}$
is generated under colimits by objects of the form
${\mathscr {C}}^{B}$
is generated under colimits by objects of the form
![]() $b_{!}Y$
for
$b_{!}Y$
for
![]() $Y\in {\mathscr {C}}$
and
$Y\in {\mathscr {C}}$
and
![]() $b\colon \textrm {pt} \to B$
. By the
$b\colon \textrm {pt} \to B$
. By the
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidexterity of q, both sides of
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidexterity of q, both sides of
![]() $(*)$
preserve colimits, and it therefore suffices to show that
$(*)$
preserve colimits, and it therefore suffices to show that
![]() $\varepsilon $
is an isomorphism at local systems of the form
$\varepsilon $
is an isomorphism at local systems of the form
![]() $X= b_! Y$
. Using the
$X= b_! Y$
. Using the
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidexterity of the map
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidexterity of the map
![]() $b\colon \textrm {pt}\to B$
, we can also identify
$b\colon \textrm {pt}\to B$
, we can also identify
![]() $b_{!}Y$
with
$b_{!}Y$
with
![]() $b_{*}Y$
.
$b_{*}Y$
.
Next, to show that
![]() $\varepsilon $
is an isomorphism at
$\varepsilon $
is an isomorphism at
![]() $b_*Y$
, it suffices to show that for every
$b_*Y$
, it suffices to show that for every
![]() $a\colon \textrm {pt} \to B$
, the map
$a\colon \textrm {pt} \to B$
, the map
![]() $a^{*}\varepsilon $
is an isomorphism at
$a^{*}\varepsilon $
is an isomorphism at
![]() $b_*Y$
. Using the identities
$b_*Y$
. Using the identities
![]() $b^{*}q^{*}=\textrm {Id}$
and
$b^{*}q^{*}=\textrm {Id}$
and
![]() $q_{*}a_{*}=\textrm {Id}$
, the map
$q_{*}a_{*}=\textrm {Id}$
, the map
assumes the form
Both the domain and the range of this map, when considered as functors in the Y-variable, are colimit-preserving and
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear. Indeed, for the domain, it follows from the colimit preservation and
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear. Indeed, for the domain, it follows from the colimit preservation and
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linearity of the relative tensor product, and for the target by Corollary 2.34 applied to the
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linearity of the relative tensor product, and for the target by Corollary 2.34 applied to the
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous space
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous space
![]() $\{a\}\times _B \{b\}$
. Moreover,
$\{a\}\times _B \{b\}$
. Moreover,
![]() $a^*\varepsilon $
is canonically a natural transformation of
$a^*\varepsilon $
is canonically a natural transformation of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear functors. Hence, it suffices to show that the above map is an isomorphism for
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear functors. Hence, it suffices to show that the above map is an isomorphism for ![]() . In this case, we obtain precisely the map from condition (3)
. In this case, we obtain precisely the map from condition (3)
which is an equivalence by assumption.
Theorem 2.38(3) provides a very practical criterion for checking affineness, which we shall use repeatedly. For now, we demonstrate its utility by deducing that affineness behaves well with respect to monoidal functors.
Proposition 2.39. Let
![]() $F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
be a functor in
$F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
be a functor in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let B be a
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let B be a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextruous space. If B is
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextruous space. If B is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then it is
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then it is
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-affine. Conversely, if B is
${\mathscr {D}}$
-affine. Conversely, if B is
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-affine and F is conservative, then B is
${\mathscr {D}}$
-affine and F is conservative, then B is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
Proof. Since F is monoidal and colimit-preserving, B is also
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
-ambidextrous; see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.3.2]. Moreover, F preserves B-shaped limits as well as
${\mathscr {D}}$
-ambidextrous; see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.3.2]. Moreover, F preserves B-shaped limits as well as
![]() $\{a\}\times _B \{b\}$
-shaped limits for every
$\{a\}\times _B \{b\}$
-shaped limits for every
![]() $a,b\in B$
; see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.2.4]. It follows that for all
$a,b\in B$
; see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.2.4]. It follows that for all
![]() $a,b\in B$
, the square
$a,b\in B$
, the square

is the image under F of the square

Since F is colimit-preserving and monoidal, the latter is a relative tensor square if the former is a relative tensor square, and the converse holds if F is conservative.
Affineness and height
In Corollary 2.34, we have seen that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affineness is closely related to
${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affineness is closely related to
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidexterity. In particular, the
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidexterity. In particular, the
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affineness of the Eilenberg–Maclane spaces
${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affineness of the Eilenberg–Maclane spaces
![]() $B^kC_p$
is closely related to the p-typical higher semiadditivity of
$B^kC_p$
is closely related to the p-typical higher semiadditivity of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
(Corollary 2.33). We shall now see that
${\mathscr {C}}$
(Corollary 2.33). We shall now see that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affineness of these spaces is closely related to the semiadditive height of
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affineness of these spaces is closely related to the semiadditive height of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, §3].
${\mathscr {C}}$
in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, §3].
Proposition 2.40. Let p be a prime, and let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
be p-typically n-semiadditive.
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
be p-typically n-semiadditive.
-
(1) If
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
 $\le n$
, then every
$\le n$
, then every
 $(n+1)$
-connected
$(n+1)$
-connected
 $\pi $
-finite p-space is
$\pi $
-finite p-space is
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. -
(2) If
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
 $\le n$
and
$\le n$
and
 $B^{n+1}C_{p}$
is
$B^{n+1}C_{p}$
is
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
 $\le (n-1)$
.Footnote
3
$\le (n-1)$
.Footnote
3
-
(3) If the spaces
 $B^kC_p$
are
$B^kC_p$
are
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine for
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine for
 $k=0,\dots ,n$
, then
$k=0,\dots ,n$
, then
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
 $\ge n$
.
$\ge n$
.
Proof. For (1), let A be an
![]() $(n+1)$
-connected
$(n+1)$
-connected
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-space, and let
$\pi $
-finite p-space, and let
![]() $q\colon A\to \textrm {pt}$
be the terminal map. Since
$q\colon A\to \textrm {pt}$
be the terminal map. Since
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
![]() $\le n$
, we get by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.3] that
$\le n$
, we get by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.3] that
![]() $q^{*}\colon {\mathscr {C}}\to {\mathscr {C}}^{A}$
is an equivalence and hence clearly affine.
$q^{*}\colon {\mathscr {C}}\to {\mathscr {C}}^{A}$
is an equivalence and hence clearly affine.
For (2), assuming
![]() $B^{n+1}C_p$
is
$B^{n+1}C_p$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, we get by Theorem 2.38 an isomorphism
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, we get by Theorem 2.38 an isomorphism
Since
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
![]() $\le n$
, by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.1], we also have an isomorphism
$\le n$
, by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.1], we also have an isomorphism ![]() . Combining the two isomorphisms, we get
. Combining the two isomorphisms, we get
By [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.1] again, this implies that
![]() $B^{n-1}C_{p}$
is
$B^{n-1}C_{p}$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-amenable – namely, that
${\mathscr {C}}$
-amenable – namely, that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
![]() $\le n-1$
.
$\le n-1$
.
For
![]() $(3)$
, let
$(3)$
, let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1} \subseteq {\mathscr {C}}$
be the full subcategory spanned by the objects of height
${\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1} \subseteq {\mathscr {C}}$
be the full subcategory spanned by the objects of height
![]() $\le n-1$
, so that
$\le n-1$
, so that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
![]() $\ge n$
if and only if
$\ge n$
if and only if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1}\simeq \textrm {pt}$
. By [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 5.2.16], the inclusion of
${\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1}\simeq \textrm {pt}$
. By [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 5.2.16], the inclusion of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1}$
into
${\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1}$
into
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
admits a symmetric monoidal reflection
${\mathscr {C}}$
admits a symmetric monoidal reflection
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1}$
. Hence, the
${\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1}$
. Hence, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1}$
is itself p-typically n-semiadditive and the space
${\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1}$
is itself p-typically n-semiadditive and the space
![]() $B^kC_p$
for
$B^kC_p$
for
![]() $k=0,\dots ,n$
are also
$k=0,\dots ,n$
are also
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1}$
-affine, by Proposition 2.39. Now, applying (2) inductively, we find that
${\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1}$
-affine, by Proposition 2.39. Now, applying (2) inductively, we find that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1}$
is of height
${\mathscr {C}}_{\le n-1}$
is of height
![]() $-1$
and hence trivial.
$-1$
and hence trivial.
For
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
of height
${\mathscr {C}}$
of height
![]() $\le n$
, we can roughly summarize the content of Proposition 2.40 regarding
$\le n$
, we can roughly summarize the content of Proposition 2.40 regarding
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affineness of
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affineness of
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-spaces as follows:
$\pi $
-finite p-spaces as follows:
-
(1) We have affineness above level
 $n+1$
for trivial reasons.
$n+1$
for trivial reasons. -
(2) To have affineness below level
 $n+1$
, the height of
$n+1$
, the height of
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
must be exactly n, in which case,
${\mathscr {C}}$
must be exactly n, in which case, -
(3) There is no affineness at level exactly
 $n+1$
.
$n+1$
.
This still leaves open, however, the question of whether for
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
of height exactly n, we actually have affineness below level
${\mathscr {C}}$
of height exactly n, we actually have affineness below level
![]() $n+1$
. In the chromatic world, Hopkins and Lurie proved in [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Theorem 5.4.3] that this is indeed the case for
$n+1$
. In the chromatic world, Hopkins and Lurie proved in [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Theorem 5.4.3] that this is indeed the case for
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}= \textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
. Their argument is rather specific though, as it relies on explicit computations with the Lubin–Tate spectrum
${\mathscr {C}}= \textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
. Their argument is rather specific though, as it relies on explicit computations with the Lubin–Tate spectrum
![]() $E_n$
. One of the goals of this paper is to bootstrap [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Theorem 5.4.3] to the telescopic localizations
$E_n$
. One of the goals of this paper is to bootstrap [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Theorem 5.4.3] to the telescopic localizations
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} = \textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
. We achieve this by placing the approach of Hopkins and Lurie in the context of a higher semiadditive Fourier transform, which we develop in the next section.
${\mathscr {C}} = \textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
. We achieve this by placing the approach of Hopkins and Lurie in the context of a higher semiadditive Fourier transform, which we develop in the next section.
3 The higher Fourier transform
Let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
be a connective p-local commutative ring spectrum and
$\mathfrak {R}$
be a connective p-local commutative ring spectrum and
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
a symmetric monoidal
${\mathscr {C}}$
a symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category. In this section, we study natural transformations
$\infty $
-category. In this section, we study natural transformations
from the group algebra of a suitably finite connective
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module spectrum M to the algebra of functions on its n-suspended Brown–Comenetz dual. We show that such natural transformations can be viewed as a generalization of the classical discrete Fourier transform and share many of its basic properties. In particular, we show that such maps are parameterized by a certain datum of an
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module spectrum M to the algebra of functions on its n-suspended Brown–Comenetz dual. We show that such natural transformations can be viewed as a generalization of the classical discrete Fourier transform and share many of its basic properties. In particular, we show that such maps are parameterized by a certain datum of an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation on
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation on
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, which generalizes roots of unity of
${\mathscr {C}}$
, which generalizes roots of unity of ![]() in the case
in the case
![]() $\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
, and satisfy familiar relations with respect to augmentations, translation and duality.
$\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
, and satisfy familiar relations with respect to augmentations, translation and duality.
3.1 Pre-orientations
Shifted Brown–Comenetz duality
The first ingredient in the construction of the higher Fourier transform is a spectral lift of Pontryagin duality for abelian groups, known as Brown–Comenetz duality. We shall work throughout with the p-local variant of this theory with respect to a fixed prime p. By Brown representability, the contravariant functor
![]() $\hom _{\textrm {Ab}}(\pi _{-*}(-),\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p)$
, from spectra to graded abelian groups, is represented by a spectrum
$\hom _{\textrm {Ab}}(\pi _{-*}(-),\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p)$
, from spectra to graded abelian groups, is represented by a spectrum
![]() $I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
, the p-local Brown–Comenetz dual (of the sphere). It is characterized by the following property: there is a natural isomorphism
$I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
, the p-local Brown–Comenetz dual (of the sphere). It is characterized by the following property: there is a natural isomorphism
for all
![]() $M \in \textrm {Sp}$
. Mapping into
$M \in \textrm {Sp}$
. Mapping into
![]() $I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
gives a contravariant endofunctor on
$I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p}$
gives a contravariant endofunctor on
![]() $\textrm {Sp}$
. For our applications, it will be useful to introduce a certain connective shifted version of it.
$\textrm {Sp}$
. For our applications, it will be useful to introduce a certain connective shifted version of it.
Definition 3.1. For
![]() $n \in \mathbb {N}$
and
$n \in \mathbb {N}$
and
![]() $M\in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
, we define the n-shifted Brown–Comenetz dual of M by
$M\in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
, we define the n-shifted Brown–Comenetz dual of M by
For a connective commutative p-local ring spectrum
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
and a connective
$\mathfrak {R}$
and a connective
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module M, the n-shifted Brown–Comenetz dual
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module M, the n-shifted Brown–Comenetz dual
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{M}$
admits a canonical
$I_p^{(n)}{M}$
admits a canonical
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module structure via the action of
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module structure via the action of
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
on the source of the mapping spectrum
$\mathfrak {R}$
on the source of the mapping spectrum
![]() $\hom (M,\Sigma ^n I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p})$
. In particular,
$\hom (M,\Sigma ^n I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p})$
. In particular,
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
itself is a connective
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
itself is a connective
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module. In fact, it represents the functor
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module. In fact, it represents the functor
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{}$
internally to connective
$I_p^{(n)}{}$
internally to connective
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules. In the following,
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules. In the following,
![]() $\hom _{\mathfrak {R}}^{\textrm {cn}}$
stands for the internal hom functor in connective
$\hom _{\mathfrak {R}}^{\textrm {cn}}$
stands for the internal hom functor in connective
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules.
Lemma 3.2. Let
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For every
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For every
![]() $M \in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{\textrm {cn}}$
, we have
$M \in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{\textrm {cn}}$
, we have
Proof. We compute using the fact that M is connective:
Terminology 3.3. With notation as above, we will refer to maps
![]() $M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
as characters of M.
$M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
as characters of M.
Next, we observe that
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{M}$
is always n-truncated and depends only on the n-truncation of M. Thus, it makes sense to restrict
$I_p^{(n)}{M}$
is always n-truncated and depends only on the n-truncation of M. Thus, it makes sense to restrict
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{}$
to the full subcategory
$I_p^{(n)}{}$
to the full subcategory
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]} \subseteq {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{\textrm {cn}}$
of n-truncated (connective)
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]} \subseteq {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{\textrm {cn}}$
of n-truncated (connective)
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules, on which it is characterized by the property
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules, on which it is characterized by the property
Remark 3.4. For
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, both the spectrum
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, both the spectrum
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
and the
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
and the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
depend only on the n-truncation of
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
depend only on the n-truncation of
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
, so we might as well assume that
$\mathfrak {R}$
, so we might as well assume that
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
is n-truncated whenever it is convenient to do so.
$\mathfrak {R}$
is n-truncated whenever it is convenient to do so.
When further restricting to the full subcategory
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}} \subseteq {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
of
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}} \subseteq {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
of
![]() $[0,n]$
-finite
$[0,n]$
-finite
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules (i.e., connective n-truncated
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules (i.e., connective n-truncated
![]() $\pi $
-finite
$\pi $
-finite
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules), the functor
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules), the functor
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{}$
becomes a contravariant self-equivalence
$I_p^{(n)}{}$
becomes a contravariant self-equivalence
Indeed, every module in
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
![]() $\pi $
-finite and p-local; hence, its homotopy groups are finite p-groups, and the claim follows from the corresponding claim for the functor
$\pi $
-finite and p-local; hence, its homotopy groups are finite p-groups, and the claim follows from the corresponding claim for the functor
![]() $\hom (-,\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p)$
.
$\hom (-,\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p)$
.
Remark 3.5. In principle, we could work with the non-p-local Pontryagin dual
![]() $\hom (-,\mathbb {Q}/\mathbb {Z})$
and general (i.e., not necessarily p-local) connective ring spectra
$\hom (-,\mathbb {Q}/\mathbb {Z})$
and general (i.e., not necessarily p-local) connective ring spectra
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
. However, in practice, the choice of the shift n will match the semiadditive height of a given higher semiadditive
$\mathfrak {R}$
. However, in practice, the choice of the shift n will match the semiadditive height of a given higher semiadditive
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, at the prime p (introduced in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a]). As
${\mathscr {C}}$
, at the prime p (introduced in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a]). As
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
will usually have different heights at different primes, it will not make much sense to have a fixed shift n. instead, we observe that a connective
${\mathscr {C}}$
will usually have different heights at different primes, it will not make much sense to have a fixed shift n. instead, we observe that a connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite spectrum M decomposes as a direct sum of its p-localizations
$\pi $
-finite spectrum M decomposes as a direct sum of its p-localizations
![]() $ M \simeq \bigoplus _{p\text { prime}} M_{(p)}. $
So for every vector
$ M \simeq \bigoplus _{p\text { prime}} M_{(p)}. $
So for every vector
![]() $\vec {n}= (n_p)$
of integers, we can define the
$\vec {n}= (n_p)$
of integers, we can define the
![]() $\vec {n}$
-shifted Brown–Comenetz dual of
$\vec {n}$
-shifted Brown–Comenetz dual of
![]() $M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
by
$M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
by
 $$ \begin{align*}I_p^{(\vec{n})}{M}:= \bigoplus _{p\text{ prime}} I_p^{(n_p)}{M_{(p)}} \quad \in \quad {\operatorname{Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{\pi \text{-}\textrm {fin}}. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}I_p^{(\vec{n})}{M}:= \bigoplus _{p\text{ prime}} I_p^{(n_p)}{M_{(p)}} \quad \in \quad {\operatorname{Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{\pi \text{-}\textrm {fin}}. \end{align*} $$
We chose to work p-locally in this paper to make things easier, but essentially everything can be generalized to this ‘global’ setting. We note that for a stable
![]() $\infty $
-category, the semiadditive height can be nonzero for at most one prime. However, there are interesting nonstable
$\infty $
-category, the semiadditive height can be nonzero for at most one prime. However, there are interesting nonstable
![]() $\infty $
-categories, such as those arising via categorification, for which the vector of semiadditive heights can be more complicated.
$\infty $
-categories, such as those arising via categorification, for which the vector of semiadditive heights can be more complicated.
Pre-orientations
Recall that the construction of the discrete Fourier transform for an m-torsion abelian group M depends on a choice of an m-th root of unity. We can view the condition that M is m-torsion as the existence of a (necessarily unique) structure of
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/m$
-module on M. Analogously, for a connective ring spectrum
$\mathbb {Z}/m$
-module on M. Analogously, for a connective ring spectrum
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
, the higher Fourier transform in an
$\mathfrak {R}$
, the higher Fourier transform in an
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, for connective
${\mathscr {C}}$
, for connective
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules, requires a choice of auxiliary data.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules, requires a choice of auxiliary data.
Definition 3.6. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
and
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
and
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For every
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For every
![]() $S \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the space of
$S \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the space of
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations of height n of S is defined and denoted as follows:
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations of height n of S is defined and denoted as follows:
where
![]() $S^{\times }$
denotes the spectrum of units of S. An
$S^{\times }$
denotes the spectrum of units of S. An
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
pre-orientation of
$\mathfrak {R}$
pre-orientation of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is a pre-orientation of
${\mathscr {C}}$
is a pre-orientation of ![]() , and the space of such is denoted by
, and the space of such is denoted by
![]() ${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. If
${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. If
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
is clear from contect, we will also refer to this data simply as a pre-orientation of
$\mathfrak {R}$
is clear from contect, we will also refer to this data simply as a pre-orientation of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
.
${\mathscr {C}}$
.
Example 3.7. We have a canonical identification
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {Z}/p^r}\simeq \Sigma ^n \mathbb {Z}/p^r.$
Hence, the notion of a
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {Z}/p^r}\simeq \Sigma ^n \mathbb {Z}/p^r.$
Hence, the notion of a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-pre-orientation of height n identifies with that of a height n root of unity of order
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-pre-orientation of height n identifies with that of a height n root of unity of order
![]() $p^r$
, in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Defnition 4.2]. More precisely, for
$p^r$
, in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Defnition 4.2]. More precisely, for
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
and
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
and
![]() $S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we have
$S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we have
where
![]() $\mu _{p^r}^{(n)}(S)$
denotes the spectrum of height n roots of unity of order
$\mu _{p^r}^{(n)}(S)$
denotes the spectrum of height n roots of unity of order
![]() $p^r$
in S. Note that, in particular,
$p^r$
in S. Note that, in particular,
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-pre-orientations of height
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-pre-orientations of height
![]() $0$
of a field
$0$
of a field
![]() $\mathbb {F}$
correspond to
$\mathbb {F}$
correspond to
![]() $p^r$
-th roots of unity in
$p^r$
-th roots of unity in
![]() $\mathbb {F}$
.
$\mathbb {F}$
.
Remark 3.8. For a p-divisible group
![]() $\mathbb {G}$
over an
$\mathbb {G}$
over an
![]() $\mathbb {E}_\infty $
-ring spectrum R, Lurie [Reference LurieLur18b, Definition 2.1.4] defines a pre-orientation of
$\mathbb {E}_\infty $
-ring spectrum R, Lurie [Reference LurieLur18b, Definition 2.1.4] defines a pre-orientation of
![]() $\mathbb {G}$
as a map of
$\mathbb {G}$
as a map of
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-modules
$\mathbb {Z}$
-modules
![]() $\Sigma \mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p \to \mathbb {G}(R)$
. Since for the multiplicative group
$\Sigma \mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p \to \mathbb {G}(R)$
. Since for the multiplicative group
![]() $\mathbb {G}_m$
we have
$\mathbb {G}_m$
we have
![]() $\mathbb {G}_m(E)\simeq \hom (\mathbb {Z},R^\times )$
, a pre-orientation of
$\mathbb {G}_m(E)\simeq \hom (\mathbb {Z},R^\times )$
, a pre-orientation of
![]() $\mathbb {G}_m$
is the same thing as a map of spectra
$\mathbb {G}_m$
is the same thing as a map of spectra
Thus, we can identify the space of
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-pre-orientations of height
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-pre-orientations of height
![]() $1$
of R, with the space of pre-orientations of the p-divisible group
$1$
of R, with the space of pre-orientations of the p-divisible group
![]() $\mathbb {G}_m$
over R. In general, we can view
$\mathbb {G}_m$
over R. In general, we can view
![]() ${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
as an ‘
${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
as an ‘
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-linear, higher height analogue’ of pre-orientations for the multiplicative p-divisible group over the unit
$\mathfrak {R}$
-linear, higher height analogue’ of pre-orientations for the multiplicative p-divisible group over the unit ![]() .
.
There is an adjoint way of viewing pre-orientations. When
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is presentable, the functor
${\mathscr {C}}$
is presentable, the functor
admits a left adjoint
which takes a connective spectrum M to its group-algebra ![]() . Hence, we can identify a pre-orientation
. Hence, we can identify a pre-orientation ![]() with an augmentation
with an augmentation
Thus,
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations of height n for commutative algebras in
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations of height n for commutative algebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
are co-represented by
${\mathscr {C}}$
are co-represented by ![]() .
.
Example 3.9. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
be the category of complex vector spaces, and let
${\mathscr {C}}$
be the category of complex vector spaces, and let
![]() $R=\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
. For an m-th root of unity
$R=\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
. For an m-th root of unity
![]() $\omega \in \mathbb {C}^\times $
, the augmentation
$\omega \in \mathbb {C}^\times $
, the augmentation
![]() $\varepsilon _\omega \colon \mathbb {C}[\mathbb {Z}/p^r]\to \mathbb {C}$
is given by
$\varepsilon _\omega \colon \mathbb {C}[\mathbb {Z}/p^r]\to \mathbb {C}$
is given by
 $$\begin{align*}\varepsilon_\omega\left (\sum_{k\in \mathbb{Z}/p^r} a_k [k]\right)= \sum_{k\in \mathbb{Z}/p^r} a_k \omega^k \quad\in\quad \mathbb{C}. \end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\varepsilon_\omega\left (\sum_{k\in \mathbb{Z}/p^r} a_k [k]\right)= \sum_{k\in \mathbb{Z}/p^r} a_k \omega^k \quad\in\quad \mathbb{C}. \end{align*}$$
Hence, we can view
![]() $\varepsilon _\omega $
in general as the map which gives
$\varepsilon _\omega $
in general as the map which gives ![]() -valued ‘exponential sums’.
-valued ‘exponential sums’.
3.2 The Fourier transform
Construction
Given an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation
![]() $\omega $
of height n, we now construct for every connective
$\omega $
of height n, we now construct for every connective
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module M a map of commutative algebras
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module M a map of commutative algebras ![]() In fact, we show that the space of such maps, that are natural in M, is parameterized by pre-orientations.
In fact, we show that the space of such maps, that are natural in M, is parameterized by pre-orientations.
Proposition 3.10. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. The space of natural transformations
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. The space of natural transformations ![]() of functors
of functors
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is naturally isomorphic to
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is naturally isomorphic to
![]() ${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
Proof. The functor that takes an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module M to the algebra
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module M to the algebra ![]() is the right Kan extension of the functor
is the right Kan extension of the functor
![]() $\textrm {pt} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
corresponding to the object
$\textrm {pt} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
corresponding to the object ![]() , along the functor
, along the functor
![]() $\textrm {pt} \to {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
corresponding to the object
$\textrm {pt} \to {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
corresponding to the object
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
:
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
:

It follows that the space of natural transformations of the form ![]() is isomorphic to the space of augmentations of the algebra
is isomorphic to the space of augmentations of the algebra ![]() , which is the same as the space
, which is the same as the space
![]() ${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
of
${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
of
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations of height n.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations of height n.
Definition 3.11. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the associated Fourier transform is the natural transformation
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the associated Fourier transform is the natural transformation
of functors
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
corresponding to
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
corresponding to
![]() $\omega $
by Proposition 3.10. We shall occasionally consider the Fourier transform as a functor
$\omega $
by Proposition 3.10. We shall occasionally consider the Fourier transform as a functor
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega \colon {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^{[1]}.$
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega \colon {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^{[1]}.$
A couple of remarks on the definition of the Fourier transform are in order.
Remark 3.12. By unwinding the definition of the Kan extension, the passage from a pre-orientation to the associated Fourier transform and vice versa can be made more explicit. First, by evaluating
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
on
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
on
![]() $M= I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
, we recover the augmentation that corresponds to
$M= I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
, we recover the augmentation that corresponds to ![]() , as the composition
, as the composition
Conversely, let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
. For every character
$M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
. For every character
![]() $\varphi \colon M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
, the composition
$\varphi \colon M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
, the composition ![]() corresponds to an augmentation
corresponds to an augmentation ![]() These assemble into a map
These assemble into a map
which is the same data as the map ![]()
Remark 3.13. In Proposition 3.10, one could replace
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
with a larger
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
with a larger
![]() $\infty $
-category such as
$\infty $
-category such as
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R^{\textrm {cn}}$
and thus define the Fourier transform for all connective
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R^{\textrm {cn}}$
and thus define the Fourier transform for all connective
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules. Though this might sometimes be technically convenient, we shall be interested primarily in the Fourier transform only for n-truncated modules. In fact, eventually, we shall be interested only in the further restriction of the Fourier transform to the full subcategory
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules. Though this might sometimes be technically convenient, we shall be interested primarily in the Fourier transform only for n-truncated modules. In fact, eventually, we shall be interested only in the further restriction of the Fourier transform to the full subcategory
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}} \subseteq {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
of
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}} \subseteq {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
of
![]() $[0,n]$
-finite modules. However, for establishing some of its formal properties, it is useful to use the characterization provided by Proposition 3.10. Having said that, if
$[0,n]$
-finite modules. However, for establishing some of its formal properties, it is useful to use the characterization provided by Proposition 3.10. Having said that, if
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
itself happens to be
$\mathfrak {R}$
itself happens to be
![]() $[0,n]$
-finite (e.g.,
$[0,n]$
-finite (e.g.,
![]() $\mathfrak {R}=\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
), then
$\mathfrak {R}=\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
), then
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
and one could also replace
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
and one could also replace
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
with
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
with
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
.
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
.
Definition 3.11 generalizes the classical discrete Fourier transform in the following sense:
Example 3.14. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
be the category of
${\mathscr {C}}$
be the category of
![]() $\mathbb {C}$
-vector spaces. For an m-th root of unity
$\mathbb {C}$
-vector spaces. For an m-th root of unity
![]() $\omega \in \mathbb {C}^\times $
and an m-torsion abelian group M, the map
$\omega \in \mathbb {C}^\times $
and an m-torsion abelian group M, the map
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega \colon \mathbb {C}[M]\to \mathbb {C}^{M^*}$
is given on
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega \colon \mathbb {C}[M]\to \mathbb {C}^{M^*}$
is given on
![]() $x\in M\subseteq \mathbb {C}[M]$
by
$x\in M\subseteq \mathbb {C}[M]$
by
In particular, if
![]() $M\simeq \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
and we identify
$M\simeq \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
and we identify
![]() $M^*$
with M using the generator
$M^*$
with M using the generator
![]() $1\in M$
, we recover the classical (inverse) Fourier matrix
$1\in M$
, we recover the classical (inverse) Fourier matrix
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega (k)(\ell )= \omega ^{k\cdot \ell }$
.
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega (k)(\ell )= \omega ^{k\cdot \ell }$
.
The Fourier transform can be enhanced to take into account a bit more structure. A character
![]() $\varphi \colon M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
induces a map
$\varphi \colon M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
induces a map ![]() , which corresponds to an augmentation
, which corresponds to an augmentation
However, thinking of
![]() $\varphi $
as a point in
$\varphi $
as a point in
![]() $\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
yields an augmentation
$\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
yields an augmentation
The Fourier transform intertwines these augmentations.
Proposition 3.15. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For every
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For every
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
and
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
and
![]() $\varphi \colon M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
in
$\varphi \colon M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
in
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
, the following diagram commutes:
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
, the following diagram commutes:

Moreover,
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
promotes uniquely to a natural transformation of functors
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
promotes uniquely to a natural transformation of functors
whose component at
![]() $\varphi \colon M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
is given by the diagram above.
$\varphi \colon M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
is given by the diagram above.
Proof. On the one hand, the Fourier transform ![]() whiskered by the forgetful functor
whiskered by the forgetful functor
![]() $({\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]})_{/I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}} \rightarrow {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
, can be viewed as a functor
$({\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]})_{/I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}} \rightarrow {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
, can be viewed as a functor
On the other hand, the construction taking
![]() $\varphi \colon M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
to
$\varphi \colon M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
to ![]() assembles into a functor
assembles into a functor
Since the forgetful functor ![]() is a right fibration, we have a pullback square of
is a right fibration, we have a pullback square of
![]() $\infty $
-categories
$\infty $
-categories

It follows that the two functors above, which agree after projecting to
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, uniquely lift to a functor
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, uniquely lift to a functor
It remains to show that for every
![]() $M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
, the map
$M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
, the map
![]() $\textrm {ev}_{\varphi } \circ {\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
is homotopic to
$\textrm {ev}_{\varphi } \circ {\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
is homotopic to
![]() $\varepsilon _{\omega \circ \varphi }$
. By the naturality of
$\varepsilon _{\omega \circ \varphi }$
. By the naturality of
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
, we have a commutative diagram:
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
, we have a commutative diagram:

By Remark 3.12, the composition of the two bottom maps is
![]() $\varepsilon _\omega $
and
$\varepsilon _\omega $
and
![]() $\varepsilon _\omega \circ \varphi = \varepsilon _{\omega \circ \varphi }$
, so the claim follows.
$\varepsilon _\omega \circ \varphi = \varepsilon _{\omega \circ \varphi }$
, so the claim follows.
Functoriality
We now explain how the Fourier transform
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}$
is functorial in the various arguments it depends on. First, given a map
${\mathfrak {F}}$
is functorial in the various arguments it depends on. First, given a map
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
in
$f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, we can regard an S-module as an
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, we can regard an S-module as an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module by restriction of scalars along f, which we denote by
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module by restriction of scalars along f, which we denote by
![]() $f_* \colon {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {S}}^{[0,n]} \to {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}.$
Similarly, given an
$f_* \colon {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {S}}^{[0,n]} \to {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}.$
Similarly, given an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation ![]() , by pre-composition with the
, by pre-composition with the
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module map
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module map
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {S}} \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
, we obtain an
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {S}} \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
, we obtain an
![]() $\mathfrak {S}$
-pre-orientation, which we denote by
$\mathfrak {S}$
-pre-orientation, which we denote by ![]() .
.
Proposition 3.16. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
in
$f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let ![]() be an
be an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation. There is a canonical isomorphism of natural transformations
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation. There is a canonical isomorphism of natural transformations
of functors
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {S}}^{[0,n]} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}}).$
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {S}}^{[0,n]} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}}).$
Proof. First, observe that for every
![]() $M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}^{\textrm {cn}}_{\mathfrak {S}}$
, we have
$M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}^{\textrm {cn}}_{\mathfrak {S}}$
, we have
Hence, both
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{f_*\omega }$
and
${\mathfrak {F}}_{f_*\omega }$
and
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{\omega } f_*$
are maps
${\mathfrak {F}}_{\omega } f_*$
are maps ![]() of functors
of functors
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {S}}^{[0,n]} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. Consequently, by Proposition 3.10, it suffices to show that
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {S}}^{[0,n]} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. Consequently, by Proposition 3.10, it suffices to show that
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{\omega } f_*$
is classified by the pre-orientation
${\mathfrak {F}}_{\omega } f_*$
is classified by the pre-orientation
![]() $f_*\omega $
. For this, it suffices to identify the corresponding augmentations. By Remark 3.12, the augmentation associated with
$f_*\omega $
. For this, it suffices to identify the corresponding augmentations. By Remark 3.12, the augmentation associated with
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{\omega } f_*$
is given by
${\mathfrak {F}}_{\omega } f_*$
is given by
The isomorphism ![]() takes the map
takes the map
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{f}\colon I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {S}}\rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
, dual to
$I_p^{(n)}{f}\colon I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {S}}\rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
, dual to
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
, to the identity map of
$f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
, to the identity map of
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {S}}$
. Hence, we can identify
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {S}}$
. Hence, we can identify
![]() $\varepsilon $
with the composition
$\varepsilon $
with the composition
By Proposition 3.15, this composition is homotopic to the composition
which is, by definition,
![]() $\varepsilon _{f_*\omega }$
.
$\varepsilon _{f_*\omega }$
.
Example 3.17. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let ![]() . The Pontryagin dual of the quotient map
. The Pontryagin dual of the quotient map
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^{r+1}\twoheadrightarrow \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
identifies with the inclusion
$\mathbb {Z}/p^{r+1}\twoheadrightarrow \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
identifies with the inclusion
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r\hookrightarrow \mathbb {Z}/p^{r+1}$
. Hence, if M is a
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r\hookrightarrow \mathbb {Z}/p^{r+1}$
. Hence, if M is a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-module, then by Proposition 3.16, we can identify the map
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-module, then by Proposition 3.16, we can identify the map
with the map
obtained by regarding M as a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^{r+1}$
-module.
$\mathbb {Z}/p^{r+1}$
-module.
Next, we discuss the functoriality of the Fourier transform with respect to the ambient
![]() $\infty $
-category. A symmetric monoidal functor
$\infty $
-category. A symmetric monoidal functor
![]() $F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
induces a functor
$F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
induces a functor
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}}) \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {D}}).$
Furthermore, given a pre-orientation
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}}) \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {D}}).$
Furthermore, given a pre-orientation ![]() in
in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, by post-composition with the map
${\mathscr {C}}$
, by post-composition with the map ![]() , we obtain a pre-orientation in
, we obtain a pre-orientation in
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
, which we denote by
${\mathscr {D}}$
, which we denote by ![]() . In fact, the same construction works under the weaker assumption that F is merely lax symmetric monoidal and unital, in the sense that the map
. In fact, the same construction works under the weaker assumption that F is merely lax symmetric monoidal and unital, in the sense that the map ![]() is an isomorphism.
is an isomorphism.
Proposition 3.18. Let
![]() $F\colon {\mathscr {C}}\to {\mathscr {D}}$
be a unital lax symmetric monoidal functor of presentably symmetric monoidal
$F\colon {\mathscr {C}}\to {\mathscr {D}}$
be a unital lax symmetric monoidal functor of presentably symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-categories, let
$\infty $
-categories, let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let ![]() be an
be an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation of
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. The diagram
${\mathscr {C}}$
. The diagram

commutes naturally in
![]() $M \in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
. Here, the vertical maps are the respective assembly maps.
$M \in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
. Here, the vertical maps are the respective assembly maps.
Proof. By Proposition 3.10, it suffices to show that the following diagram commutes:

Namely, we show that the augmentation
![]() $\varepsilon _{F(\omega )}$
is homotopic to the composition
$\varepsilon _{F(\omega )}$
is homotopic to the composition
Via the adjunction ![]() , this composition corresponds to the map
, this composition corresponds to the map
which is, by definition,
![]() $F(\omega )$
.
$F(\omega )$
.
Remark 3.19. In the situation of Proposition 3.18, if we additionally require F to preserve
![]() $\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
-shaped colimits and
$\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
-shaped colimits and
![]() $\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
-shaped limits, then the vertical maps are isomorphisms, and hence,
$\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
-shaped limits, then the vertical maps are isomorphisms, and hence,
![]() $F({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )$
identifies with
$F({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )$
identifies with
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{F(\omega )}$
. This happens, for example, if F is an n-semiadditive functor in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Definition 3.2.6].
${\mathfrak {F}}_{F(\omega )}$
. This happens, for example, if F is an n-semiadditive functor in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Definition 3.2.6].
We have one more type of functoriality to consider, which is given by rescaling the pre-orientation. For
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, the underlying space
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, the underlying space
![]() $\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
with its multiplicative monoid structure acts naturally on every
$\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
with its multiplicative monoid structure acts naturally on every
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module M. Thus, given
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module M. Thus, given
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and a pre-orientation
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and a pre-orientation
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the naturality of the Fourier transform
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the naturality of the Fourier transform ![]() makes it
makes it
![]() $\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
-equivariant. In particular, for every
$\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
-equivariant. In particular, for every
![]() $r \in \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
, we have a commutative square
$r \in \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
, we have a commutative square

natural in
![]() $M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
. Now, the diagonal map given by (either of) the compositions is also a natural transformation of the form
$M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
. Now, the diagonal map given by (either of) the compositions is also a natural transformation of the form ![]() and hence, by Proposition 3.10, is classified by the associated augmentation
and hence, by Proposition 3.10, is classified by the associated augmentation
Definition 3.20. For
![]() $r\in \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
, we denote by
$r\in \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
, we denote by
the pre-composition with
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}\xrightarrow {r\cdot } I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}. $
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}\xrightarrow {r\cdot } I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}. $
Example 3.21. For
![]() $R= \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
and
$R= \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
and
![]() $n=0$
, the operation
$n=0$
, the operation
![]() $\omega \mapsto \omega ^k$
for
$\omega \mapsto \omega ^k$
for
![]() $k\in \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
is given by raising the
$k\in \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
is given by raising the
![]() $p^r$
-th root of unity
$p^r$
-th root of unity
![]() $\omega $
to the k-th power.
$\omega $
to the k-th power.
For ease of reference, we record the following immediate consequence of the above discussion:
Proposition 3.22. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. For every
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. For every
![]() $r\in \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
, we have a commutative triangle
$r\in \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
, we have a commutative triangle

in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
naturally in
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
naturally in
![]() $M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
.
$M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
.
Proof. This follows immediately from the definition of
![]() $\omega ^r$
.
$\omega ^r$
.
Duality
We conclude this section with a discussion of the symmetry of the Fourier transform with respect to monoidal duality. Given a presentably symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
and
${\mathscr {C}}$
and
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we have for every
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we have for every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
a Fourier transform map
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
a Fourier transform map
Under the canonical identification ![]() , we also have the Fourier transform map
, we also have the Fourier transform map
We shall now show that when
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is n-semiadditive,
${\mathscr {C}}$
is n-semiadditive,
![]() $({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{I_p^{(n)}{M}}$
coincides with the monoidal dual of
$({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{I_p^{(n)}{M}}$
coincides with the monoidal dual of
![]() $({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M}$
. In fact, we show more generally that even when
$({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M}$
. In fact, we show more generally that even when
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is not assumed to be n-semiadditive, the two maps are the transpose of one another in the following sense:
${\mathscr {C}}$
is not assumed to be n-semiadditive, the two maps are the transpose of one another in the following sense:
Definition 3.23. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
.
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
.
-
(1) For
 $X\in {\mathscr {C}}$
, we define the (weak) dual to be A map
$X\in {\mathscr {C}}$
, we define the (weak) dual to be A map
 $f\colon X \to Y^\vee $
can be identified with a map
$f\colon X \to Y^\vee $
can be identified with a map  .
.
-
(2) For a map
 $f\colon X\to Y^\vee $
in
$f\colon X\to Y^\vee $
in
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
, we define the transpose of f to be the map corresponding to f via the isomorphism
${\mathscr {C}}$
, we define the transpose of f to be the map corresponding to f via the isomorphism $$\begin{align*}f^t \colon Y \longrightarrow X^\vee \quad\in\quad {\mathscr{C}}, \end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}f^t \colon Y \longrightarrow X^\vee \quad\in\quad {\mathscr{C}}, \end{align*}$$

Unwinding the definitions,
![]() $f^t$
is given by the composition
$f^t$
is given by the composition
where the first map is the canonical map from an object to its double dual. In particular, if Y is dualizable, then the transpose
![]() $f^t$
coincides with the dual
$f^t$
coincides with the dual
![]() $f^\vee $
under the canonical identification
$f^\vee $
under the canonical identification ![]() . One can think of the transpose as a useful substitute for the dual when Y is nondualizable.
. One can think of the transpose as a useful substitute for the dual when Y is nondualizable.
Remark 3.24. In general, even if f is an isomorphism,
![]() $f^t$
might not be. For example, for V an infinite dimensional vector space over a field k, the transpose of the identity map
$f^t$
might not be. For example, for V an infinite dimensional vector space over a field k, the transpose of the identity map
![]() $V^\vee \to V^\vee $
is the nonisomorphic embedding
$V^\vee \to V^\vee $
is the nonisomorphic embedding
![]() $V\hookrightarrow (V^\vee )^\vee $
of V into its double dual. This deficiency, however, disappears if we assume that X and Y are dualizable.
$V\hookrightarrow (V^\vee )^\vee $
of V into its double dual. This deficiency, however, disappears if we assume that X and Y are dualizable.
Proposition 3.25. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. We have a natural isomorphism
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. We have a natural isomorphism
as natural transformations of functors
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
.
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
.
Proof. We have
By construction, via this identification, the map ![]() corresponds to the map of spaces
corresponds to the map of spaces
By the definition of the transpose, we deduce that
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega ^t$
corresponds to the map of spaces
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega ^t$
corresponds to the map of spaces
Via the isomorphism ![]() , this map identifies with the composition
, this map identifies with the composition
which is the map corresponding to the morphism ![]() .
.
Corollary 3.26. In the situation of Proposition 3.25, if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is n-semiadditive and M is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is n-semiadditive and M is
![]() $[0,n]$
-finite, then
$[0,n]$
-finite, then
Proof. If
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is n-semiadditive, then the source and the target of both maps are dualizable [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Proposition 3.3.6], and hence, the maps
${\mathscr {C}}$
is n-semiadditive, then the source and the target of both maps are dualizable [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Proposition 3.3.6], and hence, the maps
![]() $({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M}$
and
$({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M}$
and
![]() $({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{I_p^{(n)}{M}}$
are dual to one another.
$({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{I_p^{(n)}{M}}$
are dual to one another.
3.3 Co-multiplicative properties
So far, for a presentably symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, we have constructed the Fourier transform
${\mathscr {C}}$
, we have constructed the Fourier transform
only as a map of commutative algebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. However, as in the classical case, under suitable finiteness and semiadditivity assumptions, both sides also admit natural co-multiplication and co-unit maps making them into Hopf algebras, and the Fourier transform preserves this structure.
${\mathscr {C}}$
. However, as in the classical case, under suitable finiteness and semiadditivity assumptions, both sides also admit natural co-multiplication and co-unit maps making them into Hopf algebras, and the Fourier transform preserves this structure.
Hopf algebras
We begin by recalling the definitions of coalgebras, bialgebras and Hopf algebras. First, given
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
, the
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
, the
![]() $\infty $
-category of cocommutative coalgebras in
$\infty $
-category of cocommutative coalgebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is given by
${\mathscr {C}}$
is given by
Definition 3.27. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
. We define the
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
. We define the
![]() $\infty $
-category of bialgebras in
$\infty $
-category of bialgebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
by
${\mathscr {C}}$
by
where
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
has the induced symmetric monoidal structure from
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
has the induced symmetric monoidal structure from
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
.
${\mathscr {C}}$
.
Since the induced monoidal structure on
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is coCartesian, we have, equivalently,
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is coCartesian, we have, equivalently,
Definition 3.28. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
. We define the
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
. We define the
![]() $\infty $
-category of Hopf algebras in
$\infty $
-category of Hopf algebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
to be the full subcategory
${\mathscr {C}}$
to be the full subcategory
of
![]() $\operatorname{{biCAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
$\operatorname{{biCAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
Remark 3.29. By the Yoneda lemma, Definition 3.28 is equivalent to [Reference LurieLur17, Definition 3.9.7] in terms of the functor
![]() $\operatorname{{Spec}}^{\mathscr {C}}$
. One can think of
$\operatorname{{Spec}}^{\mathscr {C}}$
. One can think of
![]() $\operatorname{{Hopf}}({\mathscr {C}})$
as opposite to the category of commutative group objects in the
$\operatorname{{Hopf}}({\mathscr {C}})$
as opposite to the category of commutative group objects in the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^{\textrm {op}}$
of ‘affine
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^{\textrm {op}}$
of ‘affine
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-schemes’.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-schemes’.
We now have the following consequence of [Reference Gepner, Groth and NikolausGGN16, Corollary 2.10]:
Proposition 3.30. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
. For every additive
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
. For every additive
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\mathscr {E}$
, composition with the forgetful functor
$\mathscr {E}$
, composition with the forgetful functor
![]() $\operatorname{{Hopf}}({\mathscr {C}}) \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
induces an equivalence
$\operatorname{{Hopf}}({\mathscr {C}}) \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
induces an equivalence
where
![]() $\operatorname{{Fun}}^\sqcup $
denotes the
$\operatorname{{Fun}}^\sqcup $
denotes the
![]() $\infty $
-category of coproduct-preserving functors.
$\infty $
-category of coproduct-preserving functors.
Proof. This follows by applying the opposite of [Reference Gepner, Groth and NikolausGGN16, Corollary 2.10] to the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
Corollary 3.31. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For every
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For every
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the Fourier transform
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the Fourier transform
lifts uniquely to a natural transformation of functors
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}} \rightarrow \operatorname {Hopf}({\mathscr {C}})$
, along the forgetful functor
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}} \rightarrow \operatorname {Hopf}({\mathscr {C}})$
, along the forgetful functor
![]() $\operatorname{{Hopf}}({\mathscr {C}}) \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
$\operatorname{{Hopf}}({\mathscr {C}}) \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
Proof. The
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is additive. The functor
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is additive. The functor ![]() is coproduct-preserving as a (restriction of a) left adjoint, and the functor
is coproduct-preserving as a (restriction of a) left adjoint, and the functor ![]() is coproduct-preserving by the n-semiadditivity assumption on
is coproduct-preserving by the n-semiadditivity assumption on
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
and Proposition 2.37. Thus, the claim follows from Proposition 3.30.
${\mathscr {C}}$
and Proposition 2.37. Thus, the claim follows from Proposition 3.30.
Remark 3.32. The co-multiplication of ![]() comes from the diagonal of M, while the multiplication uses the addition of M. In contrast, the multiplication of
comes from the diagonal of M, while the multiplication uses the addition of M. In contrast, the multiplication of ![]() uses only the diagonal map of
uses only the diagonal map of
![]() $\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
, while the co-multiplication uses the addition.
$\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
, while the co-multiplication uses the addition.
Translation equivariance
One of the main features of the classical Fourier transform is that it intertwines the translation operations on the function space
![]() $\mathbb {C}^{M^*}$
with multiplication by characters on
$\mathbb {C}^{M^*}$
with multiplication by characters on
![]() $\mathbb {C}[M]$
. In other words, the Fourier transform simultaneously diagonalizes the shift operators. We now derive a similar result for the higher Fourier transform.
$\mathbb {C}[M]$
. In other words, the Fourier transform simultaneously diagonalizes the shift operators. We now derive a similar result for the higher Fourier transform.
Definition 3.33. Given
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
and
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
and
![]() $H \in \operatorname{{Hopf}}({\mathscr {C}})$
with an augmentation
$H \in \operatorname{{Hopf}}({\mathscr {C}})$
with an augmentation ![]() as a commutative algebra, we define the translation automorphism of H (as a commutative algebra) by the composition
as a commutative algebra, we define the translation automorphism of H (as a commutative algebra) by the composition
This construction naturally assembles into a functor
where
![]() $\operatorname{{Hopf}}^\star ({\mathscr {C}})$
is the category of pairs
$\operatorname{{Hopf}}^\star ({\mathscr {C}})$
is the category of pairs
![]() $(H,\varepsilon )$
, formally given as a pullback
$(H,\varepsilon )$
, formally given as a pullback
Remark 3.34. In algebro-geometric terms, ![]() corresponds to a global element of the group scheme
corresponds to a global element of the group scheme
![]() $\operatorname{{Spec}}(H)$
, and
$\operatorname{{Spec}}(H)$
, and
![]() $T_\varepsilon $
is the translation map by that element from
$T_\varepsilon $
is the translation map by that element from
![]() $\operatorname{{Spec}}(H)$
to itself.
$\operatorname{{Spec}}(H)$
to itself.
Using the compatibility of the Fourier transform with augmentations (Proposition 3.15) and Hopf algebra structures (Corollary 3.31), we deduce that it intertwines the corresponding translation automorphisms.
Proposition 3.35. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For every
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For every
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the associated Fourier transform
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the associated Fourier transform
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
promotes uniquely to a functor
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
promotes uniquely to a functor
whose component at
![]() $\varphi \colon M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
is given by
$\varphi \colon M \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
is given by

Proof. We have a commutative diagram of functors

where the top one is provided by Proposition 3.15, the bottom one is provided by Corollary 3.31, and the other two are the canonical forgetful functors (and both compositions are the Fourier transform map). This corresponds to a functor from the top left corner into the pullback of the remaining diagram. Since raising to the power of
![]() $[1]$
preserves pullbacks, this is a functor
$[1]$
preserves pullbacks, this is a functor
Composing this functor with
![]() $(T_{(-)})^{[1]}$
yields a functor
$(T_{(-)})^{[1]}$
yields a functor
Unwinding the definitions, the component at
![]() $\varphi \colon M\rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
is as claimed.
$\varphi \colon M\rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
is as claimed.
4 Orientations and orientability
The construction of the Fourier transform in the previous section depends on a choice of a pre-orientation, which plays the role of a root of unity in classical Fourier theory. Usually, one chooses the root of unity to be primitive, so that the Fourier transform is an isomorphism. In this section, we consider an analogous property of a pre-orientation and its relation to affineness and the Eilenberg–Moore property.
4.1 Orientations
Definition and functoriality
A pre-orientation for which the associated Fourier transform is an isomorphism on all
![]() $\pi $
-finite modules will be called an orientation. More precisely, we have the following:
$\pi $
-finite modules will be called an orientation. More precisely, we have the following:
Definition 4.1. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
be a pre-orientation.
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
be a pre-orientation.
-
(1)
 $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is called
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is called
 $\omega $
-oriented if
$\omega $
-oriented if  is an isomorphism.
is an isomorphism. -
(2)
 $\omega $
is called an orientation if every
$\omega $
is called an orientation if every
 $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
 $\omega $
-oriented.
$\omega $
-oriented.
We denote the subspace of
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations by
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations by
![]() $\textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})\subseteq {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
and say that
$\textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})\subseteq {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
and say that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable if
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable if
![]() $\textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})\ne \varnothing $
.
$\textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})\ne \varnothing $
.
The following is the motivating example from the classical theory:
Example 4.2. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
be the category of (ordinary) modules over a field
${\mathscr {C}}$
be the category of (ordinary) modules over a field
![]() $\mathbb {F}$
of characteristic
$\mathbb {F}$
of characteristic
![]() $0$
. Then,
$0$
. Then,
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-pre-orientations of height
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-pre-orientations of height
![]() $0$
of
$0$
of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
are just
${\mathscr {C}}$
are just
![]() $p^r$
-th roots of unity in
$p^r$
-th roots of unity in
![]() $\mathbb {F}$
(see Example 3.7). A root of unity defines an orientation of
$\mathbb {F}$
(see Example 3.7). A root of unity defines an orientation of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
exactly when it is primitive. We note that the situation with higher roots of unity is more subtle, as we shall discuss in Section 6.2.
${\mathscr {C}}$
exactly when it is primitive. We note that the situation with higher roots of unity is more subtle, as we shall discuss in Section 6.2.
Example 4.3. As in Remark 3.8, for
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
a
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-pre-orientation
$\mathbb {Z}$
-pre-orientation
![]() $\omega \colon \Sigma \mathbb {Q}/\mathbb {Z} \to R^\times $
of R, in the sense of Definition 3.6 is the same datum as a pre-orientation
$\omega \colon \Sigma \mathbb {Q}/\mathbb {Z} \to R^\times $
of R, in the sense of Definition 3.6 is the same datum as a pre-orientation
![]() $\widetilde {\omega }\colon \mathbb {Q}/\mathbb {Z} \to \mathbb {G}_m(R)$
for the divisible group
$\widetilde {\omega }\colon \mathbb {Q}/\mathbb {Z} \to \mathbb {G}_m(R)$
for the divisible group
![]() $\mathbb {G}_m$
over R, in the sense of [Reference LurieLur18b, Definition 2.6.8]. One may show that
$\mathbb {G}_m$
over R, in the sense of [Reference LurieLur18b, Definition 2.6.8]. One may show that
![]() $\omega $
is an orientation of R if and only if
$\omega $
is an orientation of R if and only if
![]() $\widetilde {\omega }$
is an orientation of
$\widetilde {\omega }$
is an orientation of
![]() $\mathbb {G}_m$
over R in the sense of [Reference LurieLur18a, Definition 4.3.9]
$\mathbb {G}_m$
over R in the sense of [Reference LurieLur18a, Definition 4.3.9]
We now examine how the space of orientations behaves under the various operations on pre-orientations considered in Section 3. First, orientations are preserved under restriction of scalars.
Proposition 4.4. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
in
$f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. A module
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. A module
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {S}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {S}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
![]() $f_*\omega $
-oriented if and only if
$f_*\omega $
-oriented if and only if
![]() $f_* M$
is
$f_* M$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented. Consequently, if
$\omega $
-oriented. Consequently, if
![]() $\omega $
is an
$\omega $
is an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation, then
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation, then
![]() $f_*\omega $
is an
$f_*\omega $
is an
![]() $\mathfrak {S}$
-orientation.
$\mathfrak {S}$
-orientation.
Proof. Given
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {S}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, by Proposition 3.16, the component of
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {S}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, by Proposition 3.16, the component of
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
at
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
at
![]() $f_*M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is homotopic to the component of
$f_*M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is homotopic to the component of
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{f_*\omega }$
at M. Thus, M is
${\mathfrak {F}}_{f_*\omega }$
at M. Thus, M is
![]() $f_*\omega $
-oriented if and only if
$f_*\omega $
-oriented if and only if
![]() $f_*M$
is
$f_*M$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented.
$\omega $
-oriented.
Orientations are also preserved under symmetric monoidal functors which preserve n-finite limits.
Proposition 4.5. Let
![]() $F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in
$F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. If
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. If
![]() $M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
$M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented and F preserves
$\omega $
-oriented and F preserves
![]() $\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
-shaped limits, then M is
$\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
-shaped limits, then M is
![]() $F(\omega )$
-oriented. In particular, if
$F(\omega )$
-oriented. In particular, if
![]() $\omega $
is an orientation on
$\omega $
is an orientation on
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
and F preserves n-finite limits, then
${\mathscr {C}}$
and F preserves n-finite limits, then
![]() $F(\omega )$
is an orientation on
$F(\omega )$
is an orientation on
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
.
${\mathscr {D}}$
.
Proof. The assumption that F preserves
![]() $\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
-shaped limits implies that the M-components of
$\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
-shaped limits implies that the M-components of
![]() $F({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )$
and
$F({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )$
and
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{F(\omega )}$
are isomorphic; see Remark 3.19. Thus, if M is
${\mathfrak {F}}_{F(\omega )}$
are isomorphic; see Remark 3.19. Thus, if M is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented, then it is also
$\omega $
-oriented, then it is also
![]() $F(\omega )$
-oriented. If F preserves all n-finite limits, then this is true for all
$F(\omega )$
-oriented. If F preserves all n-finite limits, then this is true for all
![]() $M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
.
$M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
.
When
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
and
${\mathscr {C}}$
and
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
are n-semiadditive, every colimit-preserving functor
${\mathscr {D}}$
are n-semiadditive, every colimit-preserving functor
![]() $F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
preserves n-finite limits. If we further assume that the
$F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
preserves n-finite limits. If we further assume that the
![]() $\infty $
-categories are stable, Proposition 4.5 admits a partial converse.
$\infty $
-categories are stable, Proposition 4.5 admits a partial converse.
Definition 4.6. Recall from [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Definition 4.4.1] that a functor
![]() $F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in
$F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}}_{\textrm {st}})$
is called nil-conservative if for every
$\operatorname{{Alg}}({\textrm {Pr}}_{\textrm {st}})$
is called nil-conservative if for every
![]() $S\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
for which
$S\in \operatorname{{Alg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
for which
![]() $F(S)=0$
, we have
$F(S)=0$
, we have
![]() $S=0$
.
$S=0$
.
Proposition 4.7. Let
![]() $F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in
$F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in ![]() be nil-conservative, and let
be nil-conservative, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. An
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. An
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is an orientation on
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is an orientation on
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
if and only if
${\mathscr {C}}$
if and only if
![]() $F(\omega )$
is an orientation on
$F(\omega )$
is an orientation on
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
.
${\mathscr {D}}$
.
Proof. Since F is n-semiadditive, it preserves n-finite limits, and hence,
![]() $F({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )$
is isomorphic to
$F({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )$
is isomorphic to
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{F(\omega )}$
; see Remark 3.19. We deduce that, for every
${\mathfrak {F}}_{F(\omega )}$
; see Remark 3.19. We deduce that, for every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the map
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the map
is an isomorphism. Since F is nil-conservative, it is conservative when restricted to the dualizable objects of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Proposition 4.4.4]. By [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Proposition 2.5], both
${\mathscr {C}}$
, see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Proposition 4.4.4]. By [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Proposition 2.5], both ![]() and
and ![]() are dualizable in
are dualizable in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, and we deduce that
${\mathscr {C}}$
, and we deduce that
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
is an isomorphism at every
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
is an isomorphism at every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
if and only
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
if and only
![]() $F({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )$
is.
$F({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )$
is.
Finally, we have the following behaviour with respect to scaling:
Proposition 4.8. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
![]() $\omega \in \textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. For
$\omega \in \textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. For
![]() $r\in \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
, the pre-orientation
$r\in \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
, the pre-orientation
![]() $\omega ^r$
is an orientation, if
$\omega ^r$
is an orientation, if
![]() $r \in \mathfrak {R}^\times $
. The converse holds if R is
$r \in \mathfrak {R}^\times $
. The converse holds if R is
![]() $\pi $
-finite and
$\pi $
-finite and
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is nonzero.
${\mathscr {C}}$
is nonzero.
Proof. By Proposition 3.22, for every
![]() $M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, we have a commutative diagram
$M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, we have a commutative diagram

Since
![]() $\omega $
is an orientation, the right diagonal map is an isomorphism. By 2-out-of-3 for isomorphisms,
$\omega $
is an orientation, the right diagonal map is an isomorphism. By 2-out-of-3 for isomorphisms,
![]() $\omega ^r$
is an orientation (i.e., the left diagonal map is an isomorphism if and only if
$\omega ^r$
is an orientation (i.e., the left diagonal map is an isomorphism if and only if ![]() is an isomorphism for all
is an isomorphism for all
![]() $M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
). Clearly, if r is invertible, then this is the case. Conversely, assuming R is
$M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
). Clearly, if r is invertible, then this is the case. Conversely, assuming R is
![]() $\pi $
-finite, we get that the map
$\pi $
-finite, we get that the map ![]() is an isomorphism. Applying
is an isomorphism. Applying ![]() , we get an isomorphism
, we get an isomorphism ![]() . Since
. Since
![]() $\pi _0(R)$
is a retract of
$\pi _0(R)$
is a retract of
![]() $\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
, we get an isomorphism
$\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
, we get an isomorphism ![]() to which we can apply
to which we can apply
![]() $\pi _0$
, which preserves products, and get an isomorphism
$\pi _0$
, which preserves products, and get an isomorphism ![]() . Since multiplication by r is not invertible on
. Since multiplication by r is not invertible on
![]() $\pi _0(R)$
, the last map can be an isomorphism only if
$\pi _0(R)$
, the last map can be an isomorphism only if ![]() , which would imply that
, which would imply that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is zero.
${\mathscr {C}}$
is zero.
Oriented modules
To study the question of whether a given
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation
![]() $\omega $
is in fact an orientation, it is useful to know that the collection of
$\omega $
is in fact an orientation, it is useful to know that the collection of
![]() $\omega $
-oriented
$\omega $
-oriented
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules is closed under a variety of operations. We shall assume higher semiadditivity throughout. We begin by showing that orientability is preserved under shifted Brown–Comenetz duality.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules is closed under a variety of operations. We shall assume higher semiadditivity throughout. We begin by showing that orientability is preserved under shifted Brown–Comenetz duality.
Proposition 4.9. Let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, let ![]() and let
and let
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. An
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. An
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented if and only if
$\omega $
-oriented if and only if
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{M} \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
$I_p^{(n)}{M} \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented.
$\omega $
-oriented.
Proof. By Corollary 3.26, the maps
![]() $({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M}$
and
$({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M}$
and
![]() $({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{I_p^{(n)}{M}}$
are dual to one another. Hence one is an isomorphism if and only if the other is.
$({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{I_p^{(n)}{M}}$
are dual to one another. Hence one is an isomorphism if and only if the other is.
Oriented modules are also closed under finite direct sums.
Proposition 4.10. Let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, let ![]() and let
and let
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. For every
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. For every
![]() $\omega $
-oriented
$\omega $
-oriented
![]() $M,N \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the module
$M,N \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the module
![]() $M\oplus N$
is also
$M\oplus N$
is also
![]() $\omega $
-oriented.
$\omega $
-oriented.
Proof. The Fourier transform ![]() is a natural transformation between two functors, which both preserve finite coproducts – indeed,
is a natural transformation between two functors, which both preserve finite coproducts – indeed, ![]() by being a (restriction of a) left adjoint, and
by being a (restriction of a) left adjoint, and ![]() by the n-semiadditivity assumption on
by the n-semiadditivity assumption on
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
and Proposition 2.37.
${\mathscr {C}}$
and Proposition 2.37.
Next, we consider the behavior of orientability under cofibers and extensions of
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules.
Proposition 4.11. Let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, let ![]() and let
and let
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. Consider an exact sequence in
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. Consider an exact sequence in
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
of the form
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
of the form
such that
![]() $M_0$
is
$M_0$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented and
$\omega $
-oriented and
![]() $\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M_0}}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M_0}}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Then,
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Then,
![]() $M_1$
is
$M_1$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented if and only if
$\omega $
-oriented if and only if
![]() $M_2$
is
$M_2$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented.
$\omega $
-oriented.
Proof. Consider the following commutative diagram in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, where the diagonal arrows represent the components of the Fourier transform
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, where the diagonal arrows represent the components of the Fourier transform
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
for the objects
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
for the objects
![]() $0, M_0, M_1$
and
$0, M_0, M_1$
and
![]() $M_2$
:
$M_2$
:

The two solid diagonal maps are isomorphisms by assumption, and we have to show that if either of the dashed diagonal maps is an isomorphism, then so is the other. Since the functor ![]() is a left adjoint, the back face of the diagram is a pushout. Since we assumed that
is a left adjoint, the back face of the diagram is a pushout. Since we assumed that
![]() $\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M_0}}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M_0}}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, the front face is also a pushout (Theorem 2.38). Thus, if the top dashed diagonal
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, the front face is also a pushout (Theorem 2.38). Thus, if the top dashed diagonal
![]() $({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M_1}$
is an isomorphism, then so is the bottom one
$({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M_1}$
is an isomorphism, then so is the bottom one
![]() $({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M_2}$
.
$({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M_2}$
.
Now, assume that the bottom dashed diagonal is an isomorphism. We can view the diagram as living in commutative algebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
under
${\mathscr {C}}$
under ![]() or, equivalently, as commutative algebras in
or, equivalently, as commutative algebras in ![]() . By the definition of affineness, we have an equivalence of categories
. By the definition of affineness, we have an equivalence of categories
The collection of functors
![]() $\varphi ^*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^{\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M_0}}\rfloor }\rightarrow {\mathscr {C}}$
for all
$\varphi ^*\colon {\mathscr {C}}^{\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M_0}}\rfloor }\rightarrow {\mathscr {C}}$
for all
![]() $\varphi \in \lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M_0}}\rfloor $
is jointly conservative. By Corollary 2.17, these functors correspond under the above equivalence to the extension of scalars functors
$\varphi \in \lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M_0}}\rfloor $
is jointly conservative. By Corollary 2.17, these functors correspond under the above equivalence to the extension of scalars functors
where ![]() is the unit
is the unit ![]() with the
with the ![]() -algebra structure given by
-algebra structure given by ![]() For example, in the above cubical diagram, the left vertical map in the front face is
For example, in the above cubical diagram, the left vertical map in the front face is ![]() . Thus, the fact that the back and the front faces are pushouts implies that
. Thus, the fact that the back and the front faces are pushouts implies that
which is, by assumption, an isomorphism. To show that
![]() $F_\varphi (({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M_1})$
is an isomorphism for all
$F_\varphi (({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M_1})$
is an isomorphism for all
![]() $\varphi \in \lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M_0}}\rfloor $
, we shall use the translation invariance of the Fourier transform and the case
$\varphi \in \lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M_0}}\rfloor $
, we shall use the translation invariance of the Fourier transform and the case
![]() $\varphi =0$
. By the long exact sequence of homotopy groups associated with the cofiber sequence
$\varphi =0$
. By the long exact sequence of homotopy groups associated with the cofiber sequence
the map
![]() $\pi _n M_0 \to \pi _n M_1$
is injective, which implies that the map
$\pi _n M_0 \to \pi _n M_1$
is injective, which implies that the map
![]() $\pi _0(I_p^{(n)}{M_1}) \rightarrow \pi _0 (I_p^{(n)}{M_0})$
is surjective. Hence, we can lift
$\pi _0(I_p^{(n)}{M_1}) \rightarrow \pi _0 (I_p^{(n)}{M_0})$
is surjective. Hence, we can lift
![]() $\varphi $
to an element
$\varphi $
to an element
![]() $\overline {\varphi } \in \lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M_1}}\rfloor $
. By Proposition 3.35, we get a commutative diagram
$\overline {\varphi } \in \lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M_1}}\rfloor $
. By Proposition 3.35, we get a commutative diagram

where the vertical maps are the respective translation automorphisms. Pasting this diagram on top of
![]() $(*)$
yields a cubical diagram analogous to
$(*)$
yields a cubical diagram analogous to
![]() $(*)$
, where the left vertical map of the front face is
$(*)$
, where the left vertical map of the front face is ![]() As before, we get that
As before, we get that
![]() $F_\varphi (({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M_1})$
identifies with
$F_\varphi (({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M_1})$
identifies with
![]() $({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M_2}$
and hence is an isomorphism. Thus,
$({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M_2}$
and hence is an isomorphism. Thus,
![]() $({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M_1}$
is itself an isomorphism.
$({\mathfrak {F}}_\omega )_{M_1}$
is itself an isomorphism.
Similarly, we have a dual statement for fibers.
Proposition 4.12. Let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, let ![]() and let
and let
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. Consider an exact sequence in
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. Consider an exact sequence in
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
of the form
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
of the form
such that
![]() $M_2$
is
$M_2$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented and
$\omega $
-oriented and
![]() $\lfloor {M_2}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {M_2}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Then,
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Then,
![]() $M_1$
is
$M_1$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented if and only if
$\omega $
-oriented if and only if
![]() $M_0$
is
$M_0$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented.
$\omega $
-oriented.
Proof. By Proposition 4.9, a module
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented if and only if
$\omega $
-oriented if and only if
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{M}$
is. Thus, the claim follows from Proposition 4.11 applied to the exact sequence
$I_p^{(n)}{M}$
is. Thus, the claim follows from Proposition 4.11 applied to the exact sequence
4.2
 $\mathfrak {R}$
-Cyclotomic extensions
$\mathfrak {R}$
-Cyclotomic extensions
We now construct for every
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and ![]() a universal
a universal
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-oriented commutative algebra (of height n) in
$\mathfrak {R}$
-oriented commutative algebra (of height n) in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, denoted by
${\mathscr {C}}$
, denoted by ![]() , which we call the
, which we call the
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension (of height n).
$\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension (of height n).
Universally oriented categories
We begin by working one categorical level up, which does not require any higher semiadditivity assumptions. The adjunction unit ![]() exhibits
exhibits ![]() as the universal R-pre-oriented (of height n) commutative algebra in
as the universal R-pre-oriented (of height n) commutative algebra in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. Our first goal is to establish a categorification of this fact.
${\mathscr {C}}$
. Our first goal is to establish a categorification of this fact.
Proposition 4.13. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. The functor
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. The functor
is co-representable by ![]() .
.
Proof. Using the adjunctions
and
we get
naturally in
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
, which finishes the proof.
${\mathscr {D}}\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
, which finishes the proof.
We shall thus use the following notation:
Definition 4.14. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. We define
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. We define
and denote by
the tautological
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation of
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation of
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
given by the unit of the adjunction
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
given by the unit of the adjunction ![]()
Remark 4.15. By Proposition 4.13,
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
co-represents
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
co-represents
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations of height n for
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations of height n for
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear presentably symmetric monoidal
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear presentably symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-categories. Explicitly, given
$\infty $
-categories. Explicitly, given
![]() $F\colon {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}} \rightarrow {\mathscr {D}}$
in
$F\colon {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}} \rightarrow {\mathscr {D}}$
in
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}(\Pr )$
, the associated
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}(\Pr )$
, the associated
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation of
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation of
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
is
${\mathscr {D}}$
is
![]() $F(\omega _{\textrm {taut}})$
.
$F(\omega _{\textrm {taut}})$
.
We now consider the co-representability of the subfunctor
![]() $\textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}(-)\subseteq {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}(-)$
.
$\textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}(-)\subseteq {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}(-)$
.
Definition 4.16. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. We define
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. We define
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}} \subseteq {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}} $
to be the full subcategory of objects
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}} \subseteq {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}} $
to be the full subcategory of objects
![]() $X\in {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
such that
$X\in {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
such that
is an isomorphism for all
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
.
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
.
Equivalently, by Proposition 3.25,
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
can be identified with the left localization of
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
can be identified with the left localization of
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
with respect to the collection of morphisms of the form
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
with respect to the collection of morphisms of the form
In particular, it is a
![]() $\otimes $
-localization of
$\otimes $
-localization of
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
and hence can be seen as an object of
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
and hence can be seen as an object of
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}({\textrm {Pr}}))$
, and it is equipped with a symmetric monoidal localization functor
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}({\textrm {Pr}}))$
, and it is equipped with a symmetric monoidal localization functor
![]() $L^{\textrm {or}}\colon {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}} \rightarrow {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
.
$L^{\textrm {or}}\colon {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}} \rightarrow {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
.
Proposition 4.17. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. The localization functor
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. The localization functor
co-represents the fully faithful embedding
![]() $\textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}(-)\subseteq {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}(-)$
.
$\textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}(-)\subseteq {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}(-)$
.
Proof. Since
![]() $L^{\textrm {or}}$
is a localization, pre-composition with it exhibits
$L^{\textrm {or}}$
is a localization, pre-composition with it exhibits
![]() $\operatorname {Map}_{\operatorname {CAlg}({\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathscr {C}}(\textrm {Pr}))}({{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}},-)$
as a subfunctor of
$\operatorname {Map}_{\operatorname {CAlg}({\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathscr {C}}(\textrm {Pr}))}({{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}},-)$
as a subfunctor of
Thus, it would suffice to show that a functor
![]() $F\colon {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}} \rightarrow {\mathscr {D}}$
in
$F\colon {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}} \rightarrow {\mathscr {D}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}({\textrm {Pr}}))$
factors through the localization functor
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}({\textrm {Pr}}))$
factors through the localization functor
![]() $L^{\textrm {or}}$
if and only if
$L^{\textrm {or}}$
if and only if
![]() $F(\omega _{\textrm {taut}})$
is an orientation of
$F(\omega _{\textrm {taut}})$
is an orientation of
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
.
${\mathscr {D}}$
.
By Proposition 3.18, we have
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{L^{\textrm {or}}(\omega _{\textrm {taut}})} \simeq L^{\textrm {or}}({\mathfrak {F}}_{\omega _{\textrm {taut}}})$
on
${\mathfrak {F}}_{L^{\textrm {or}}(\omega _{\textrm {taut}})} \simeq L^{\textrm {or}}({\mathfrak {F}}_{\omega _{\textrm {taut}}})$
on
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, which is an isomorphism by the definition of
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, which is an isomorphism by the definition of
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
. This implies that if F factors through
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
. This implies that if F factors through
![]() $L^{\textrm {or}}$
, then
$L^{\textrm {or}}$
, then
![]() $F(\omega _{\textrm {taut}})$
is an orientation.
$F(\omega _{\textrm {taut}})$
is an orientation.
Conversely, assuming that
![]() $F(\omega _{\textrm {taut}})$
is an orientation, we shall show that F factors through
$F(\omega _{\textrm {taut}})$
is an orientation, we shall show that F factors through
![]() $L^{\textrm {or}}$
. For this, it suffices to show that the essential image of the right adjoint
$L^{\textrm {or}}$
. For this, it suffices to show that the essential image of the right adjoint
![]() $G\colon {\mathscr {D}} \rightarrow {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
of F lies in
$G\colon {\mathscr {D}} \rightarrow {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
of F lies in
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}\subseteq {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
. By the definition of
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}\subseteq {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
. By the definition of
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
, this is if and only if, for every
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
, this is if and only if, for every
![]() $X\in {\mathscr {D}}$
and every
$X\in {\mathscr {D}}$
and every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the morphism
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the morphism
is an isomorphism. Since F is symmetric monoidal, we have a natural isomorphism
for all
![]() $Y\in {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
, so it would suffice to show that
$Y\in {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
, so it would suffice to show that
is an isomorphism for every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
. But this follows from our assumption that
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
. But this follows from our assumption that
![]() $F({\omega _{\textrm {taut}}})$
is an orientation.
$F({\omega _{\textrm {taut}}})$
is an orientation.
Universally oriented algebras
Proposition 4.17 shows that there is a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear symmetric monoidal
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
carrying a universal
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
carrying a universal
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n. We now show that if
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n. We now show that if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is n-semiadditive, then
${\mathscr {C}}$
is n-semiadditive, then
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
is in fact the
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
is in fact the
![]() $\infty $
-category of modules over a universally
$\infty $
-category of modules over a universally
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-oriented commutative algebra in
$\mathfrak {R}$
-oriented commutative algebra in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
.
${\mathscr {C}}$
.
Proposition 4.18. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. Then, there is an idempotent commutative
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. Then, there is an idempotent commutative ![]() -algebra
-algebra ![]() such that
such that
Proof. By [Reference Ragimov and SchlankRS22, Theorem 7.6], it suffices to show that
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
is closed under all limits, all colimits, tensoring with any object of
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
is closed under all limits, all colimits, tensoring with any object of
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
and taking internal
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
and taking internal
![]() $\hom $
from any object of
$\hom $
from any object of
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
. Now, the functor
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
. Now, the functor
![]() $(X,Y)\mapsto \hom (Y,X)$
is limit-preserving in the X-argument and satisfies
$(X,Y)\mapsto \hom (Y,X)$
is limit-preserving in the X-argument and satisfies
These imply that
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
is closed under limits and applying
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
is closed under limits and applying
![]() $\hom (Y,-)$
for
$\hom (Y,-)$
for
![]() $Y\in {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
. However, by the n-seimadditivity assumption on
$Y\in {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
. However, by the n-seimadditivity assumption on
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, for every
${\mathscr {C}}$
, for every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the objects
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the objects ![]() and
and ![]() are dualizable. Hence, we can identify the morphisms
are dualizable. Hence, we can identify the morphisms
of pre-composition with
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
, with the tensor product
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
, with the tensor product
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega ^\vee \otimes X$
. This implies that
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega ^\vee \otimes X$
. This implies that
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
is also closed under all colimits and tensoring with any object of
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {or}}$
is also closed under all colimits and tensoring with any object of
![]() ${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
.
${{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}^{\textrm {por}}$
.
Finally, since the functor
is fully faithful, it follows from Proposition 4.17 that indeed
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations of commutative algebras in
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations of commutative algebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
are co-represented by
${\mathscr {C}}$
are co-represented by ![]() .
.
From the above proposition follows that
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations of commutative algebras in
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations of commutative algebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
are co-represented by
${\mathscr {C}}$
are co-represented by ![]() . In other words,
. In other words, ![]() carries a universal
carries a universal
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n, which motivates the following:
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n, which motivates the following:
Definition 4.19. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. We refer to
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. We refer to ![]() as the
as the
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension of height n.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension of height n.
In general, the functoriality of the construction ![]() in
in ![]() is rather subtle. However, there is one relatively simple, yet useful, case.
is rather subtle. However, there is one relatively simple, yet useful, case.
Proposition 4.20. Let
![]() $F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in
$F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. If F admits a conservative right adjoint, then
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. If F admits a conservative right adjoint, then ![]() .
.
Proof. Let G be a right adjoint of F. Then, G is lax symmetric monoidal and hence maps commutative algebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
to commutative algebras in
${\mathscr {D}}$
to commutative algebras in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. Moreover, for
${\mathscr {C}}$
. Moreover, for
![]() $S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {D}})$
, we have a natural identification
$S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {D}})$
, we have a natural identification
![]() $G(S)^\times \simeq S^\times $
, and hence, we can identify pre-orientations of S with pre-orientations of
$G(S)^\times \simeq S^\times $
, and hence, we can identify pre-orientations of S with pre-orientations of
![]() $G(S)$
.
$G(S)$
.
The object ![]() co-represents
co-represents
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations of height n in
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations of height n in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {D}})$
, while
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {D}})$
, while ![]() co-represents the functors
co-represents the functors
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {D}})\to \mathcal{S}$
given by
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {D}})\to \mathcal{S}$
given by
![]() $S\mapsto \textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}};G(S)). $
Both these functors are sub-functors of
$S\mapsto \textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}};G(S)). $
Both these functors are sub-functors of
![]() ${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {D}};-)$
. Hence, to identify them, it would suffice to show that, for
${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {D}};-)$
. Hence, to identify them, it would suffice to show that, for
![]() $S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {D}})$
with pre-orientation
$S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {D}})$
with pre-orientation
![]() $\omega \colon I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}} \rightarrow S^\times \simeq G(S)^\times $
and every
$\omega \colon I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}} \rightarrow S^\times \simeq G(S)^\times $
and every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the morphism
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the morphism
is an isomorphism if and only if
is an isomorphism. The functor G is limit-preserving, and hence, it preserves also
![]() $\pi $
-finite colimits; see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.2.4]. Consequently, the map
$\pi $
-finite colimits; see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.2.4]. Consequently, the map
![]() $(**)$
is the image under G of the map
$(**)$
is the image under G of the map
![]() $(*)$
. Since G is assumed to be conservative, we deduce that
$(*)$
. Since G is assumed to be conservative, we deduce that
![]() $(**)$
is an isomorphism if and only if
$(**)$
is an isomorphism if and only if
![]() $(*)$
is an isomorphism, and the result follows.
$(*)$
is an isomorphism, and the result follows.
Corollary 4.21. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For every
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. For every
![]() $S \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we have
$S \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we have
Proof. Apply Proposition 4.20 to the extension of scalars functor
![]() $ S\otimes (-) \colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_S({\mathscr {C}}). $
$ S\otimes (-) \colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_S({\mathscr {C}}). $
Equivariance and Galois
Recall that ![]() admits an action of the multiplicative monoid
admits an action of the multiplicative monoid
![]() $\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
. This induces an action of
$\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
. This induces an action of
![]() $\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
on the functor
$\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
on the functor
![]() ${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}(-;{\mathscr {C}})$
it co-represents. This action is given by scaling, and hence, by Proposition 4.8, the action of the submonoid
${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}(-;{\mathscr {C}})$
it co-represents. This action is given by scaling, and hence, by Proposition 4.8, the action of the submonoid
![]() $\mathfrak {R}^\times \subseteq \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
preserves the subspace
$\mathfrak {R}^\times \subseteq \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
preserves the subspace
We thus obtain an action of
![]() $\mathfrak {R}^\times $
on the co-representing object
$\mathfrak {R}^\times $
on the co-representing object ![]() and an
and an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}^\times $
-equivariant map
$\mathfrak {R}^\times $
-equivariant map
Proposition 4.22. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
be n-finite. If the
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
be n-finite. If the
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension
$\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension ![]() is faithful, then it is
is faithful, then it is
![]() $\mathfrak {R}^\times $
-Galois.
$\mathfrak {R}^\times $
-Galois.
Proof. By our assumptions, both
![]() $B\mathfrak {R}^\times $
and
$B\mathfrak {R}^\times $
and
![]() $\mathfrak {R}^\times $
are
$\mathfrak {R}^\times $
are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous spaces. Thus, the tensor product of
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous spaces. Thus, the tensor product of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
preserves the respective limits in conditions (G1) and (G2) of a Galois extension (Definition 2.25). Hence, since
${\mathscr {C}}$
preserves the respective limits in conditions (G1) and (G2) of a Galois extension (Definition 2.25). Hence, since ![]() is faithful, it suffices to show that it is Galois after base-change along itself – namely, after applying the functor
is faithful, it suffices to show that it is Galois after base-change along itself – namely, after applying the functor
In other words, we may assume without loss of generality that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. We shall show that in this case,
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. We shall show that in this case, ![]() is in fact split Galois. The Fourier transform, associated with any
is in fact split Galois. The Fourier transform, associated with any
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation
![]() $\omega $
of height n, provides an isomorphism
$\omega $
of height n, provides an isomorphism
which is equivariant with respect to the multiplicative monoid
![]() $\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
and hence, in particular, with respect to
$\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
and hence, in particular, with respect to
![]() $\mathfrak {R}^\times $
. Consider the composition
$\mathfrak {R}^\times $
. Consider the composition
where the second map is given by restriction along the inclusion
![]() $\mathfrak {R}^\times \hookrightarrow \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
. Since
$\mathfrak {R}^\times \hookrightarrow \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor $
. Since ![]() is co-induced as an
is co-induced as an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}^\times $
-object, this map corresponds to a nonequivariant map
$\mathfrak {R}^\times $
-object, this map corresponds to a nonequivariant map ![]() given by evaluation at
given by evaluation at
![]() $1 \in \mathfrak {R}^\times $
. By unwinding the definitions, this is exactly the orientation
$1 \in \mathfrak {R}^\times $
. By unwinding the definitions, this is exactly the orientation
![]() $\omega $
and hence factors through
$\omega $
and hence factors through ![]() . Consequently, we get the following commutative square in
. Consequently, we get the following commutative square in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^{B\mathfrak {R}^\times }$
:
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^{B\mathfrak {R}^\times }$
:

Since the top map is an isomorphism, it would suffice to show that
![]() $(*)$
is a pushout square, as this would imply that the bottom map is an isomorphism as well. Furthermore, as the forgetful functor
$(*)$
is a pushout square, as this would imply that the bottom map is an isomorphism as well. Furthermore, as the forgetful functor
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^{B\mathfrak {R}^\times } \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is colimit-preserving and conservative, it suffices to check that
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})^{B\mathfrak {R}^\times } \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is colimit-preserving and conservative, it suffices to check that
![]() $(*)$
is a pushout square nonequivariantly. Namely, we need to show that for every
$(*)$
is a pushout square nonequivariantly. Namely, we need to show that for every ![]() in
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the composition
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the composition
is an orientation on S if and only if f factors through the projection ![]() . The ‘if’ part is clear from the existence of the commutative square
. The ‘if’ part is clear from the existence of the commutative square
![]() $(*)$
. For the ‘only if’ part, it suffices to show that if
$(*)$
. For the ‘only if’ part, it suffices to show that if
![]() $\omega _f$
is an orientation, then the pushout
$\omega _f$
is an orientation, then the pushout ![]() vanishes. Since the space
vanishes. Since the space
![]() $\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor \smallsetminus \mathfrak {R}^\times $
is
$\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor \smallsetminus \mathfrak {R}^\times $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous, it is
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous, it is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affine (Corollary 2.34), so by Proposition 2.4, we have a fully faithful embedding
${\mathscr {C}}$
-semi-affine (Corollary 2.34), so by Proposition 2.4, we have a fully faithful embedding
Furthermore, by Corollary 2.17, the jointly conservative functors
![]() $r^* \colon {\mathscr {C}}^{\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor \smallsetminus \mathfrak {R}^\times } \to {\mathscr {C}}$
correspond to the functors
$r^* \colon {\mathscr {C}}^{\lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor \smallsetminus \mathfrak {R}^\times } \to {\mathscr {C}}$
correspond to the functors ![]() . Therefore, by the associativity of the relative tensor product, it suffices to show that
. Therefore, by the associativity of the relative tensor product, it suffices to show that ![]() vanishes for every
vanishes for every
![]() $r\in \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor \smallsetminus \mathfrak {R}^\times $
. Now, consider the diagram, where the right square a pushout square and the left square commutes by Proposition 3.22 and Proposition 3.15:
$r\in \lfloor {\mathfrak {R}}\rfloor \smallsetminus \mathfrak {R}^\times $
. Now, consider the diagram, where the right square a pushout square and the left square commutes by Proposition 3.22 and Proposition 3.15:

Comparing the composition along the top and then right maps with the composition along the left and the bottom maps provides an isomorphism
Since we assumed that
![]() $\omega _f$
is an orientation, it follows by Proposition 4.4 that the left-hand side is an orientation. However, since R is
$\omega _f$
is an orientation, it follows by Proposition 4.4 that the left-hand side is an orientation. However, since R is
![]() $\pi $
-finite and r is assumed to be noninvertible, it follows by Proposition 4.8 that the right-hand side is not an orientation unless
$\pi $
-finite and r is assumed to be noninvertible, it follows by Proposition 4.8 that the right-hand side is not an orientation unless
![]() $S_r=0$
.
$S_r=0$
.
4.3 Virtual orientability and affineness
In Proposition 2.40, we have seen that having semiadditive height n for an
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
implies the affineness of
${\mathscr {C}}$
implies the affineness of
![]() $(n+1)$
-connected
$(n+1)$
-connected
![]() $\pi $
-finite spaces with respect to
$\pi $
-finite spaces with respect to
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. We shall now show that the existence of an
${\mathscr {C}}$
. We shall now show that the existence of an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n implies the affineness of all n-truncated
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n implies the affineness of all n-truncated
![]() $\pi $
-finite spaces which admit an
$\pi $
-finite spaces which admit an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module structure. In fact, many
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module structure. In fact, many
![]() $\infty $
-categories of interest
$\infty $
-categories of interest
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
are not themselves
${\mathscr {C}}$
are not themselves
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable, yet they possess an
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable, yet they possess an
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable commutative algebra S, which is faithful in the sense that the functor
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable commutative algebra S, which is faithful in the sense that the functor
![]() $S\otimes - \colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
is conservative. This allows one to use the Fourier transform over
$S\otimes - \colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}$
is conservative. This allows one to use the Fourier transform over
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{S}({\mathscr {C}})$
together with ‘faithful descent’ along the morphism
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{S}({\mathscr {C}})$
together with ‘faithful descent’ along the morphism ![]() to derive structural properties, such as affineness, for
to derive structural properties, such as affineness, for
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
.
${\mathscr {C}}$
.
Virtual orientability
The above discussion leads to the following definition:
Definition 4.23. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. We say that the
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. We say that the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable if there exists a faithful commutative algebra S in
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable if there exists a faithful commutative algebra S in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, which admits an
${\mathscr {C}}$
, which admits an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n.
In the higher semiadditive setting, we have the universal commutative algebra ![]() in
in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
that carries an
${\mathscr {C}}$
that carries an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation. In this case, its faithfulness is equivalent to virtual orientability of
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation. In this case, its faithfulness is equivalent to virtual orientability of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
.
${\mathscr {C}}$
.
Proposition 4.24. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. Then,
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. Then,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable if and only if
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable if and only if ![]() is faithful.
is faithful.
Proof. Since ![]() admits an
admits an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n, if it is faithful, then
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n, if it is faithful, then
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. Conversely, assume that
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. Conversely, assume that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable, and let
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable, and let
![]() $S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
be a faithful algebra which admits an
$S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
be a faithful algebra which admits an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n. The extension of scalars functor
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n. The extension of scalars functor
![]() $S\otimes -\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_S({\mathscr {C}})$
admits a conservative right adjoint, which, by Proposition 4.20, implies that
$S\otimes -\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_S({\mathscr {C}})$
admits a conservative right adjoint, which, by Proposition 4.20, implies that ![]() . Now, S admits an
. Now, S admits an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation, which in turn provides an augmentation
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation, which in turn provides an augmentation
Since S is faithful, we deduce that ![]() is faithful and hence that
is faithful and hence that ![]() is faithful.
is faithful.
Example 4.25. The field of rational numbers
![]() $\mathbb {Q}$
does not admit a
$\mathbb {Q}$
does not admit a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-orientation of height 0 (i.e., a primitive
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-orientation of height 0 (i.e., a primitive
![]() $p^r$
-th root of unity) unless
$p^r$
-th root of unity) unless
![]() $p=2$
and
$p=2$
and
![]() $r=1$
. However, it is still virtually
$r=1$
. However, it is still virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}/p^r ,0)$
-orientable, as we can pass to the cyclotomic extension
$(\mathbb {Z}/p^r ,0)$
-orientable, as we can pass to the cyclotomic extension
![]() $\mathbb {Q}(\omega _{p^r})$
, which is clearly faithful over
$\mathbb {Q}(\omega _{p^r})$
, which is clearly faithful over
![]() $\mathbb {Q}$
.
$\mathbb {Q}$
.
By localizing with respect to ![]() , we obtain the universal virtually
, we obtain the universal virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable localization of
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable localization of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
.
${\mathscr {C}}$
.
Definition 4.26. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. We define
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. We define
![]() $\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
to be the Bousfield localization of
$\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
to be the Bousfield localization of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
with respect to
${\mathscr {C}}$
with respect to ![]() .
.
Namely,
![]() $\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
is obtained from
$\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
is obtained from
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
by inverting all the morphisms
${\mathscr {C}}$
by inverting all the morphisms
![]() $X\to Y$
in
$X\to Y$
in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
for which the induced morphism
${\mathscr {C}}$
for which the induced morphism ![]() is an isomorphism. The
is an isomorphism. The
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
classifies the property of being virtually
$\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
classifies the property of being virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable among localizations of
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable among localizations of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
.
${\mathscr {C}}$
.
Proposition 4.27. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. The
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. The
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
is the initial symmetric monoidal localization of
$\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
is the initial symmetric monoidal localization of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
in
${\mathscr {C}}$
in ![]() which is virtually
which is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable.
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable.
Proof. First, since
![]() $\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
is a Bousfield localization of
$\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
is a Bousfield localization of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, it is a symmetric monoidal localization of
${\mathscr {C}}$
, it is a symmetric monoidal localization of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. Let
${\mathscr {C}}$
. Let
![]() $L\colon {\mathscr {C}} \rightarrow \widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
be the localization functor. By Proposition 4.20, and since L admits a fully faithful (and in particular conservative) right adjoint, we have
$L\colon {\mathscr {C}} \rightarrow \widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
be the localization functor. By Proposition 4.20, and since L admits a fully faithful (and in particular conservative) right adjoint, we have ![]() . Since, by construction,
. Since, by construction, ![]() is faithful in
is faithful in
![]() $\operatorname {CAlg}(\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n})$
, we deduce from Proposition 4.24 that
$\operatorname {CAlg}(\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n})$
, we deduce from Proposition 4.24 that
![]() $\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
is virtually
$\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. It remains to show that
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. It remains to show that
![]() $\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
is initial with respect to being virtually
$\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
is initial with respect to being virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. Let
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. Let
![]() $L_1\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
be any symmetric monoidal localization in
$L_1\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
be any symmetric monoidal localization in ![]() for which
for which
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {D}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. By Proposition 4.20 again, we have that
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. By Proposition 4.20 again, we have that ![]() , which is faithful by our assumption on
, which is faithful by our assumption on
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
. This implies that
${\mathscr {D}}$
. This implies that
![]() $L_1$
factors through the Bousfield localization with respect to
$L_1$
factors through the Bousfield localization with respect to ![]() – that is, through
– that is, through
![]() $L\colon {\mathscr {C}} \rightarrow \widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
.
$L\colon {\mathscr {C}} \rightarrow \widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathfrak {R},n}$
.
Affineness of modules
The existence of an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation for an
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation for an
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
allows one to relate group algebras and algebras of functions on
${\mathscr {C}}$
allows one to relate group algebras and algebras of functions on
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules. Since the functor
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules. Since the functor ![]() preserves pushouts, we can use the Fourier transform to deduce Eilenberg–Moore type properties for
preserves pushouts, we can use the Fourier transform to deduce Eilenberg–Moore type properties for
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. In fact, virtual orientability suffices.
${\mathscr {C}}$
. In fact, virtual orientability suffices.
Proposition 4.28. Let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, and let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, and let ![]() be virtually
be virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. For every exact square
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. For every exact square
![]() $(*)$
in
$(*)$
in
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the associated square
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the associated square
![]() $(**)$
is a pushout in
$(**)$
is a pushout in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.

Remark 4.29. The square
![]() $(*)$
is exact (see the conventions) in
$(*)$
is exact (see the conventions) in
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
if and only if it is a pushout square in
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
if and only if it is a pushout square in
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}(\textrm {Sp})$
.
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}(\textrm {Sp})$
.
Proof. Let
![]() $S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
be a faithful algebra which admits an
$S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
be a faithful algebra which admits an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n. Since the tensor product in
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n. Since the tensor product in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
preserves n-finite limits in each coordinate, tensoring the square
${\mathscr {C}}$
preserves n-finite limits in each coordinate, tensoring the square
![]() $(**)$
with S gives the analogous square in
$(**)$
with S gives the analogous square in
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_S({\mathscr {C}})$
. Since S is faithful, we may replace
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_S({\mathscr {C}})$
. Since S is faithful, we may replace
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
by
${\mathscr {C}}$
by
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_S({\mathscr {C}})$
and assume without loss of generality that
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_S({\mathscr {C}})$
and assume without loss of generality that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
admits an
${\mathscr {C}}$
admits an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation ![]() .
.
The exact square
![]() $(*)$
in
$(*)$
in
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
induces another exact square in
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
induces another exact square in
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
:
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
:

which is also exact in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
. The functor
$\textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
. The functor
preserves colimits so that the square

is a pushout square in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. Now, the (inverse of the) Fourier transform
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. Now, the (inverse of the) Fourier transform ![]() identifies the pushout square
identifies the pushout square
![]() $(***)$
with the square
$(***)$
with the square
![]() $(**)$
in the claim, which is therefore a pushout square as well.
$(**)$
in the claim, which is therefore a pushout square as well.
This implies the following affineness result:
Proposition 4.30. Let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, and let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, and let ![]() be virtually
be virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. For every
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. For every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the space
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the space
![]() $\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
Proof. First, we have a map
![]() $\lfloor {M}\rfloor \to \pi _0 \lfloor {M}\rfloor $
whose fibers are all isomorphic to
$\lfloor {M}\rfloor \to \pi _0 \lfloor {M}\rfloor $
whose fibers are all isomorphic to
![]() $\lfloor {\tau _{\ge 1} M}\rfloor $
. Thus, by Proposition 2.18((2) and (3)), it suffices to prove that
$\lfloor {\tau _{\ge 1} M}\rfloor $
. Thus, by Proposition 2.18((2) and (3)), it suffices to prove that
![]() $\lfloor {\pi _0 M}\rfloor $
and
$\lfloor {\pi _0 M}\rfloor $
and
![]() $\lfloor {\tau _{\ge 1}M}\rfloor $
are
$\lfloor {\tau _{\ge 1}M}\rfloor $
are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Since
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Since
![]() $\lfloor {\pi _0 M}\rfloor $
is finite, it is
$\lfloor {\pi _0 M}\rfloor $
is finite, it is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine by Example 2.35. Hence, we are reduced to the case that M is connected. For connected M, all the path spaces
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine by Example 2.35. Hence, we are reduced to the case that M is connected. For connected M, all the path spaces
![]() $P_{a,b}\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
for
$P_{a,b}\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
for
![]() $a,b\in \lfloor {M}\rfloor $
are isomorphic to
$a,b\in \lfloor {M}\rfloor $
are isomorphic to
![]() $\lfloor {\Omega M}\rfloor \simeq \Omega \lfloor {M}\rfloor $
. By Theorem 2.38, to show that
$\lfloor {\Omega M}\rfloor \simeq \Omega \lfloor {M}\rfloor $
. By Theorem 2.38, to show that
![]() $\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, it suffices to show that the square
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, it suffices to show that the square

is a pushout square in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. This, in turn, follows from Proposition 4.28.
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. This, in turn, follows from Proposition 4.28.
Remark 4.31. The conclusion of Proposition 4.30 is far from being the best possible. Since
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine spaces are closed under extensions (Proposition 2.18), to deduce that an n-finite space A is
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine spaces are closed under extensions (Proposition 2.18), to deduce that an n-finite space A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, it suffices to be able to build A from
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, it suffices to be able to build A from
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules by iterated extensions. We exploit this fact in Theorem 6.2 to show that already virtual
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules by iterated extensions. We exploit this fact in Theorem 6.2 to show that already virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability implies the
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability implies the
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affineness of all n-finite p-spaces.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affineness of all n-finite p-spaces.
Higher Kummer theory
When one actually has an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n, we obtain a variant of Kummer theory, providing a classification of certain abelian Galois extensions of a ring in terms of its units.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n, we obtain a variant of Kummer theory, providing a classification of certain abelian Galois extensions of a ring in terms of its units.
Proposition 4.32. Let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, and let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, and let ![]() be
be
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. For every
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable. For every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
and
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
and
![]() $S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we have an isomorphism of spaces
$S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, we have an isomorphism of spaces
Proof. By Proposition 4.30, the space
![]() $\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Hence, by Proposition 2.30, we have
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Hence, by Proposition 2.30, we have
Since
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable, the Fourier transform, associated with any
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable, the Fourier transform, associated with any
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation
![]() $\omega $
of height n, provides an isomorphism
$\omega $
of height n, provides an isomorphism
Plugging this into the above, we get
Example 4.33. If
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable for some
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable for some
![]() $n\ge 1$
, then applying the above to
$n\ge 1$
, then applying the above to
![]() $M= \Sigma C_p$
, we get
$M= \Sigma C_p$
, we get
That is,
![]() $C_p$
-Galois extensions are classified by p-th roots of unity of height
$C_p$
-Galois extensions are classified by p-th roots of unity of height
![]() $n-1$
.
$n-1$
.
Remark 4.34. The case
![]() $n=0$
is excluded, and does not even make sense, in Example 4.33. However, we have shown in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Theorem 3.18] that if
$n=0$
is excluded, and does not even make sense, in Example 4.33. However, we have shown in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Theorem 3.18] that if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is additive and admits a primitive m-th root of unity, then we have an isomorphism
${\mathscr {C}}$
is additive and admits a primitive m-th root of unity, then we have an isomorphism
Furthermore, we have explained how this recovers and extends classical Kummer theory. The above isomorphism and the one in Example 4.33 can be combined into a single uniform claim (see Theorem 7.34).
4.4 Detection for local rings
We shall now show that Proposition 4.4 admits a partial converse when
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is higher semiadditive and
${\mathscr {C}}$
is higher semiadditive and
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
is a strict map of local ring spectra in the following sense:
$f\colon \mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
is a strict map of local ring spectra in the following sense:
Definition 4.35. Let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
be a connective commutative ring spectrum. We say that
$\mathfrak {R}$
be a connective commutative ring spectrum. We say that
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
is local if
$\mathfrak {R}$
is local if
![]() $\pi _0(\mathfrak {R})$
is local. In this case, we refer to the residue field k of
$\pi _0(\mathfrak {R})$
is local. In this case, we refer to the residue field k of
![]() $\pi _0(\mathfrak {R})$
as the residue field of
$\pi _0(\mathfrak {R})$
as the residue field of
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
. We shall implicitly assume that k is of characteristic p, which implies that
$\mathfrak {R}$
. We shall implicitly assume that k is of characteristic p, which implies that
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
is p-local. We say that a map
$\mathfrak {R}$
is p-local. We say that a map
![]() $\mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
of local ring spectra is strict if it induces an isomorphism on residue fields.
$\mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
of local ring spectra is strict if it induces an isomorphism on residue fields.
For a local ring spectrum
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field k, the
$\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field k, the
![]() $\infty $
-categories
$\infty $
-categories
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
and
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
and
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{k}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
are closely related.
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{k}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
are closely related.
Definition 4.36. Let
![]() $\mathscr {E}$
be a pointed
$\mathscr {E}$
be a pointed
![]() $\infty $
-category, and let
$\infty $
-category, and let
![]() $\mathscr {E}_0$
be a full subcategory of
$\mathscr {E}_0$
be a full subcategory of
![]() $\mathscr {E}$
.
$\mathscr {E}$
.
-
(1) We say that
 $\mathscr {E}_0 \subseteq \mathscr {E}$
is closed under extensions if for every exact sequence in
$\mathscr {E}_0 \subseteq \mathscr {E}$
is closed under extensions if for every exact sequence in $$\begin{align*}M \to N \to L \end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}M \to N \to L \end{align*}$$
 $\mathscr {E}$
such that
$\mathscr {E}$
such that
 $M,L\in \mathscr {E}_0$
, we also have
$M,L\in \mathscr {E}_0$
, we also have
 $N\in \mathscr {E}_0$
.
$N\in \mathscr {E}_0$
.
-
(2) We say that
 $\mathscr {E}_0$
generates
$\mathscr {E}_0$
generates
 $\mathscr {E}$
under extensions if the only subcategory of
$\mathscr {E}$
under extensions if the only subcategory of
 $\mathscr {E}$
containing
$\mathscr {E}$
containing
 $\mathscr {E}_0$
and closed under extensions is
$\mathscr {E}_0$
and closed under extensions is
 $\mathscr {E}$
itself.
$\mathscr {E}$
itself.
Proposition 4.37. Let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
be local with residue field k. The
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
be local with residue field k. The
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is generated under extensions from the essential image of the restriction of scalars functor
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is generated under extensions from the essential image of the restriction of scalars functor
induced by the residue map
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R} \to k$
.
$f\colon \mathfrak {R} \to k$
.
Proof. Let
![]() $\mathscr {E}$
denote the minimal subcategory of
$\mathscr {E}$
denote the minimal subcategory of
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
which is closed under extensions and contains the essential image of
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
which is closed under extensions and contains the essential image of
![]() $f_*$
. Given
$f_*$
. Given
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, we wish to show that
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, we wish to show that
![]() $M\in \mathscr {E}$
. Consider the Postnikov tower
$M\in \mathscr {E}$
. Consider the Postnikov tower
of M. For every
![]() $1\le t \le n$
, we have an exact sequence
$1\le t \le n$
, we have an exact sequence
Hence, by induction on the tower, and using that
![]() $\mathscr {E}$
is closed under extensions, it would suffice to show that for every
$\mathscr {E}$
is closed under extensions, it would suffice to show that for every
![]() $0\le t \le n$
, the
$0\le t \le n$
, the
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module
![]() $\Sigma ^t\pi _t(M)$
belongs to
$\Sigma ^t\pi _t(M)$
belongs to
![]() $\mathscr {E}$
. In particular, it would suffice to show that for every discrete, finite
$\mathscr {E}$
. In particular, it would suffice to show that for every discrete, finite
![]() $\pi _0(R)$
module N and every
$\pi _0(R)$
module N and every
![]() $0\le t\le n$
, we have
$0\le t\le n$
, we have
![]() $\Sigma ^t N \in \mathscr {E}$
.
$\Sigma ^t N \in \mathscr {E}$
.
Let
![]() $\mathfrak {m}$
be the maximal ideal of
$\mathfrak {m}$
be the maximal ideal of
![]() $\pi _0(R)$
. Since
$\pi _0(R)$
. Since
![]() $\pi _0(R)$
is a local ring and N is finite, we have
$\pi _0(R)$
is a local ring and N is finite, we have
![]() $\mathfrak {m}^\ell N= 0$
for some
$\mathfrak {m}^\ell N= 0$
for some
![]() $\ell \ge 0$
. We shall proceed by induction on
$\ell \ge 0$
. We shall proceed by induction on
![]() $\ell $
, where the case
$\ell $
, where the case
![]() $\ell = 0$
holds trivially. Let
$\ell = 0$
holds trivially. Let
![]() $N[\mathfrak {m}]$
denote the
$N[\mathfrak {m}]$
denote the
![]() $\mathfrak {m}$
-torsion in N (i.e., the submodule of elements killed by
$\mathfrak {m}$
-torsion in N (i.e., the submodule of elements killed by
![]() $\mathfrak {m}$
). Then, we have an exact sequence
$\mathfrak {m}$
). Then, we have an exact sequence
The object
![]() $\Sigma ^tN[\mathfrak {m}]$
is a restriction of scalars of a
$\Sigma ^tN[\mathfrak {m}]$
is a restriction of scalars of a
![]() $\kappa $
-module, so it belongs to
$\kappa $
-module, so it belongs to
![]() $\mathscr {E}$
. Also, by construction, we have
$\mathscr {E}$
. Also, by construction, we have
![]() $\mathfrak {m}^{\ell - 1} \left (N/N[\mathfrak {m}]\right )= 0$
. By our inductive hypothesis, this implies that
$\mathfrak {m}^{\ell - 1} \left (N/N[\mathfrak {m}]\right )= 0$
. By our inductive hypothesis, this implies that
![]() $ \Sigma ^t N/N[\mathfrak {m}]\in \mathscr {E}$
, and since
$ \Sigma ^t N/N[\mathfrak {m}]\in \mathscr {E}$
, and since
![]() $\mathscr {E}$
is closed under extensions, we deduce that
$\mathscr {E}$
is closed under extensions, we deduce that
![]() $\Sigma ^t N\in \mathscr {E}$
.
$\Sigma ^t N\in \mathscr {E}$
.
In particular, this allows us to bootstrap affineness from k-modules to
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules.
Corollary 4.38. Let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
be local with residue field k, and let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
be local with residue field k, and let ![]() be virtually
be virtually
![]() $(k,n)$
-orientable. Then, for every
$(k,n)$
-orientable. Then, for every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the space
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the space
![]() $\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
Proof. By Proposition 4.30, the space
![]() $\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine for
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine for
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module M in the essential image of the functor
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module M in the essential image of the functor
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{k}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}} \rightarrow {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
. By Proposition 2.18, the
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{k}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}} \rightarrow {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
. By Proposition 2.18, the
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules M for which
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules M for which
![]() $\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine are closed under extensions. The result now follows from Proposition 4.37.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine are closed under extensions. The result now follows from Proposition 4.37.
Finally, we can show that the orientation property of a pre-orientation is detected at the residue field.
Theorem 4.39. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
be a strict map in
$f\colon \mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
be a strict map in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. A pre-orientation
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. A pre-orientation
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is an
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation if and only if
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation if and only if
![]() $f_*\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {S}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is an
$f_*\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {S}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is an
![]() $\mathfrak {S}$
-orientation.
$\mathfrak {S}$
-orientation.
Proof. The ‘only if’ direction follows from Proposition 4.4. Thus, for the ‘if’ direction, it suffices to consider the case where
![]() $f\colon R \to k$
is the quotient map to the residue field. We now have to show that all objects of
$f\colon R \to k$
is the quotient map to the residue field. We now have to show that all objects of
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
are
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
are
![]() $\omega $
-oriented assuming that all objects of
$\omega $
-oriented assuming that all objects of
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{k}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
are
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{k}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
are
![]() $f_*\omega $
-oriented. By Proposition 4.4, all the objects in the image of
$f_*\omega $
-oriented. By Proposition 4.4, all the objects in the image of
![]() $f_*$
are
$f_*$
are
![]() $\omega $
-oriented. Since these generate
$\omega $
-oriented. Since these generate
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
under extensions (Proposition 4.37), it would suffice to show that the collection of
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
under extensions (Proposition 4.37), it would suffice to show that the collection of
![]() $\omega $
-oriented
$\omega $
-oriented
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-modules is closed under extensions. Since for every
$\mathfrak {R}$
-modules is closed under extensions. Since for every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the space
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the space
![]() $\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine (Corollary 4.38), this follows from Proposition 4.11.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine (Corollary 4.38), this follows from Proposition 4.11.
Remark 4.40. The above result reduces the verification of the
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientability of an S-oriented
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientability of an S-oriented
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
to a lifting problem. Namely, to
${\mathscr {C}}$
to a lifting problem. Namely, to
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orient
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orient
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, it will suffice to have any map
${\mathscr {C}}$
, it will suffice to have any map ![]() which makes the following diagram commutative:
which makes the following diagram commutative:

Theorem 4.39 has the following consequence regrading the functoriality of the construction ![]() in
in
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
:
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
:
Proposition 4.41. Let ![]() . For every strict map
. For every strict map
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
in
$f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, we have
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, we have
Proof. Passing to the co-representable functors, the claim is equivalent to the existence of a natural isomorphism
for
![]() $T\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. Both sides are naturally subspaces of
$T\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. Both sides are naturally subspaces of
![]() ${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}(T;{\mathscr {C}})$
– the left-hand side consisting of those pre-orientations which are orientations and the right-hand side those pre-orientations
${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}(T;{\mathscr {C}})$
– the left-hand side consisting of those pre-orientations which are orientations and the right-hand side those pre-orientations
![]() $\omega $
for which
$\omega $
for which
![]() $f_*\omega $
is an orientation. By Theorem 4.39, these two subspaces are equal for every
$f_*\omega $
is an orientation. By Theorem 4.39, these two subspaces are equal for every
![]() $T\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, and the result follows.
$T\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, and the result follows.
Corollary 4.42. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
be a strict map in
$f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
be a strict map in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. If
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. If
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable, then it is virtually
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable, then it is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {S},n)$
-orientable.
$(\mathfrak {S},n)$
-orientable.
5 Categorification and redshift
In this section, we shall study the interaction of the various notions developed in this paper (affineness, (pre)orientations and the Fourier transform) with categorification.
5.1 Categorification
For
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
a presentably symmetric monoidal
${\mathscr {C}}$
a presentably symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category, the
$\infty $
-category, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
of presentably
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
of presentably
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear
![]() $\infty $
-categories admits a canonical symmetric monoidal structure (see [Reference LurieLur, Corollary 5.1.2.6]). Hence, we could try to apply the theory developed in the previous sections to
$\infty $
-categories admits a canonical symmetric monoidal structure (see [Reference LurieLur, Corollary 5.1.2.6]). Hence, we could try to apply the theory developed in the previous sections to
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}(\Pr )$
in place of
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}(\Pr )$
in place of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. However,
${\mathscr {C}}$
. However,
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}(\Pr )$
is usually not presentable itself. To avoid set-theoretical complications, we follow the strategy of [Reference LurieLur, §5.3.2] and adopt the following convention:
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}(\Pr )$
is usually not presentable itself. To avoid set-theoretical complications, we follow the strategy of [Reference LurieLur, §5.3.2] and adopt the following convention:
Convention 5.1. For every presentable
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, there exists an uncountable regular cardinal
${\mathscr {C}}$
, there exists an uncountable regular cardinal
![]() $\kappa $
, such that
$\kappa $
, such that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $\kappa $
-compactly generated. We shall always implicitly choose such
$\kappa $
-compactly generated. We shall always implicitly choose such
![]() $\kappa $
and treat
$\kappa $
and treat
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
as an object of the
${\mathscr {C}}$
as an object of the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa $
, which is presentable by [Reference LurieLur, Lemma 5.3.2.9]. If needed, we shall allow ourselves to implicitly replace
${\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa $
, which is presentable by [Reference LurieLur, Lemma 5.3.2.9]. If needed, we shall allow ourselves to implicitly replace
![]() $\kappa $
by some larger
$\kappa $
by some larger
![]() $\kappa '$
using the canonical (nonfull) inclusion
$\kappa '$
using the canonical (nonfull) inclusion
![]() ${\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa \hookrightarrow {\textrm {Pr}}_{\kappa '}.$
If
${\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa \hookrightarrow {\textrm {Pr}}_{\kappa '}.$
If
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is furthermore presentably
${\mathscr {C}}$
is furthermore presentably
![]() $\mathbb {E}_n$
-monoidal, we let
$\mathbb {E}_n$
-monoidal, we let
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
be the presentably
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
be the presentably
![]() $\mathbb {E}_{n-1}$
-monoidal
$\mathbb {E}_{n-1}$
-monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}({\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa )$
, for
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}({\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa )$
, for
![]() $\kappa $
as in [Reference LurieLur, Lemma 5.3.2.12].
$\kappa $
as in [Reference LurieLur, Lemma 5.3.2.12].
Semiadditivity of
 ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
An important feature, for our discussion, of
![]() ${\textrm {Pr}}$
is that it is
${\textrm {Pr}}$
is that it is
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditive (see [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Example 4.3.11]). In view of Convention 5.1, we shall need the analogous property of
$\infty $
-semiadditive (see [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Example 4.3.11]). In view of Convention 5.1, we shall need the analogous property of
![]() ${\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa $
.
${\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa $
.
Proposition 5.2. For every uncountable regular cardinal
![]() $\kappa $
, the
$\kappa $
, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa $
is
${\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa $
is
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditive.
$\infty $
-semiadditive.
Proof. Let
![]() $\operatorname{{Cat}}_{\kappa \text {-}\textrm {small}} \subset \operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty $
be the (nonfull) subcategory of
$\operatorname{{Cat}}_{\kappa \text {-}\textrm {small}} \subset \operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty $
be the (nonfull) subcategory of
![]() $\infty $
-categories that admit
$\infty $
-categories that admit
![]() $\kappa $
-small colimits and functors preserving them. Since
$\kappa $
-small colimits and functors preserving them. Since
![]() $\kappa $
is assumed to be uncountable, we have an equivalence of
$\kappa $
is assumed to be uncountable, we have an equivalence of
![]() $\infty $
-categories
$\infty $
-categories
![]() ${\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa \simeq \operatorname{{Cat}}_{\kappa \text {-}\textrm {small}},$
by [Reference LurieLur09, Proposition 5.5.7.10]. Similarly, for every integer m, let
${\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa \simeq \operatorname{{Cat}}_{\kappa \text {-}\textrm {small}},$
by [Reference LurieLur09, Proposition 5.5.7.10]. Similarly, for every integer m, let
![]() $\operatorname{{Cat}}_{m \text {-}\textrm {fin}} \subset \operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty $
be the (nonfull) subcategory of
$\operatorname{{Cat}}_{m \text {-}\textrm {fin}} \subset \operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty $
be the (nonfull) subcategory of
![]() $\infty $
-categories that admit m-finite colimits and functors preserving them. By [Reference HarpazHar20, Propoistion 5.26], the
$\infty $
-categories that admit m-finite colimits and functors preserving them. By [Reference HarpazHar20, Propoistion 5.26], the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\operatorname{{Cat}}_{m \text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is m-semiadditive. Recall, from [Reference LurieLur09, §5.3.6], the functor
$\operatorname{{Cat}}_{m \text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
is m-semiadditive. Recall, from [Reference LurieLur09, §5.3.6], the functor
which adds formally
![]() $\kappa $
-small colimits while fixing the m-finite ones. This functor preserves all small and, in particular, m-finite colimits by [Reference LurieLur09, Corollary 5.3.6.10]. Moreover, by [Reference LurieLur, Remark 4.8.1.8], it is also symmetric monoidal with respect to the canonical symmetric monoidal structures on the source and target, which preserve colimits in each coordinate by [Reference LurieLur, Remark 4.8.1.6]. Thus, by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.3.2], the
$\kappa $
-small colimits while fixing the m-finite ones. This functor preserves all small and, in particular, m-finite colimits by [Reference LurieLur09, Corollary 5.3.6.10]. Moreover, by [Reference LurieLur, Remark 4.8.1.8], it is also symmetric monoidal with respect to the canonical symmetric monoidal structures on the source and target, which preserve colimits in each coordinate by [Reference LurieLur, Remark 4.8.1.6]. Thus, by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.3.2], the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\operatorname{{Cat}}_{\kappa \text {-}\textrm {small}} \simeq {\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa $
is m-semiadditive as well.
$\operatorname{{Cat}}_{\kappa \text {-}\textrm {small}} \simeq {\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa $
is m-semiadditive as well.
Corollary 5.3. For every
![]() $n\ge 2$
and
$n\ge 2$
and
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_n}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, the
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_n}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditive.
$\infty $
-semiadditive.
Proof. Let
![]() $\kappa $
be the cardinal for which
$\kappa $
be the cardinal for which
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}= {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}({\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa )$
. By Proposition 5.2, the
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}= {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}({\textrm {Pr}}_\kappa )$
. By Proposition 5.2, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\Pr _\kappa $
is
$\Pr _\kappa $
is
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditive. Therefore, the claim follows from [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.3.2], applied to the monoidal functor
$\infty $
-semiadditive. Therefore, the claim follows from [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 3.3.2], applied to the monoidal functor
Affineness revisited
By [Reference LurieLur, §4.8.5 and §5.3.2], for every
![]() $1\le n \le \infty $
and a presentably
$1\le n \le \infty $
and a presentably
![]() $\mathbb {E}_n$
-monoidal
$\mathbb {E}_n$
-monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, we have a monoidal, fully faithful embedding
${\mathscr {C}}$
, we have a monoidal, fully faithful embedding
taking an
![]() $\mathbb {E}_n$
algebra R in
$\mathbb {E}_n$
algebra R in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
to the
${\mathscr {C}}$
to the
![]() $\infty $
-category of left modules
$\infty $
-category of left modules
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
in
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. Furthermore,
${\mathscr {C}}$
. Furthermore,
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
admits a right adjoint, which takes an
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
admits a right adjoint, which takes an
![]() $\mathbb {E}_{n-1}$
-monoidal
$\mathbb {E}_{n-1}$
-monoidal
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
to the endomorphism object of the unit
${\mathscr {D}}$
to the endomorphism object of the unit ![]() We shall reserve a special notation for the value of this right adjoint on morphisms.
We shall reserve a special notation for the value of this right adjoint on morphisms.
Notation 5.4. For
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_n}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_n}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and
![]() $F\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to \mathscr {E}$
in
$F\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to \mathscr {E}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_{n-1}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
, we denote by
$\operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_{n-1}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
, we denote by
the map induced by F between the endomorphism objects of the units of
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
and
${\mathscr {D}}$
and
![]() $\mathscr {E}$
, and we refer to it as the decategorifcation of F.
$\mathscr {E}$
, and we refer to it as the decategorifcation of F.
Remark 5.5. By [Reference LurieLur, Proposition 4.8.5.1], the functor
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
is compatible with base-change in the sense that for every
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
is compatible with base-change in the sense that for every
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in
${\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_n}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, we have a commutative square
$\operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_n}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, we have a commutative square

Specializing the above discussion to
![]() $n=2$
, we can characterize the essential image of
$n=2$
, we can characterize the essential image of
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
in terms of the affineness.
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
in terms of the affineness.
Proposition 5.6. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_2}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. An
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_2}({\textrm {Pr}})$
. An
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_1}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
belongs to the essential image of the functor
${\mathscr {D}}\in \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_1}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
belongs to the essential image of the functor
if and only if the unit functor
![]() $u^*\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
is affine.
$u^*\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
is affine.
Proof. Since
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
is fully faithful,
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
is fully faithful,
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
belongs to its essential image if and only if the counit map
${\mathscr {D}}$
belongs to its essential image if and only if the counit map ![]() is an isomorphism. Moreover, we have
is an isomorphism. Moreover, we have
and the above counit map identifies with ![]() Thus, the claim follows from the very definition of affineness.
Thus, the claim follows from the very definition of affineness.
The above characterization of module categories has an immediate consequence for detecting equivalences of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear
![]() $\infty $
-categories.
$\infty $
-categories.
Proposition 5.7. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_2}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_2}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $F\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to \mathscr {E}$
in
$F\colon {\mathscr {D}} \to \mathscr {E}$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_1}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
, such that the unit functors
$\operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_1}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
, such that the unit functors
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
and
${\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
and
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \to \mathscr {E}$
are affine. Then, F is an equivalence if and only if the map
${\mathscr {C}} \to \mathscr {E}$
are affine. Then, F is an equivalence if and only if the map
is an isomorphism.
Proof. By Proposition 5.6, the
![]() $\infty $
-categories
$\infty $
-categories
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
and
${\mathscr {D}}$
and
![]() $\mathscr {E}$
are in the essential image of the fully faithful embedding
$\mathscr {E}$
are in the essential image of the fully faithful embedding
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}\colon \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_2}({\mathscr {C}})\hookrightarrow \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_1}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}).$
Hence, F is an equivalence if and only if its image under the right adjoint of
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}\colon \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_2}({\mathscr {C}})\hookrightarrow \operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_1}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}).$
Hence, F is an equivalence if and only if its image under the right adjoint of
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
is an equivalence. Finally, this right adjoint is given by taking the endomorphism object of the unit and takes F to
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
is an equivalence. Finally, this right adjoint is given by taking the endomorphism object of the unit and takes F to
![]() ${F}^{\mathfrak {d}}$
.
${F}^{\mathfrak {d}}$
.
We conclude this subsection by comparing affineness with respect to
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
and affineness with respect to
${\mathscr {C}}$
and affineness with respect to
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
.
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
.
Proposition 5.8. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let A be a
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let A be a
![]() $\pi $
-finite
$\pi $
-finite
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous space. If A and
${\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous space. If A and
![]() $\Omega _a A$
, for every
$\Omega _a A$
, for every
![]() $a\in A$
, are
$a\in A$
, are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then A is
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then A is
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
Proof. By Corollary 5.3, the space A is
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous, and so by Theorem 2.38, it would suffice to show that for every
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
-ambidextrous, and so by Theorem 2.38, it would suffice to show that for every
![]() $a,b\in A$
, the square
$a,b\in A$
, the square

is a relative tensor square in
![]() $\operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_1}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
. Now, the space A is
$\operatorname{{Alg}}_{\mathbb {E}_1}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
. Now, the space A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine by assumption, and the space
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine by assumption, and the space
![]() $\{a\}\times _A \{b\}$
is either empty or isomorphic to
$\{a\}\times _A \{b\}$
is either empty or isomorphic to
![]() $\Omega _a A$
, and hence
$\Omega _a A$
, and hence
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine as well. Since
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine as well. Since
![]() $\textrm {pt}$
is obviously
$\textrm {pt}$
is obviously
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, we can identify the square
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, we can identify the square
![]() $(*)$
with the image under the functor
$(*)$
with the image under the functor
of the square

Since
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
is colimit-preserving, and relative tensor squares of commutative algebras are pushout squares,
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
is colimit-preserving, and relative tensor squares of commutative algebras are pushout squares,
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
takes relative tensor squares in
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}$
takes relative tensor squares in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
to relative tensor squares in
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
to relative tensor squares in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
. Thus, it would suffice to show that
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
. Thus, it would suffice to show that
![]() $(**)$
is a relative tensor square. Since, by our assumption, A is
$(**)$
is a relative tensor square. Since, by our assumption, A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, this follows again from Theorem 2.38.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, this follows again from Theorem 2.38.
5.2 The categorical Fourier transform
In this subsection, we compare the Fourier transform for a presentably symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, with the Fourier transform for its categorification
${\mathscr {C}}$
, with the Fourier transform for its categorification
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
.
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
.
Looping pre-orientations
We begin with the observation that height n pre-orientations for
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
are essentially the same thing as height
${\mathscr {C}}$
are essentially the same thing as height
![]() $n+1$
pre-orientations for
$n+1$
pre-orientations for
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
. More precisely, for
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
. More precisely, for
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, an
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
, an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation of height
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation of height
![]() $n+1$
for
$n+1$
for
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is a map
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is a map
where
![]() $\textrm {pic}({\mathscr {C}})$
is the Picard spectrum of
$\textrm {pic}({\mathscr {C}})$
is the Picard spectrum of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, consisting of
${\mathscr {C}}$
, consisting of
![]() $\otimes $
-invertible objects. By applying the functor
$\otimes $
-invertible objects. By applying the functor
![]() $\Omega \colon \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}} \to \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
to
$\Omega \colon \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}} \to \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
to
![]() $\omega $
, we get a morphism
$\omega $
, we get a morphism
which we can view as an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation of
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientation of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
of height n. Under the (natural) assumption that R is n-truncated, taking loops provides an isomorphism between
${\mathscr {C}}$
of height n. Under the (natural) assumption that R is n-truncated, taking loops provides an isomorphism between
![]() ${\textrm {POr}}^{(n+1)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\operatorname {Mod}}_{{\mathscr {C}}})$
and
${\textrm {POr}}^{(n+1)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\operatorname {Mod}}_{{\mathscr {C}}})$
and
![]() ${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
${\textrm {POr}}^{(n)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
Proposition 5.9. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. If
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. If
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
is n-truncated, we get an isomorphism of spaces
$\mathfrak {R}$
is n-truncated, we get an isomorphism of spaces
Proof. Since
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
is n-truncated we get
$\mathfrak {R}$
is n-truncated we get
![]() $\pi _0(I_p^{(n+1)}{\mathfrak {R}})= 0$
. Consequently, for every
$\pi _0(I_p^{(n+1)}{\mathfrak {R}})= 0$
. Consequently, for every
![]() $M \in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
,
$M \in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
,
The result follows by taking
![]() $M= \textrm {pic}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
$M= \textrm {pic}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
Categorical group algebras
Given
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n+1)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
, we get for every
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n+1)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
, we get for every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n+1]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
the categorical Fourier transform
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n+1]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
the categorical Fourier transform
The range is the functor category
![]() $\operatorname {Fun}(\lfloor {I_p^{(n+1)}{M}}\rfloor , {\mathscr {C}})$
endowed with the pointwise symmetric monoidal structure. We shall now show that the domain (i.e., the categorical group algebra
$\operatorname {Fun}(\lfloor {I_p^{(n+1)}{M}}\rfloor , {\mathscr {C}})$
endowed with the pointwise symmetric monoidal structure. We shall now show that the domain (i.e., the categorical group algebra
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}[M]$
) is also the functor category
${\mathscr {C}}[M]$
) is also the functor category
![]() $\operatorname{{Fun}}(\lfloor {M}\rfloor ,{\mathscr {C}})$
, albeit with the Day convolution symmetric monoidal structure. That is, the categorical Fourier transform is a
$\operatorname{{Fun}}(\lfloor {M}\rfloor ,{\mathscr {C}})$
, albeit with the Day convolution symmetric monoidal structure. That is, the categorical Fourier transform is a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear, colimit-preserving symmetric monoidal functor
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear, colimit-preserving symmetric monoidal functor
where the subscripts ‘Day’ and ‘Ptw’ stand for the Day convolution and pointwise symmetric monoidal structures, respectively.
Proposition 5.10. For every
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and
![]() $M\in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
, we have a natural isomorphism
$M\in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
, we have a natural isomorphism
Proof. On the one hand,
and on the other, by [Reference Moshe and SchlankMS21, Proposition 3.10],
Thus, the general case follows from the case
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}= \mathcal{S}$
. It remains to show that the functor
${\mathscr {C}}= \mathcal{S}$
. It remains to show that the functor
is left adjoint to the functor
By [Reference HinichHin21], for every
![]() ${\mathscr {D}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, we have
${\mathscr {D}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, we have
Since as a symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category,
$\infty $
-category,
![]() $\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is an
$\lfloor {M}\rfloor $
is an
![]() $\infty $
-groupoid with all objects
$\infty $
-groupoid with all objects
![]() $\otimes $
-invertible, we have
$\otimes $
-invertible, we have
The claim follows by stringing together the two isomorphisms above.
When M is connected, we can also identify the categorical group algebra
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}[M]$
with the
${\mathscr {C}}[M]$
with the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category ![]() of modules over the ordinary group algebra of
of modules over the ordinary group algebra of
![]() $\Omega M$
in
$\Omega M$
in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
(as symmetric monoidal
${\mathscr {C}}$
(as symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-categories).
$\infty $
-categories).
Proposition 5.11. For every
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and a connected
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
and a connected
![]() $M\in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
, we have a natural isomorphism
$M\in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
, we have a natural isomorphism
Proof. We shall show that both objects co-represent naturally isomorphic functors from
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
into
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
into
![]() $\mathcal{S}$
. For every
$\mathcal{S}$
. For every
![]() ${\mathscr {D}} \in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
, we have a natural isomorphism
${\mathscr {D}} \in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
, we have a natural isomorphism
Since M is connected, we have a natural isomorphism
However, we have
Thus, both
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}[M]$
and
${\mathscr {C}}[M]$
and ![]() co-represent the functor
co-represent the functor ![]() and are hence isomorphic by the Yoneda lemma.
and are hence isomorphic by the Yoneda lemma.
Remark 5.12. The isomorphism provided by the proof of Proposition 5.11 can be succinctly summarized as follows. The object
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}[M]$
co-represents maps
${\mathscr {C}}[M]$
co-represents maps
![]() $M \to \textrm {pic}(-)$
, and the object
$M \to \textrm {pic}(-)$
, and the object ![]() co-represents maps
co-represents maps ![]() . When M is connected, the two types of data are equivalent by taking
. When M is connected, the two types of data are equivalent by taking
![]() $\Omega $
and using the identification
$\Omega $
and using the identification ![]() .
.
Decategorifying the Fourier transform
We shall now explain how the Fourier transform for
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is essentially the decategorification of the Fourier transform for
${\mathscr {C}}$
is essentially the decategorification of the Fourier transform for
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
. Given
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
. Given
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n+1)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
and
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n+1)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\mathscr {C}})$
and
![]() $M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R^{[0,n+1]}$
, the categorical Fourier transform decategorifies to a natural transformation
$M\in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R^{[0,n+1]}$
, the categorical Fourier transform decategorifies to a natural transformation
We now interpret the source and target in terms of familiar commutative algebras. First, we have
And second, when M is connected, we have by Proposition 5.11,
Furthermore, for every
![]() $M \in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
, we also have a natural isomorphism
$M \in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]}$
, we also have a natural isomorphism
Using these isomorphisms, we have the following:
Proposition 5.13. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n+1)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
. The following diagram of functors
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n+1)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
. The following diagram of functors
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
commutes:
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]} \to \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
commutes:

5.3 Orientations and categorification
For every
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, we have constructed a map
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, we have constructed a map
between the respective spaces of
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations. Both the domain and the range have distinguished subspaces consisting of the
$\mathfrak {R}$
-pre-orientations. Both the domain and the range have distinguished subspaces consisting of the
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations. We shall now show that in the higher semiadditive setting, these are preserved and detected by
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientations. We shall now show that in the higher semiadditive setting, these are preserved and detected by
![]() $\Omega $
.
$\Omega $
.
Proposition 5.14. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n+1)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\operatorname {Mod}}_{{\mathscr {C}}})$
. For every
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n+1)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\operatorname {Mod}}_{{\mathscr {C}}})$
. For every
![]() $M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, if
$M\in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, if
![]() $\Sigma M$
is
$\Sigma M$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented, then M is
$\omega $
-oriented, then M is
![]() $\Omega \omega $
-oriented. The converse holds if
$\Omega \omega $
-oriented. The converse holds if
![]() $\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
Proof. By Proposition 5.13,
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{\Omega \omega }$
is an isomorphism at M if and only if
${\mathfrak {F}}_{\Omega \omega }$
is an isomorphism at M if and only if
![]() ${{\mathfrak {F}}}^{\mathfrak {d}}_\omega $
is an isomorphism at
${{\mathfrak {F}}}^{\mathfrak {d}}_\omega $
is an isomorphism at
![]() $\Sigma M$
. Now,
$\Sigma M$
. Now,
![]() ${{\mathfrak {F}}}^{\mathfrak {d}}_\omega $
is an isomorphism at
${{\mathfrak {F}}}^{\mathfrak {d}}_\omega $
is an isomorphism at
![]() $\Sigma M$
if
$\Sigma M$
if
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
is an isomorphism at
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
is an isomorphism at
![]() $\Sigma M$
, and the converse holds if the source and target of
$\Sigma M$
, and the converse holds if the source and target of
have affine units (Proposition 5.7). For the source, since
![]() $\Sigma M$
is connected, the unit
$\Sigma M$
is connected, the unit
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}[\Sigma M]$
is affine by Proposition 5.11 and Proposition 5.6. For the target, by assumption, the space
${\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {C}}[\Sigma M]$
is affine by Proposition 5.11 and Proposition 5.6. For the target, by assumption, the space
![]() $\lfloor {I_p^{(n+1)}{(\Sigma M)}}\rfloor \simeq \lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {I_p^{(n+1)}{(\Sigma M)}}\rfloor \simeq \lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, and hence, the unit
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, and hence, the unit
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \rightarrow {\mathscr {C}}^{\lfloor {I_p^{(n+1)}{(\Sigma M)}}\rfloor }$
is affine.
${\mathscr {C}} \rightarrow {\mathscr {C}}^{\lfloor {I_p^{(n+1)}{(\Sigma M)}}\rfloor }$
is affine.
Theorem 5.15. Let ![]() , let
, let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
and let
![]() $\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n+1)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\operatorname {Mod}}_{{\mathscr {C}}})$
. Then,
$\omega \in {\textrm {POr}}^{(n+1)}_{\mathfrak {R}}({\operatorname {Mod}}_{{\mathscr {C}}})$
. Then,
![]() $\omega $
is an orientation of
$\omega $
is an orientation of
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
if and only if
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
if and only if
![]() $\Omega \omega $
is an orientation of
$\Omega \omega $
is an orientation of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
.
${\mathscr {C}}$
.
Proof. By Proposition 5.14, if
![]() $\omega $
is an orientation on
$\omega $
is an orientation on
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
, then
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
, then
![]() $\Omega \omega $
is an orientation on
$\Omega \omega $
is an orientation on
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. Conversely, assume that
${\mathscr {C}}$
. Conversely, assume that
![]() $\omega $
is an orientation on
$\omega $
is an orientation on
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. We first observe that by Proposition 4.30, for every
${\mathscr {C}}$
. We first observe that by Proposition 4.30, for every
![]() $M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the space
$M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the space
![]() $\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, and hence, by Proposition 5.14 again,
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, and hence, by Proposition 5.14 again,
![]() $\Sigma M$
is
$\Sigma M$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented. In other words, we get that all
$\omega $
-oriented. In other words, we get that all
![]() $1$
-connective
$1$
-connective
![]() $N \in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[1,n+1]\text {-fin}}$
are
$N \in {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[1,n+1]\text {-fin}}$
are
![]() $\omega $
-oriented. By Proposition 4.9,
$\omega $
-oriented. By Proposition 4.9,
![]() $\omega $
-oriented modules are closed under the operation
$\omega $
-oriented modules are closed under the operation
![]() $M \mapsto I_p^{(n+1)}{M}=N$
, and hence, also all
$M \mapsto I_p^{(n+1)}{M}=N$
, and hence, also all
![]() $M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
are
$M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
are
![]() $\omega $
-oriented. Finally, for a general
$\omega $
-oriented. Finally, for a general
![]() $M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n+1]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, we have an exact sequence
$M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n+1]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, we have an exact sequence
The modules
![]() $\tau _{\ge 1} M$
and
$\tau _{\ge 1} M$
and
![]() $\tau _{\le 0} M$
are
$\tau _{\le 0} M$
are
![]() $\omega $
-oriented by the above. Moreover, the finite set
$\omega $
-oriented by the above. Moreover, the finite set
![]() $\lfloor {\tau _{\le 0} M}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {\tau _{\le 0} M}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, as
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, as
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is 0-semiadditive (Example 2.35). We conclude by Proposition 4.12 that M is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is 0-semiadditive (Example 2.35). We conclude by Proposition 4.12 that M is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented.
$\omega $
-oriented.
Corollary 5.16. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. If
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
. If
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
is n-truncated, we get an isomorphism of spaces
$\mathfrak {R}$
is n-truncated, we get an isomorphism of spaces
In particular,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable if and only if
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable if and only if
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n+1)$
-orientable.
$(\mathfrak {R},n+1)$
-orientable.
Proof. By Theorem 5.15, the analogous isomorphism of the corresponding spaces of pre-orientations, provided by Proposition 5.9, restricts to an isomorphism between the subspaces of orientations. In particular, the domain is nonempty if and only if the range is nonempty.
When
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable, we get for every
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable, we get for every
![]() $M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n+1]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
an equivalence of
$M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n+1]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
an equivalence of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear presentable symmetric monoidal
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear presentable symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-categories
$\infty $
-categories
By Proposition 5.13, we recover the ordinary Fourier transform at
![]() $M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
,
$M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathfrak {R}}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
,
by applying the functor ![]() to
to
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
at
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
at
![]() $\Sigma M$
. However, in the oriented case, we can also go the other way around. By Proposition 5.11, we have
$\Sigma M$
. However, in the oriented case, we can also go the other way around. By Proposition 5.11, we have
and by Proposition 4.30, the space
![]() $\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{M}}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, so that we have
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, so that we have
Thus, the categorical Fourier transform
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
at
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
at
![]() $\Sigma M$
can be recovered from the ordinary Fourier transform
$\Sigma M$
can be recovered from the ordinary Fourier transform
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{\Omega \omega }$
at M by applying the functor
${\mathfrak {F}}_{\Omega \omega }$
at M by applying the functor
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{(-)}({\mathscr {C}})$
.
Remark 5.17. To be precise, the above procedure recovers
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
at
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
at
![]() $\Sigma M$
from
$\Sigma M$
from
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{\Omega \omega }$
at M only as an equivalence of plain (
${\mathfrak {F}}_{\Omega \omega }$
at M only as an equivalence of plain (
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear)
${\mathscr {C}}$
-linear)
![]() $\infty $
-categories. The equivalence as symmetric monoidal
$\infty $
-categories. The equivalence as symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-categories can be deduced from the fact that
$\infty $
-categories can be deduced from the fact that
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_{\Omega \omega }$
is an isomorphism of Hopf algebras (Corollary 3.31), though we shall not prove nor use this.
${\mathfrak {F}}_{\Omega \omega }$
is an isomorphism of Hopf algebras (Corollary 3.31), though we shall not prove nor use this.
In contrast, for nonconnected modules
![]() $M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{R}^{[0,n+1]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the categorical Fourier transform provides some new information.
$M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{R}^{[0,n+1]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the categorical Fourier transform provides some new information.
Example 5.18. When M is discrete (i.e., a finite abelian group), the inverse of the categorical Fourier transform at its Pontryagin dual
![]() $M^*$
assumes the form
$M^*$
assumes the form
This should be thought of as providing a decomposition of every
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-valued representation of the group
${\mathscr {C}}$
-valued representation of the group
![]() $\Omega B^{n+1} M= B^n M$
into a sum of characters. For
$\Omega B^{n+1} M= B^n M$
into a sum of characters. For
![]() $R = \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
and height
$R = \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
and height
![]() $n=0$
, this reproduces the Fourier transform considered in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Definition 3.12].
$n=0$
, this reproduces the Fourier transform considered in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Definition 3.12].
Another consequence of Corollary 5.16 is that the categorical
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension is simply the
$\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension is simply the
![]() $\infty $
-category of modules over the usual
$\infty $
-category of modules over the usual
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extension.
Corollary 5.19. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
be n-truncated. We have a natural isomorphism
$\mathfrak {R}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
be n-truncated. We have a natural isomorphism
Proof. Since R is n-truncated,
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
is connected, and hence, by Proposition 5.11, we have an isomorphism
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
is connected, and hence, by Proposition 5.11, we have an isomorphism
This isomorphism corresponds to the natural isomorphism of the associated co-representable functors
for
![]() ${\mathscr {D}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
. Corollary 5.16 implies that the above isomorphism restricts to an isomorphism between the corresponding subspaces of orientations, when
${\mathscr {D}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
. Corollary 5.16 implies that the above isomorphism restricts to an isomorphism between the corresponding subspaces of orientations, when
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}= {\mathscr {C}}$
. However, by base-changing from
${\mathscr {D}}= {\mathscr {C}}$
. However, by base-changing from
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
to
${\mathscr {C}}$
to
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
, this implies that the same holds for an arbitrary
${\mathscr {D}}$
, this implies that the same holds for an arbitrary
![]() ${\mathscr {D}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
. From this, we deduce the isomorphism in the claim as these are the objects co-representing the corresponding subspaces of orientations.
${\mathscr {D}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
. From this, we deduce the isomorphism in the claim as these are the objects co-representing the corresponding subspaces of orientations.
6 Orientations for thickenings of
 $\mathbb {F}_p$
$\mathbb {F}_p$
In the definition of an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n of an
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation of height n of an
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, the main role of the ring spectrum
${\mathscr {C}}$
, the main role of the ring spectrum
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
is to determine which objects of
$\mathfrak {R}$
is to determine which objects of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
admit a Fourier transform – namely, those admitting an
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
admit a Fourier transform – namely, those admitting an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-module structure. It is natural to restrict attention to the subcategory of local rings
$\mathfrak {R}$
-module structure. It is natural to restrict attention to the subcategory of local rings
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field
$\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
and strict maps in the sense of Definition 4.35. The minimal choice
$\mathbb {F}_p$
and strict maps in the sense of Definition 4.35. The minimal choice
![]() $\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {F}_p$
(i.e., the terminal object) gives rise to a Fourier transform for
$\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {F}_p$
(i.e., the terminal object) gives rise to a Fourier transform for
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-vector spaces. The maximal choice
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-vector spaces. The maximal choice
![]() $\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
(i.e., the initial object) gives rise to a Fourier transform for all p-local spectra. In between, we also have the finite rings
$\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
(i.e., the initial object) gives rise to a Fourier transform for all p-local spectra. In between, we also have the finite rings
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
, the p-local integers
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
, the p-local integers
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
, and the Postnikov truncations of the p-local sphere
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
, and the Postnikov truncations of the p-local sphere
![]() $\tau _{\le d} \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
. In this section, we study these particular cases and their special features, interrelations and implications.
$\tau _{\le d} \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
. In this section, we study these particular cases and their special features, interrelations and implications.
6.1
 $\mathbb {F}_p$
-Orientations and affineness
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-Orientations and affineness
We start with the minimal case
![]() $\mathfrak {R}= \mathbb {F}_p$
and show that virtual
$\mathfrak {R}= \mathbb {F}_p$
and show that virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability already has several significant consequences.
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability already has several significant consequences.
Semiadditive height
To begin with, in the definition of a pre-orientation, the height was a free parameter. However, in the higher semiadditive setting, if the pre-orientation is an orientation, then its height is strongly constrained by the higher semiadditive structure of the
![]() $\infty $
-category.
$\infty $
-category.
Proposition 6.1. Let ![]() . If
. If
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of semiadditive height n at p.
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of semiadditive height n at p.
Proof. First, by Proposition 4.30, the spaces
![]() $B^kC_p= \lfloor {\Sigma ^k C_p}\rfloor $
are
$B^kC_p= \lfloor {\Sigma ^k C_p}\rfloor $
are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine for all
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine for all
![]() $k = 0,\dots ,n$
. Hence, by Proposition 2.40(3),
$k = 0,\dots ,n$
. Hence, by Proposition 2.40(3),
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height
![]() $\ge n$
at p. To show that
$\ge n$
at p. To show that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is also of height
${\mathscr {C}}$
is also of height
![]() $\le n$
at p, it would suffice, by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.1], to show that
$\le n$
at p, it would suffice, by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.1], to show that ![]() . Furthermore, it suffices to show this after extending scalars along a faithful commutative algebra, so without loss of generality, we may assume that
. Furthermore, it suffices to show this after extending scalars along a faithful commutative algebra, so without loss of generality, we may assume that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
itself is
${\mathscr {C}}$
itself is
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. Now, the commutative algebra
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. Now, the commutative algebra ![]() is the pushout of the following diagram:
is the pushout of the following diagram:
Applying the Fourier transform associated to any
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of height n of
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of height n of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, we get that
${\mathscr {C}}$
, we get that ![]() is also the pushout of the isomorphic diagram
is also the pushout of the isomorphic diagram
Finally, since
![]() $\lfloor {C_p}\rfloor $
is
$\lfloor {C_p}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine (see Example 2.35), by Theorem 2.38, we have
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine (see Example 2.35), by Theorem 2.38, we have
Affineness for p-spaces
Virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability also implies the affineness (and nonaffineness) of a large class of spaces.
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability also implies the affineness (and nonaffineness) of a large class of spaces.
Theorem 6.2. Let ![]() be nonzero and virtually
be nonzero and virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. A
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. A
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-space A is
$\pi $
-finite p-space A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine if and only if
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine if and only if
![]() $\pi _{n+1}(A,a)= 0$
for all
$\pi _{n+1}(A,a)= 0$
for all
![]() $a\colon \textrm {pt} \to A$
.
$a\colon \textrm {pt} \to A$
.
Proof. By Proposition 2.18, the collection of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine spaces is closed under extensions. That is, given a map of spaces
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine spaces is closed under extensions. That is, given a map of spaces
![]() $f\colon B\to B'$
, if
$f\colon B\to B'$
, if
![]() $B'$
and all the fibers of f are
$B'$
and all the fibers of f are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then so is B. Combined with Example 2.35, we are reduced to considering only connected A. Now, assuming that
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then so is B. Combined with Example 2.35, we are reduced to considering only connected A. Now, assuming that
![]() $\pi _{n+1}(A,a)= 0$
, the Postnikov tower of A can be refined to a tower
$\pi _{n+1}(A,a)= 0$
, the Postnikov tower of A can be refined to a tower
in which the fiber of each map is of the form
![]() $B^k C_p$
for
$B^k C_p$
for
![]() $k \neq n+1$
. By Proposition 6.1, we get that
$k \neq n+1$
. By Proposition 6.1, we get that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height n at p. Therefore, for
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height n at p. Therefore, for
![]() $k\ge n+2$
, the spaces
$k\ge n+2$
, the spaces
![]() $B^k C_p$
are
$B^k C_p$
are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine by Proposition 2.40(1). For
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine by Proposition 2.40(1). For
![]() $k \le n$
, the spaces
$k \le n$
, the spaces
![]() $B^k C_p= \lfloor {\Sigma ^k C_p}\rfloor $
are
$B^k C_p= \lfloor {\Sigma ^k C_p}\rfloor $
are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine by Proposition 4.30. Thus, by Proposition 2.18 again, we conclude that A is
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine by Proposition 4.30. Thus, by Proposition 2.18 again, we conclude that A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
Conversely, by Proposition 6.1,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height n at p, and hence by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.3], we have
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height n at p, and hence by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.3], we have
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}^A \simeq {\mathscr {C}}^{\tau _{\le n+1}A}$
. We can thus assume without loss of generality that A is
${\mathscr {C}}^A \simeq {\mathscr {C}}^{\tau _{\le n+1}A}$
. We can thus assume without loss of generality that A is
![]() $(n+1)$
-finite. Hence, if
$(n+1)$
-finite. Hence, if
![]() $\pi _{n+1} A \neq 0$
, then by refining the Postnikov tower of A as above, we have a fiber sequence
$\pi _{n+1} A \neq 0$
, then by refining the Postnikov tower of A as above, we have a fiber sequence
with B also
![]() $(n+1)$
-finite. In particular,
$(n+1)$
-finite. In particular,
![]() $\Omega B$
, being n-finite, is
$\Omega B$
, being n-finite, is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine by Theorem 6.2. Thus, if A were
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine by Theorem 6.2. Thus, if A were
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, by applying Proposition 2.18(2) to the map
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, by applying Proposition 2.18(2) to the map
![]() $B^{n+1}C_p \to A$
, we would deduce that
$B^{n+1}C_p \to A$
, we would deduce that
![]() $B^{n+1}C_p$
is
$B^{n+1}C_p$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, contradicting Proposition 2.40(2).
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, contradicting Proposition 2.40(2).
Remark 6.3. In Theorem 6.2, if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is further assumed to be p-local, as is often the case (e.g., if
${\mathscr {C}}$
is further assumed to be p-local, as is often the case (e.g., if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is stable and
${\mathscr {C}}$
is stable and
![]() $n\ge 1$
), then the collection of
$n\ge 1$
), then the collection of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine spaces includes the larger class of
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine spaces includes the larger class of
![]() $\pi $
-finite spaces A, such that for every
$\pi $
-finite spaces A, such that for every
![]() $a\colon \textrm {pt} \to A$
,
$a\colon \textrm {pt} \to A$
,
-
(1)
 $\pi _{1}(A,a)$
is a p-group,
$\pi _{1}(A,a)$
is a p-group, -
(2)
 $\pi _{n+1}(A,a)$
is of order prime to p.
$\pi _{n+1}(A,a)$
is of order prime to p.
The proof proceeds by the exact same argument as in the proof of Theorem 6.2, with the additional ingredient that for every prime
![]() $\ell \neq p$
, the spaces
$\ell \neq p$
, the spaces
![]() $B^k C_\ell $
are
$B^k C_\ell $
are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine for all
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine for all
![]() $k\ge 2$
. Indeed, if
$k\ge 2$
. Indeed, if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is p-local, then it is of semiadditive height
${\mathscr {C}}$
is p-local, then it is of semiadditive height
![]() $0$
at
$0$
at
![]() $\ell $
, so the said claim follows again from Proposition 2.40.
$\ell $
, so the said claim follows again from Proposition 2.40.
Bootstrapping virtual orientability
By Corollary 4.42, for every local ring spectrum
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field
$\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
, virtual
$\mathbb {F}_p$
, virtual
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientability implies virtual
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientability implies virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability. Conversely, we have the following bootstrap result:
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability. Conversely, we have the following bootstrap result:
Proposition 6.4. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $\mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
be a strict map of local rings (in the sense of Definition 4.35) with residue field
$\mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
be a strict map of local rings (in the sense of Definition 4.35) with residue field
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
, such that
$\mathbb {F}_p$
, such that
-
(1) Its fiber is
 $\pi $
-finite.
$\pi $
-finite. -
(2) It is surjective on
 $\pi _0$
and
$\pi _0$
and
 $\pi _n$
.
$\pi _n$
.
Then,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable if and only if it is virtually
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable if and only if it is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {S},n)$
-orientable.
$(\mathfrak {S},n)$
-orientable.
Proof. By Corollary 4.42, if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable, then it is virtually
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable, then it is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {S},n)$
-orientable, so we only need to prove the converse. By Proposition 4.24, we need to show that
$(\mathfrak {S},n)$
-orientable, so we only need to prove the converse. By Proposition 4.24, we need to show that ![]() is faithful under the assumption that
is faithful under the assumption that ![]() is faithful. Using Corollary 4.42 for the map
is faithful. Using Corollary 4.42 for the map
![]() $\mathfrak {S}\to \mathbb {F}_p$
, we deduce that
$\mathfrak {S}\to \mathbb {F}_p$
, we deduce that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. Moreover, since
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. Moreover, since ![]() is faithful (again, by Proposition 4.24), it suffices to show that
is faithful (again, by Proposition 4.24), it suffices to show that ![]() is faithful, so we can replace
is faithful, so we can replace
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
with the
${\mathscr {C}}$
with the
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable
![]() $\infty $
-category of
$\infty $
-category of ![]() -modules in
-modules in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. In other words, we can assume without loss of generality that
${\mathscr {C}}$
. In other words, we can assume without loss of generality that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
itself is
${\mathscr {C}}$
itself is
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable.
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable.
We shall say that a map
![]() $A \to B$
in
$A \to B$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is faithful if the functor
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
is faithful if the functor
![]() $B\otimes _A - \colon {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_A \to {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_B$
is conservative. In particular, A is faithful if the unit map
$B\otimes _A - \colon {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_A \to {{\operatorname {Mod}}}_B$
is conservative. In particular, A is faithful if the unit map ![]() is faithful. Since faithful maps are clearly closed under composition, and
is faithful. Since faithful maps are clearly closed under composition, and ![]() is faithful by assumption, it suffices to show that the map
is faithful by assumption, it suffices to show that the map ![]() is faithful. By Proposition 4.41, the map
is faithful. By Proposition 4.41, the map
![]() $\mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
induces the following pushout square in
$\mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
induces the following pushout square in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
:
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
:

It is easy to see that faithful maps are also closed under cobase-change, so it actually suffices to show that the map ![]() is faithful. By Remark 3.4, we may assume without loss of generality that both
is faithful. By Remark 3.4, we may assume without loss of generality that both
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
and
$\mathfrak {R}$
and
![]() $\mathfrak {S}$
are n-truncated, in addition to being connective. The assumption that
$\mathfrak {S}$
are n-truncated, in addition to being connective. The assumption that
![]() $\mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
is surjective on
$\mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
is surjective on
![]() $\pi _0$
and
$\pi _0$
and
![]() $\pi _n$
implies that
$\pi _n$
implies that
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {S}} \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
is a map of connective n-truncated spectra, which is injective on
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {S}} \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
is a map of connective n-truncated spectra, which is injective on
![]() $\pi _n$
and
$\pi _n$
and
![]() $\pi _0$
.
$\pi _0$
.
We shall prove, more generally, that for every map of n-truncated connective spectra
![]() $f\colon M \to N$
, such that,
$f\colon M \to N$
, such that,
-
(1) the fiber of f is p-local and
 $\pi $
-finite, and
$\pi $
-finite, and -
(2) f is injective on
 $\pi _0$
and
$\pi _0$
and
 $\pi _n$
,
$\pi _n$
,
the induced map ![]() is faithful. The first stage of the relative Postnikov tower factors f as
is faithful. The first stage of the relative Postnikov tower factors f as
![]() $M\to N_0 \to N$
, where
$M\to N_0 \to N$
, where
![]() $M\to N_0$
is a surjection on
$M\to N_0$
is a surjection on
![]() $\pi _0$
and
$\pi _0$
and
![]() $N_0 \to N$
is an injection on
$N_0 \to N$
is an injection on
![]() $\pi _0$
and an isomorphism on
$\pi _0$
and an isomorphism on
![]() $\pi _k$
for
$\pi _k$
for
![]() $k\ge 1$
. It follows that
$k\ge 1$
. It follows that ![]() is a free
is a free ![]() -module, and hence, the map
-module, and hence, the map ![]() is faithful. It thus remains to show that the map
is faithful. It thus remains to show that the map ![]() is faithful. Since f is an injection on
is faithful. Since f is an injection on
![]() $\pi _0$
, it follows that
$\pi _0$
, it follows that
![]() $M\to N_0$
is in fact an isomorphism on
$M\to N_0$
is in fact an isomorphism on
![]() $\pi _0$
. In other words, we can assume without loss of generality that f itself is an isomorphism on
$\pi _0$
. In other words, we can assume without loss of generality that f itself is an isomorphism on
![]() $\pi _0$
. Consequently, the fiber of f is connective. Moreover, since M and N are n-truncated and f is injective on
$\pi _0$
. Consequently, the fiber of f is connective. Moreover, since M and N are n-truncated and f is injective on
![]() $\pi _n$
, the fiber of f is also
$\pi _n$
, the fiber of f is also
![]() $(n-1)$
-truncated. Therefore, by refining the Postnikov tower of f, we get a tower
$(n-1)$
-truncated. Therefore, by refining the Postnikov tower of f, we get a tower
of connective n-truncated spectra, where the fiber of each map
![]() $M_i \to M_{i+1}$
is isomorphic to
$M_i \to M_{i+1}$
is isomorphic to
![]() $\Sigma ^d C_p$
for some
$\Sigma ^d C_p$
for some
![]() $0\le d \le n-1$
. Since faithful maps are closed under composition, we can assume without loss of generality that the fiber of f itself is of this form. Now, the exact sequence
$0\le d \le n-1$
. Since faithful maps are closed under composition, we can assume without loss of generality that the fiber of f itself is of this form. Now, the exact sequence
induces a a pushout square in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
,
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
,

By the same consideration as above, it would suffice to show that the map ![]() is faithful. Applying the Fourier transform associated with any
is faithful. Applying the Fourier transform associated with any
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, this map identifies, by Proposition 3.15, with
${\mathscr {C}}$
, this map identifies, by Proposition 3.15, with
for
![]() $e\colon \textrm {pt} \to B^{n-d}C_p$
the base point. Finally, by Proposition 4.30, the space
$e\colon \textrm {pt} \to B^{n-d}C_p$
the base point. Finally, by Proposition 4.30, the space
![]() $B^{n-d}C_p$
is
$B^{n-d}C_p$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, and so the functor
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, and so the functor
identifies, by Corollary 2.17, with
which is conservative because
![]() $n-d\ge 1$
, and hence,
$n-d\ge 1$
, and hence,
![]() $B^{n-d}C_p$
is connected.
$B^{n-d}C_p$
is connected.
In particular, virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability bootstraps to
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability bootstraps to
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientability for a large class of ring spectra
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientability for a large class of ring spectra
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
.
$\mathfrak {R}$
.
Corollary 6.5. If ![]() is virtually
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then it is virtually
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then it is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable for every
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable for every
![]() $\pi $
-finite local ring spectrum
$\pi $
-finite local ring spectrum
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field
$\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
(e.g.,
$\mathbb {F}_p$
(e.g.,
![]() $\mathfrak {R}=\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
).
$\mathfrak {R}=\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
).
Proof. Apply Proposition 6.4 to the map
![]() $\mathfrak {R} \to \mathbb {F}_p$
.
$\mathfrak {R} \to \mathbb {F}_p$
.
6.2
 $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-Orientations and higher roots of unity
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-Orientations and higher roots of unity
Higher roots of unity
We now turn to the case
![]() $\mathfrak {R}= \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
for some
$\mathfrak {R}= \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
for some
![]() $r\in \mathbb {N}$
. Since the shifted Brown–Comenetz dual of
$r\in \mathbb {N}$
. Since the shifted Brown–Comenetz dual of
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
is given by
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
is given by
a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-pre-orientation of height n of
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-pre-orientation of height n of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is the same thing as a
${\mathscr {C}}$
is the same thing as a
![]() $p^r$
-th root of unity of height n in
$p^r$
-th root of unity of height n in ![]() , in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Definition 4.2] (see Example 3.7). To compare the theory developed in this paper with the one in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b], we shall further assume that
, in the sense of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Definition 4.2] (see Example 3.7). To compare the theory developed in this paper with the one in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b], we shall further assume that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is stable. At height
${\mathscr {C}}$
is stable. At height
![]() $n=0$
, a
$n=0$
, a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-pre-orientation is an orientation if and only if the corresponding root of unity is primitive. At higher heights, the situation is, in general, more subtle, but this does continue to hold under the assumption that
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-pre-orientation is an orientation if and only if the corresponding root of unity is primitive. At higher heights, the situation is, in general, more subtle, but this does continue to hold under the assumption that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. More precisely, we have the following:
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. More precisely, we have the following:
Proposition 6.6. Let ![]() , and let
, and let ![]() . If
. If
![]() $\omega $
is an orientation, then it is a primitive
$\omega $
is an orientation, then it is a primitive
![]() $p^r$
-th root of unity. The converse holds if
$p^r$
-th root of unity. The converse holds if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable.
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable.
Proof. Assume that
![]() $\omega $
is an orientation. First, by Proposition 6.1,
$\omega $
is an orientation. First, by Proposition 6.1,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height n at p. Second, it follows by Proposition 4.5 that for every commutative algebra
${\mathscr {C}}$
is of height n at p. Second, it follows by Proposition 4.5 that for every commutative algebra
![]() $S \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the composition
$S \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the composition ![]() , which we denote by
, which we denote by
![]() $\omega _S$
, is an orientation on S. Now, if
$\omega _S$
, is an orientation on S. Now, if
then we have a commutative triangle in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
,
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
,

But then, by Proposition 3.22, the map
![]() $S[C_{p^r}] \xrightarrow {p^{r-1}} S[C_{p^r}]$
factors through the augmentation
$S[C_{p^r}] \xrightarrow {p^{r-1}} S[C_{p^r}]$
factors through the augmentation
![]() $S[C_{p^r}] \xrightarrow {\;\varepsilon _0\;} S$
, which implies
$S[C_{p^r}] \xrightarrow {\;\varepsilon _0\;} S$
, which implies
![]() $S=0$
.
$S=0$
.
Conversely, assume that
![]() $\omega $
is primitive and that
$\omega $
is primitive and that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. By Corollary 6.5,
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. By Corollary 6.5,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}/p^r,n)$
-orientable, and since we can check that
$(\mathbb {Z}/p^r,n)$
-orientable, and since we can check that
![]() $\omega $
is an orientation after a faithful extension of scalars, we can in fact assume without loss of generality that
$\omega $
is an orientation after a faithful extension of scalars, we can in fact assume without loss of generality that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}/p^r,n)$
-orientable. Choose some
$(\mathbb {Z}/p^r,n)$
-orientable. Choose some
![]() $\zeta \in \textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathbb {Z}/p^r}({\mathscr {C}})$
, and consider the composition
$\zeta \in \textrm {Or}^{(n)}_{\mathbb {Z}/p^r}({\mathscr {C}})$
, and consider the composition
This map is represented by a sequence of orthogonal idempotents ![]() , with the property
, with the property
![]() $e_0 + \dots + e_{p^r-1}= 1$
. Thus, we get a decomposition
$e_0 + \dots + e_{p^r-1}= 1$
. Thus, we get a decomposition
Since the subfunctor
is co-representable, it preserves products. It therefore suffices to show that each of the compositions
for
![]() $j=0,\dots ,p^r-1$
, corresponds to an orientation. We observe that by Proposition 3.22, for each such j, we have
$j=0,\dots ,p^r-1$
, corresponds to an orientation. We observe that by Proposition 3.22, for each such j, we have
If j is divisible by p, then
By the primitivity of j, we get that ![]() , and hence,
, and hence,
![]() $\pi _j(\omega )$
is trivially an orientation. For j that is not divisible by p, the induced map
$\pi _j(\omega )$
is trivially an orientation. For j that is not divisible by p, the induced map ![]() is an isomorphism, and hence,
is an isomorphism, and hence,
![]() $\zeta ^j$
is an orientation. Consequently,
$\zeta ^j$
is an orientation. Consequently,
![]() $\pi _j(\omega )= \pi _j(\zeta ^j)$
is an orientation as well.
$\pi _j(\omega )= \pi _j(\zeta ^j)$
is an orientation as well.
Higher cyclotomic extensions
In Proposition 4.18, we have shown that
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-orientations of height n are classified by a certain commutative algebra called
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-orientations of height n are classified by a certain commutative algebra called ![]() , which was constructed in a rather indirect manner. In contrast, primitive
, which was constructed in a rather indirect manner. In contrast, primitive
![]() $p^r$
-th roots of unity of height n are classified by the higher cyclotomic extension
$p^r$
-th roots of unity of height n are classified by the higher cyclotomic extension ![]() , which was constructed in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Definition 4.7] by a fairly explicit formula – namely, by splitting a certain idempotent in the group algebra
, which was constructed in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Definition 4.7] by a fairly explicit formula – namely, by splitting a certain idempotent in the group algebra ![]() . As a consequence of Proposition 6.6, these two algebras coincide under the assumption of virtual
. As a consequence of Proposition 6.6, these two algebras coincide under the assumption of virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability.
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability.
Corollary 6.7. Let ![]() be virtually
be virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. For every
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. For every
![]() $r\in \mathbb {N}$
,
$r\in \mathbb {N}$
,
Proof. By Proposition 6.6, both objects co-represent the same subfunctor of
Hence, the claim follows from the Yoneda lemma.
Using higher cyclotomic extensions and the comparison between higher roots of unity and orientations, we can also show that nil-conservative functors detect virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability. We first need a lemma regarding the functoriality of primitive roots of unity.
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability. We first need a lemma regarding the functoriality of primitive roots of unity.
Lemma 6.8. Let
![]() $F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in
$F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in ![]() . For every
. For every
![]() $R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
of height n at p, the induced map
$R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
of height n at p, the induced map
![]() $\mu _{p^r}^{(n)}(R) \rightarrow \mu _{p^r}^{(n)}(F(R))$
takes primitive roots to primitive roots.
$\mu _{p^r}^{(n)}(R) \rightarrow \mu _{p^r}^{(n)}(F(R))$
takes primitive roots to primitive roots.
Proof. Using the adjunction
a root ![]() is primitive if and only if
is primitive if and only if
Since F is symmetric monoidal and colimit-preserving, applying F to the left-hand side, we obtain
which is zero if and only if
![]() $F(\omega )$
is primitive.
$F(\omega )$
is primitive.
Proposition 6.9. Let
![]() $F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in
$F\colon {\mathscr {C}} \to {\mathscr {D}}$
in ![]() be nil-conservative. If
be nil-conservative. If
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {D}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then so is
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then so is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
.
${\mathscr {C}}$
.
Proof. First, by Proposition 6.1,
![]() ${\mathscr {D}}$
is of height n at p and therefore so is
${\mathscr {D}}$
is of height n at p and therefore so is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 4.4.2]. It follows that we can consider
${\mathscr {C}}$
, by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 4.4.2]. It follows that we can consider ![]() , the p-th cyclotomic extension of height n in
, the p-th cyclotomic extension of height n in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. By [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Proposition 4.9(2)], the commutative algebra
${\mathscr {C}}$
. By [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Proposition 4.9(2)], the commutative algebra ![]() is faithful; hence, if we show that it is
is faithful; hence, if we show that it is
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, the claim will follow. Consider the tautological
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, the claim will follow. Consider the tautological
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-pre-orientation (i.e., root of unity)
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-pre-orientation (i.e., root of unity) ![]() . Since F is nil-conservative, by Proposition 4.7, for
. Since F is nil-conservative, by Proposition 4.7, for
![]() $\omega $
to be an orientation, it suffices that
$\omega $
to be an orientation, it suffices that ![]() is an orientation. Since
is an orientation. Since
![]() $\omega $
is a primitive root of unity, by Lemma 6.8, so is
$\omega $
is a primitive root of unity, by Lemma 6.8, so is
![]() $F(\omega )$
, which is therefore an orientation by Proposition 6.6.
$F(\omega )$
, which is therefore an orientation by Proposition 6.6.
Remark 6.10. In fact, under the assumptions of Corollary 6.7, one can write an ‘explicit formula’ for ![]() , for any local ring spectrum
, for any local ring spectrum
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field
$\mathfrak {R}$
with residue field
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
. Indeed, let
$\mathbb {F}_p$
. Indeed, let ![]() be the idempotent for which
be the idempotent for which ![]() , and denote by
, and denote by ![]() its image under the map
its image under the map ![]() By Proposition 4.41, we have
By Proposition 4.41, we have
The results above show also that virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability implies that the higher cyclotomic extensions are Galois.
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability implies that the higher cyclotomic extensions are Galois.
Proposition 6.11. Let ![]() be virtually
be virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. For every
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. For every
![]() $r\in \mathbb {N}$
, the cyclotomic extension
$r\in \mathbb {N}$
, the cyclotomic extension ![]() is faithful
is faithful
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^\times $
-Galois.
$(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^\times $
-Galois.
Proof. By Corollary 6.7, we have ![]() . By Corollary 6.5,
. By Corollary 6.5,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}/p^r,n)$
-orientable, so
$(\mathbb {Z}/p^r,n)$
-orientable, so ![]() is faithful by Proposition 4.24. Thus, the claim follows from Proposition 4.22.
is faithful by Proposition 4.24. Thus, the claim follows from Proposition 4.22.
Warning 6.12. For a general, nonvirtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable,
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, ![]() , it may happen that
, it may happen that ![]() fails to be Galois. In particular, it is possible that
fails to be Galois. In particular, it is possible that ![]() , and so a primitive root of unity fails to be an orientation. This occurs in some examples constructed by Allen Yuan using the Segal conjecture; see [Reference YuanYua22].
, and so a primitive root of unity fails to be an orientation. This occurs in some examples constructed by Allen Yuan using the Segal conjecture; see [Reference YuanYua22].
We have shown that a virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable ![]() enjoys the following two, seemingly unrelated, properties:
enjoys the following two, seemingly unrelated, properties:
-
(1) All the higher cyclotomic extensions
 are
are
 $(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^\times $
-Galois (Proposition 6.11).
$(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^\times $
-Galois (Proposition 6.11). -
(2) All n-finite p-spaces are
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine (Theorem 6.2).
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine (Theorem 6.2).
However, taken together, they turn out to characterize virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability in the stable setting. In fact, the converse implication requires only the following a priori weaker versions of the above two properties:
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability in the stable setting. In fact, the converse implication requires only the following a priori weaker versions of the above two properties:
Proposition 6.13. Let ![]() be of height n at p. Then
be of height n at p. Then
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable if and only if the following holds:
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable if and only if the following holds:
-
(1) The higher cyclotomic extension
 is
is
 $\mathbb {F}_p^\times $
-Galois.
$\mathbb {F}_p^\times $
-Galois. -
(2) The spaces
 $B^k C_p$
, for
$B^k C_p$
, for
 $k= \lceil \frac {n}{2}\rceil + 1,\dots ,n$
, are
$k= \lceil \frac {n}{2}\rceil + 1,\dots ,n$
, are
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
Proof. As noted above, virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability implies conditions (1) and (2) by Proposition 6.11 and Theorem 6.2, respectively, so it remains to prove the converse. Since
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability implies conditions (1) and (2) by Proposition 6.11 and Theorem 6.2, respectively, so it remains to prove the converse. Since
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $1$
-semiadditive and
$1$
-semiadditive and ![]() is Galois, it is also faithful ([Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Remark 2.3] using [Reference RognesRog08, Proposition 6.3.3]). Thus, it will suffice to show that the canonical primitive p-th root of unity of height n of
is Galois, it is also faithful ([Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Remark 2.3] using [Reference RognesRog08, Proposition 6.3.3]). Thus, it will suffice to show that the canonical primitive p-th root of unity of height n of ![]() is an
is an
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation. Equivalently, by base-changing to
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation. Equivalently, by base-changing to ![]() , it suffices to show that if
, it suffices to show that if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
itself admits a primitive p-th root of unity
${\mathscr {C}}$
itself admits a primitive p-th root of unity ![]() , then
, then
![]() $\omega $
is an
$\omega $
is an
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation. We will first use condition (1) to show that
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation. We will first use condition (1) to show that
![]() $\Sigma ^n \mathbb {F}_p$
is an
$\Sigma ^n \mathbb {F}_p$
is an
![]() $\omega $
-oriented
$\omega $
-oriented
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-module and then use condition (2), and the various closure properties of oriented modules, to deduce that all the modules in
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-module and then use condition (2), and the various closure properties of oriented modules, to deduce that all the modules in
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathbb {F}_p}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
are
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathbb {F}_p}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
are
![]() $\omega $
-oriented.
$\omega $
-oriented.
Since ![]() is assumed to be Galois, the existence of the augmentation
is assumed to be Galois, the existence of the augmentation ![]() implies that it is split Galois. That is, we have an isomorphism
implies that it is split Galois. That is, we have an isomorphism ![]() which in the k-th coordinate is given by
which in the k-th coordinate is given by ![]() Thus, we get the following composite isomorphism:
Thus, we get the following composite isomorphism:
Observing that the canonical augmentation ![]() can be thought of as
can be thought of as
![]() $\omega ^0$
, it follows by Proposition 3.22 that the above isomorphism coincides with
$\omega ^0$
, it follows by Proposition 3.22 that the above isomorphism coincides with
![]() ${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
at
${\mathfrak {F}}_\omega $
at
![]() $\Sigma ^n \mathbb {F}_p$
. In other words, the module
$\Sigma ^n \mathbb {F}_p$
. In other words, the module
![]() $\Sigma ^n \mathbb {F}_p$
is
$\Sigma ^n \mathbb {F}_p$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented.
$\omega $
-oriented.
Next, for each
![]() $k= \lceil {\frac {n}{2}}\rceil + 1,\dots , n$
, consider the exact sequence
$k= \lceil {\frac {n}{2}}\rceil + 1,\dots , n$
, consider the exact sequence
By assumption,
![]() $B^k C_p= \lfloor {\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p}\rfloor $
is
$B^k C_p= \lfloor {\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p}\rfloor $
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Hence, by Proposition 4.12, if
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Hence, by Proposition 4.12, if
![]() $\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p$
is
$\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p$
is
![]() $\omega $
-orientable, then
$\omega $
-orientable, then
![]() $\Sigma ^{k-1}\mathbb {F}_p$
is
$\Sigma ^{k-1}\mathbb {F}_p$
is
![]() $\omega $
-orientable as well. Thus, by descending induction starting form
$\omega $
-orientable as well. Thus, by descending induction starting form
![]() $k=n$
, we get that
$k=n$
, we get that
![]() $\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p$
is
$\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented for all
$\omega $
-oriented for all
![]() $k=\lceil {\frac {n}{2}}\rceil ,\dots ,n$
. Furthermore, by Proposition 4.9, if
$k=\lceil {\frac {n}{2}}\rceil ,\dots ,n$
. Furthermore, by Proposition 4.9, if
![]() $\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p$
is
$\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented, then so is
$\omega $
-oriented, then so is
![]() $\Sigma ^{n-k}\mathbb {F}_p \simeq I_p^{(n)}{(\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p)}$
. Therefore,
$\Sigma ^{n-k}\mathbb {F}_p \simeq I_p^{(n)}{(\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p)}$
. Therefore,
![]() $\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p$
is
$\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p$
is
![]() $\omega $
-oriented for all
$\omega $
-oriented for all
![]() $k=0,\dots , n$
. Finally, every object of
$k=0,\dots , n$
. Finally, every object of
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathbb {F}_p}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
can be written as a finite direct sum of objects of the form
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathbb {F}_p}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
can be written as a finite direct sum of objects of the form
![]() $\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p$
for
$\Sigma ^k \mathbb {F}_p$
for
![]() $k=0,\dots ,n$
. Thus, we deduce from the above and Proposition 4.10 that all such modules are
$k=0,\dots ,n$
. Thus, we deduce from the above and Proposition 4.10 that all such modules are
![]() $\omega $
-oriented and hence that
$\omega $
-oriented and hence that
![]() $\omega $
is an orientation.
$\omega $
is an orientation.
Remark 6.14. Every ![]() of height
of height
![]() $n=0$
is virtually
$n=0$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,0)$
-orientable. At height
$(\mathbb {F}_p,0)$
-orientable. At height
![]() $n=1$
, condition (2) of Proposition 6.13 is vacuous. Hence,
$n=1$
, condition (2) of Proposition 6.13 is vacuous. Hence,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,1)$
-orientable if and only if
$(\mathbb {F}_p,1)$
-orientable if and only if ![]() is Galois, which is, however, not always the case (see Warning 6.12). At heights
is Galois, which is, however, not always the case (see Warning 6.12). At heights
![]() $n\ge 2$
, condition (2) is nonvacuous, but we do not know whether it is implied by condition (1) or not.
$n\ge 2$
, condition (2) is nonvacuous, but we do not know whether it is implied by condition (1) or not.
6.3
 $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-Orientations
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-Orientations
 $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientability
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientability
In this subsection, we shall consider orientations for the ring
![]() $\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
. We begin with the observation that for every height, the data of a
$\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
. We begin with the observation that for every height, the data of a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-pre-orientation is nothing but a compatible sequence of
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-pre-orientation is nothing but a compatible sequence of
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-pre-orientations for all
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-pre-orientations for all
![]() $r\in \mathbb {N}$
. The quotient maps
$r\in \mathbb {N}$
. The quotient maps
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)} \twoheadrightarrow \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
induce a system of compatible maps
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)} \twoheadrightarrow \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
induce a system of compatible maps
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {Z}/p^r} \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}}$
.
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {Z}/p^r} \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}}$
.
Lemma 6.15. The assembly map
![]() $\underrightarrow {\operatorname {lim}}\, I_p^{(n)}{{(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)}}\rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}}$
is an isomorphism, so that we have
$\underrightarrow {\operatorname {lim}}\, I_p^{(n)}{{(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)}}\rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}}$
is an isomorphism, so that we have
Proof. Under the identification
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{{(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)}} \simeq \Sigma ^n \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
, the tower of maps
$I_p^{(n)}{{(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)}} \simeq \Sigma ^n \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
, the tower of maps
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^{r+1} \twoheadrightarrow \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
induces the sequence of maps
$\mathbb {Z}/p^{r+1} \twoheadrightarrow \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
induces the sequence of maps
![]() $\Sigma ^n \mathbb {Z}/p^r \hookrightarrow \Sigma ^n \mathbb {Z}/p^{r+1}$
, whose colimit is
$\Sigma ^n \mathbb {Z}/p^r \hookrightarrow \Sigma ^n \mathbb {Z}/p^{r+1}$
, whose colimit is
![]() $\Sigma ^n \mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p$
. Since the canonical map
$\Sigma ^n \mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p$
. Since the canonical map
is an isomorphism, the map
![]() $\underrightarrow {\operatorname {lim}}\, I_p^{(n)}{{(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)}} \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}} $
induces an isomorphism on homotopy groups and is thus an isomorphism as well.
$\underrightarrow {\operatorname {lim}}\, I_p^{(n)}{{(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)}} \rightarrow I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}} $
induces an isomorphism on homotopy groups and is thus an isomorphism as well.
Remark 6.16. It might seem more natural to speak of
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_p$
-(pre-)orientations rather than
$\mathbb {Z}_p$
-(pre-)orientations rather than
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-(pre-)orientations, but that would require us to take into account the p-adic topology of
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-(pre-)orientations, but that would require us to take into account the p-adic topology of
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_p$
in the construction of the Pontryagin/Brown–Comenetz dual, which is a technical complication we preferred to avoid. Namely, while the composition
$\mathbb {Z}_p$
in the construction of the Pontryagin/Brown–Comenetz dual, which is a technical complication we preferred to avoid. Namely, while the composition
is an isomorphism, the first map is merely an inclusion, which identifies the left-hand side, and hence
![]() $\hom _{\textrm {Ab}}(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}, \mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p)$
, with the subgroup of continuous group homomorphisms
$\hom _{\textrm {Ab}}(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}, \mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p)$
, with the subgroup of continuous group homomorphisms
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_p \to \mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p$
. The most adequate general framework appears to be that of commutative pro-
$\mathbb {Z}_p \to \mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p$
. The most adequate general framework appears to be that of commutative pro-
![]() $[0,n]$
-finite ring spectra, but it is outside the scope of this paper.
$[0,n]$
-finite ring spectra, but it is outside the scope of this paper.
We deduce the corresponding statement for orientations.
Proposition 6.17. Let ![]() . We have a canonical isomorphism
. We have a canonical isomorphism
Proof. By Lemma 6.15 and the fact that the group algebra functor preserves colimits, we have
Thus, by applying Proposition 4.41 to
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)} \twoheadrightarrow \mathbb {F}_p$
, we have
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)} \twoheadrightarrow \mathbb {F}_p$
, we have
Applying Proposition 4.41 to
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r \twoheadrightarrow \mathbb {F}_p$
, we get
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r \twoheadrightarrow \mathbb {F}_p$
, we get
Combining this with the above, we obtain the claimed isomorphism.
As in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Definition 4.10], we set
In the stable setting, we then obtain the following:
Corollary 6.18. Let ![]() be virtually
be virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. We have a canonical isomorphism
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. We have a canonical isomorphism
Virtual
 $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientability
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientability
At height
![]() $n=0$
, Corollary 6.18 implies that if
$n=0$
, Corollary 6.18 implies that if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is stable and virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is stable and virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,0)$
-orientable, then it is also virtually
$(\mathbb {F}_p,0)$
-orientable, then it is also virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},0)$
-orientable. Indeed,
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},0)$
-orientable. Indeed, ![]() is then the ordinary infinite cyclotomic extension
is then the ordinary infinite cyclotomic extension ![]() , which is always faithful (since, say, it has
, which is always faithful (since, say, it has ![]() as a retract). However, for higher heights n, virtual
as a retract). However, for higher heights n, virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability need not imply virtual
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability need not imply virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability, even in the stable setting. Namely, even though each
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability, even in the stable setting. Namely, even though each ![]() is faithful, the filtered colimit
is faithful, the filtered colimit ![]() may no longer be. Nevertheless, there are still some general observations that can be made. Recall from Definition 4.26, that the Bousfield localization of
may no longer be. Nevertheless, there are still some general observations that can be made. Recall from Definition 4.26, that the Bousfield localization of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
with respect to
${\mathscr {C}}$
with respect to ![]() is denoted by
is denoted by
![]() $\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n}$
. We shall show that this localization is smashing and identify its unit. The commutative algebra
$\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n}$
. We shall show that this localization is smashing and identify its unit. The commutative algebra ![]() is acted on by the group
is acted on by the group
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_p^\times $
, whose torsion subgroup is
$\mathbb {Z}_p^\times $
, whose torsion subgroup is
 $$\begin{align*}T_p= \begin{cases} \mathbb{Z}/(p-1) & p \text{ is odd}. \\ \mathbb{Z}/2 & p=2. \end{cases} \end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}T_p= \begin{cases} \mathbb{Z}/(p-1) & p \text{ is odd}. \\ \mathbb{Z}/2 & p=2. \end{cases} \end{align*}$$
Furthermore, using the p-adic logarithm, we get an isomorphism
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_p^\times \simeq T_p \times \mathbb {Z}_p,$
which provides a distinguished dense subgroup
$\mathbb {Z}_p^\times \simeq T_p \times \mathbb {Z}_p,$
which provides a distinguished dense subgroup
Proposition 6.19. Let ![]() be virtually
be virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable for some
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable for some
![]() $n\ge 1$
. Then,
$n\ge 1$
. Then,
![]() $\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n}$
is a smashing localization of
$\widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n}$
is a smashing localization of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
with unit
${\mathscr {C}}$
with unit ![]() In other words, the corresponding localization functor
In other words, the corresponding localization functor
![]() $L\colon {\mathscr {C}} \rightarrow \widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n}$
is given by
$L\colon {\mathscr {C}} \rightarrow \widehat {{\mathscr {C}}}_{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n}$
is given by
Proof. We need to show that ![]() is an idempotent algebra in the same Bousfield class as
is an idempotent algebra in the same Bousfield class as ![]() . We first observe that since
. We first observe that since
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is both
${\mathscr {C}}$
is both
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditive and stable, we have
$\infty $
-semiadditive and stable, we have
Hence, the operation
![]() $(-)^{h G} \simeq ((-)^{hT_p})^{h\mathbb {Z}}$
commutes with colimits and the tensor product. In particular, for every
$(-)^{h G} \simeq ((-)^{hT_p})^{h\mathbb {Z}}$
commutes with colimits and the tensor product. In particular, for every
![]() $X\in {\mathscr {C}}$
, we have
$X\in {\mathscr {C}}$
, we have
where we set ![]() . Now, on the one hand, we have a map
. Now, on the one hand, we have a map
Hence, every R-acyclic object is also ![]() -acyclic. On the other hand, if
-acyclic. On the other hand, if
![]() $X\in {\mathscr {C}}$
is
$X\in {\mathscr {C}}$
is ![]() -acyclic, then we have
-acyclic, then we have
so X is also R-acyclic. Consequently, R and ![]() are Bousfield equivalent.
are Bousfield equivalent.
Next, we show that R is an idempotent algebra. Using the notation
we have
and thus
It remains to show that the commutative R-algebra unit map
![]() $R \to C(\mathbb {Z}_p; R)^{h\mathbb {Z}}$
is an isomorphism. In fact, this holds for every stable p-complete presentably symmetric monoidal
$R \to C(\mathbb {Z}_p; R)^{h\mathbb {Z}}$
is an isomorphism. In fact, this holds for every stable p-complete presentably symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
and
${\mathscr {C}}$
and
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, such as our
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, such as our
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
(by Proposition 6.1 and the assumption
${\mathscr {C}}$
(by Proposition 6.1 and the assumption
![]() $n\ge 1$
). It suffices to check this in the universal case
$n\ge 1$
). It suffices to check this in the universal case
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}= \widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_p$
and for the unit
${\mathscr {C}}= \widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_p$
and for the unit
![]() $R= \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
. Furthermore, since both sides are connective, it suffices to check this after tensoring with
$R= \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
. Furthermore, since both sides are connective, it suffices to check this after tensoring with
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_p)$
. Denoting by
$\mathbb {F}_p \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_p)$
. Denoting by
![]() $\sigma $
the action of
$\sigma $
the action of
![]() $1\in \mathbb {Z}$
on
$1\in \mathbb {Z}$
on
![]() $C(\mathbb {Z}_p; \mathbb {F}_p)$
, the claim becomes equivalent to the exactness of the short sequence of abelian groups
$C(\mathbb {Z}_p; \mathbb {F}_p)$
, the claim becomes equivalent to the exactness of the short sequence of abelian groups
which can be easily verified by an explicit computation.
Finally, virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability can be bootstrapped ‘all the way up’.
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability can be bootstrapped ‘all the way up’.
Proposition 6.20. Let ![]() . If
. If
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable, then it is virtually
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable, then it is virtually
![]() $(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable for every local ring spectrum R with residue field
$(\mathfrak {R},n)$
-orientable for every local ring spectrum R with residue field
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
.
$\mathbb {F}_p$
.
Namely, by replacing virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability with virtual
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability with virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability, we can remove the
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability, we can remove the
![]() $\pi $
-finiteness assumption from Corollary 6.5.
$\pi $
-finiteness assumption from Corollary 6.5.
Proof. By Corollary 4.42, it suffices to consider the initial case
![]() $R = \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
, and by Remark 3.4, we can further reduce to
$R = \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
, and by Remark 3.4, we can further reduce to
![]() $R = \tau _{\le n} \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
. The result now follows from Proposition 6.4 applied to the map
$R = \tau _{\le n} \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
. The result now follows from Proposition 6.4 applied to the map
6.4
 $\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-Orientations and connectedness
$\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-Orientations and connectedness
By Proposition 6.20, a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientation of height n for
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientation of height n for ![]() can be lifted to an
can be lifted to an
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation after a faithful extension of scalars. To study the existence of such a lift in
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation after a faithful extension of scalars. To study the existence of such a lift in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
itself, we proceed in steps by climbing up the Postnikov tower of
${\mathscr {C}}$
itself, we proceed in steps by climbing up the Postnikov tower of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
. In general, for each
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
. In general, for each
![]() $d=0,\dots ,n$
, there will be an obstruction for lifting a
$d=0,\dots ,n$
, there will be an obstruction for lifting a
![]() $\tau _{\le d-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation to a
$\tau _{\le d-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation to a
![]() $\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation. Here, by convention, we set
$\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation. Here, by convention, we set
To study this extension problem, we shall introduce a certain d-connectedness property of the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
that will be closely related to the vanishing of these obstructions.
${\mathscr {C}}$
that will be closely related to the vanishing of these obstructions.
Spherical cyclotomic extensions
We begin by showing that the truncated spherical cyclotomic extensions are pro-Galois extensions. We proceed by approximating
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
by
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
by
![]() $\pi $
-finite local rings, using an argument we learned from Dustin Clausen. Consider the standard cosimplicial resolution (aka Amitsur complex) of the map
$\pi $
-finite local rings, using an argument we learned from Dustin Clausen. Consider the standard cosimplicial resolution (aka Amitsur complex) of the map
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}\to \mathbb {F}_p$
:
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}\to \mathbb {F}_p$
:
The partial totalizations
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{p,s} := \textrm {Tot}^s (\mathbb {F}_p^{\otimes _{\mathbb {S}} (\bullet + 1)})$
for
$\mathbb {S}_{p,s} := \textrm {Tot}^s (\mathbb {F}_p^{\otimes _{\mathbb {S}} (\bullet + 1)})$
for
![]() $s\ge 0$
assemble into a tower in
$s\ge 0$
assemble into a tower in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
under
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}})$
under
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
.
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
.
Lemma 6.21. For every
![]() $s \ge 0$
, the partial totalization
$s \ge 0$
, the partial totalization
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
has finite homotopy groups and is a local ring spectrum with residue field
$\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
has finite homotopy groups and is a local ring spectrum with residue field
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
. Moreover, for every
$\mathbb {F}_p$
. Moreover, for every
![]() $t\ge 0$
, we have
$t\ge 0$
, we have
![]() $\underleftarrow {\operatorname {lim}\,} \pi _t(\mathbb {S}_{p,s}) \simeq \pi _t(\mathbb {S}_p)$
.
$\underleftarrow {\operatorname {lim}\,} \pi _t(\mathbb {S}_{p,s}) \simeq \pi _t(\mathbb {S}_p)$
.
Proof. By the computation of the dual Steenrod algebra, the ring spectrum
![]() $\mathcal{A}^\vee = \mathbb {F}_p \otimes _{\mathbb {S}} \mathbb {F}_p$
has finite homotopy groups and
$\mathcal{A}^\vee = \mathbb {F}_p \otimes _{\mathbb {S}} \mathbb {F}_p$
has finite homotopy groups and
![]() $\pi _0 \mathcal{A}^\vee \simeq \mathbb {F}_p$
. Hence, the same holds for
$\pi _0 \mathcal{A}^\vee \simeq \mathbb {F}_p$
. Hence, the same holds for
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p^{\otimes _{\mathbb {S}} (k+1)} \simeq (\mathcal{A}^\vee )^{\otimes _{\mathbb {F}_p} k}$
for every
$\mathbb {F}_p^{\otimes _{\mathbb {S}} (k+1)} \simeq (\mathcal{A}^\vee )^{\otimes _{\mathbb {F}_p} k}$
for every
![]() $k \ge 0$
. Now, each
$k \ge 0$
. Now, each
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
can be written as a finite limit of the rings
$\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
can be written as a finite limit of the rings
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p^{\otimes _{\mathbb {S}} (k+1)}$
for
$\mathbb {F}_p^{\otimes _{\mathbb {S}} (k+1)}$
for
![]() $k=0,\dots s$
. From this, we deduce that the homotopy groups of
$k=0,\dots s$
. From this, we deduce that the homotopy groups of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
are also finite. Moreover, since the functor of units
$\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
are also finite. Moreover, since the functor of units
![]() $(-)^\times $
is a right adjoint, it preserves limits. It follows that an element in (the underlying space of)
$(-)^\times $
is a right adjoint, it preserves limits. It follows that an element in (the underlying space of)
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
is invertible if and only if its image is invertible in each
$\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
is invertible if and only if its image is invertible in each
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p^{\otimes _{\mathbb {S}} (k+1)}$
. We conclude that
$\mathbb {F}_p^{\otimes _{\mathbb {S}} (k+1)}$
. We conclude that
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
is local with residue field
$\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
is local with residue field
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
. Alternatively, from a more computational perspective, the above facts may be deduced from the multiplicative spectral sequence arising from the finite filtration of
$\mathbb {F}_p$
. Alternatively, from a more computational perspective, the above facts may be deduced from the multiplicative spectral sequence arising from the finite filtration of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
by the lower partial totalizations.
$\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
by the lower partial totalizations.
Finally, by the convergence of the Adams spectral sequence at
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{p}$
, we have
$\mathbb {S}_{p}$
, we have
![]() $\underleftarrow {\operatorname {lim}\,} \mathbb {S}_{p,s} \simeq \mathbb {S}_p$
. Since all the homotopy groups of all the partial totalizations
$\underleftarrow {\operatorname {lim}\,} \mathbb {S}_{p,s} \simeq \mathbb {S}_p$
. Since all the homotopy groups of all the partial totalizations
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
are finite, the Mittag-Leffler condition is satisfied, and therefore, for all
$\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
are finite, the Mittag-Leffler condition is satisfied, and therefore, for all
![]() $t \ge 0$
, we have
$t \ge 0$
, we have
![]() $\underleftarrow {\operatorname {lim}\,} \pi _t(\mathbb {S}_{p,s}) \simeq \pi _t(\mathbb {S}_p)$
.
$\underleftarrow {\operatorname {lim}\,} \pi _t(\mathbb {S}_{p,s}) \simeq \pi _t(\mathbb {S}_p)$
.
Next, we show that the Brown–Comenetz duals of (the truncations of)
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
also approximate the Brown–Comenetz dual of (the truncations of)
$\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
also approximate the Brown–Comenetz dual of (the truncations of)
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
.
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
.
Lemma 6.22. For all
![]() $0 \le d \le n$
, the augmented tower
$0 \le d \le n$
, the augmented tower
induces an isomorphism
Proof. By Lemma 6.21, for all
![]() $t \ge 0$
,
$t \ge 0$
,
 $$\begin{align*}\underleftarrow{\operatorname{lim}\,}_s (\pi_t\mathbb{S}_{p,s}) \simeq \pi_t\mathbb{S}_p = \begin{cases} \mathbb{Z}_p & t = 0 \\ p\textrm{-finite} & t > 0. \end{cases} \end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\underleftarrow{\operatorname{lim}\,}_s (\pi_t\mathbb{S}_{p,s}) \simeq \pi_t\mathbb{S}_p = \begin{cases} \mathbb{Z}_p & t = 0 \\ p\textrm{-finite} & t > 0. \end{cases} \end{align*}$$
Since both
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_p$
and all finite abelian groups are topologically finitely generated, we deduce that the above isomorphism holds as pro-finite abelian groups and therefore induces an isomorphism on continuous Pontryagin duals. This implies that the composition
$\mathbb {Z}_p$
and all finite abelian groups are topologically finitely generated, we deduce that the above isomorphism holds as pro-finite abelian groups and therefore induces an isomorphism on continuous Pontryagin duals. This implies that the composition
is an isomorphism (see Remark 6.16), which implies the claim.
We deduce that the (truncated) spherical cyclotomic extension can be well approximated by the (truncated)
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
-cyclotomic extensions.
$\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
-cyclotomic extensions.
Proposition 6.23. Let ![]() . For all
. For all
![]() $0 \le d \le n$
, there is an isomorphism
$0 \le d \le n$
, there is an isomorphism
Proof. Applying the colimit-preserving functor ![]() to the isomorphism in Lemma 6.22, we get
to the isomorphism in Lemma 6.22, we get
Since all the maps in the augmented tower are strict maps of local rings, by Proposition 4.41, we get the desired isomorphism by tensoring with ![]() over
over ![]() .
.
Theorem 6.24. Let ![]() be virtually
be virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p.n)$
-orientable. For every
$(\mathbb {F}_p.n)$
-orientable. For every
![]() $0 \le d \le n$
, the truncated spherical cyclotomic extension
$0 \le d \le n$
, the truncated spherical cyclotomic extension ![]() is pro-Galois with respect to the pro-
is pro-Galois with respect to the pro-
![]() $\pi $
-finite group
$\pi $
-finite group
![]() $\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_p^\times = \underleftarrow{\operatorname {lim}\,}_s (\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{p,s}^\times )$
.
$\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_p^\times = \underleftarrow{\operatorname {lim}\,}_s (\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{p,s}^\times )$
.
Proof. Each
![]() $\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
is n-truncated and
$\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{p,s}$
is n-truncated and
![]() $\pi $
-finite. Hence, by Corollary 6.5,
$\pi $
-finite. Hence, by Corollary 6.5,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {S}_{p,s},n)$
-orientable, and by Proposition 4.22,
$(\mathbb {S}_{p,s},n)$
-orientable, and by Proposition 4.22, ![]() is
is
![]() $\tau _{\leq d}\mathbb {S}_{p,s}^\times $
-Galois. By naturality, these actions are compatible when s varies. It remains to observe that the limit of
$\tau _{\leq d}\mathbb {S}_{p,s}^\times $
-Galois. By naturality, these actions are compatible when s varies. It remains to observe that the limit of
![]() $\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{p,s}^\times $
is
$\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{p,s}^\times $
is
![]() $\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_p^\times $
. Indeed, by Lemma 6.21,
$\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_p^\times $
. Indeed, by Lemma 6.21,
![]() $\underleftarrow {\operatorname {lim}\,} \tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{p,s} \simeq \tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_p$
, and taking the spectrum of units
$\underleftarrow {\operatorname {lim}\,} \tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{p,s} \simeq \tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_p$
, and taking the spectrum of units
![]() $(-)^\times $
preserves limits.
$(-)^\times $
preserves limits.
Categorical connectedness
To study the problem of constructing truncated spherical orientations, we introduce the following notion:
Definition 6.25. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
${\mathscr {C}}\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
, and let
![]() $d\ge -2$
be an integer. We say that
$d\ge -2$
be an integer. We say that
-
(1) A space A is
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective if the canonical map is an isomorphism.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective if the canonical map is an isomorphism.
-
(2)
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
is said to be d-connected at a prime p if every d-finite p-space A is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is said to be d-connected at a prime p if every d-finite p-space A is
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective.
Remark 6.26. If A happens to be
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then by Proposition 2.30, we have an isomorphism
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine, then by Proposition 2.30, we have an isomorphism
and the canonical inclusion of A into the above space corresponds to the trivial A-Galois extensions. Thus, A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective if and only if all the A-Galois extensions of
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective if and only if all the A-Galois extensions of ![]() are trivial. Furthermore, if every d-finite p-space A is
are trivial. Furthermore, if every d-finite p-space A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine – for example, if
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine – for example, if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable for some
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable for some
![]() $n\ge d$
(Theorem 6.2) – then
$n\ge d$
(Theorem 6.2) – then
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p if and only if it has no nontrivial Galois extensions over such spaces.
${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p if and only if it has no nontrivial Galois extensions over such spaces.
The first few values of d recover some familiar notions:
Example 6.27. First, since ![]() is initial in
is initial in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, every
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, every
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is (
${\mathscr {C}}$
is (
![]() $-2$
)-connected. Second, since
$-2$
)-connected. Second, since ![]() is the zero ring,
is the zero ring,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is (
${\mathscr {C}}$
is (
![]() $-1$
)-connected if and only if
$-1$
)-connected if and only if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \neq 0$
.
${\mathscr {C}} \neq 0$
.
Next, we have the following characterization of
![]() $0$
-connectedness:
$0$
-connectedness:
Proposition 6.28. For ![]() , the following are equivalent:
, the following are equivalent:
-
(1)
 ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
 $0$
-connected.
$0$
-connected. -
(2)
 is indecomposable.
is indecomposable. -
(3) For every decomposition
 $1 = \varepsilon + \delta $
in
$1 = \varepsilon + \delta $
in  such that
such that
 $\varepsilon $
and
$\varepsilon $
and
 $\delta $
are idempotents with
$\delta $
are idempotents with
 $\varepsilon \delta = 0$
, we have either
$\varepsilon \delta = 0$
, we have either
 $\varepsilon = 1$
and
$\varepsilon = 1$
and
 $\delta = 0$
or vice versa.
$\delta = 0$
or vice versa.
Proof. To show that (1) implies (2), we assume by contradiction that ![]() decomposes as
decomposes as ![]() with both R and S nonzero. Then, the set
with both R and S nonzero. Then, the set

contains at least 4 elements. It follows that the set with two elements is not
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective, contradicting (1).
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective, contradicting (1).
Now, (2) implies (3) because for every pair of idempotents ![]() as in (3), we have a decomposition of commutative rings
as in (3), we have a decomposition of commutative rings ![]() , and (2) implies that one of the factors is zero and hence
, and (2) implies that one of the factors is zero and hence
![]() $\varepsilon = 1$
and
$\varepsilon = 1$
and
![]() $\delta = 0$
, or vice versa.
$\delta = 0$
, or vice versa.
It remains to prove that (3) implies (1). For a finite set A, the ring ![]() admits a collection of orthogonal idempotents
admits a collection of orthogonal idempotents ![]() for
for
![]() $a\in A$
, such that
$a\in A$
, such that
![]() $\sum _{a\in A}\varepsilon _a= 1$
. Thus, by (3), every map
$\sum _{a\in A}\varepsilon _a= 1$
. Thus, by (3), every map ![]() has to send exactly one of the idempotents
has to send exactly one of the idempotents
![]() $\varepsilon _a$
to
$\varepsilon _a$
to ![]() . We get
. We get
Example 6.29. For an ordinary commutative ring R, Proposition 6.28 implies that the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_R$
is
![]() $0$
-connected if and only if the scheme
$0$
-connected if and only if the scheme
![]() $\operatorname{{Spec}}(R)$
is connected.
$\operatorname{{Spec}}(R)$
is connected.
As an application of Proposition 6.28, we deduce that
![]() $0$
-connectedness interacts well with categorification.
$0$
-connectedness interacts well with categorification.
Corollary 6.30. Let ![]() . Then,
. Then,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $0$
-connected if and only if
$0$
-connected if and only if
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{\mathscr {C}}}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{\mathscr {C}}}$
is
![]() $0$
-connected.
$0$
-connected.
Proof. By Proposition 6.28, it suffices to show that ![]() is indecomposable in
is indecomposable in
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
if and only if
${\mathscr {C}}$
if and only if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is indecomposable in
${\mathscr {C}}$
is indecomposable in
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
. First, assume
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
. First, assume ![]() is indecomposable, and let
is indecomposable, and let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}= {\mathscr {C}}_0\times {\mathscr {C}}_1$
in
${\mathscr {C}}= {\mathscr {C}}_0\times {\mathscr {C}}_1$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
. We get
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}})$
. We get
By our assumption, either ![]() or
or ![]() , and hence, either
, and hence, either
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_0\simeq 0$
or
${\mathscr {C}}_0\simeq 0$
or
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_1 \simeq 0$
.
${\mathscr {C}}_1 \simeq 0$
.
Conversely, given
![]() $R \simeq R_0\times R_1$
in
$R \simeq R_0\times R_1$
in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, then as in the proof of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 5.1.11], the 0-semiadditivity of
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, then as in the proof of [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 5.1.11], the 0-semiadditivity of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
implies that
${\mathscr {C}}$
implies that
By the indecomposability of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
, we get either
${\mathscr {C}}$
, we get either
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{R_0}({\mathscr {C}})= 0$
or
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{R_0}({\mathscr {C}})= 0$
or
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{R_1}({\mathscr {C}}) = 0$
, which implies either
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{R_1}({\mathscr {C}}) = 0$
, which implies either
![]() $R_0 = 0$
or
$R_0 = 0$
or
![]() $R_1 = 0$
.
$R_1 = 0$
.
The higher notions of connectedness depend on the prime p and are more subtle. A classical example is provided by Mandell’s theorem [Reference MandellMan01].
Example 6.31 (Mandell).
The
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\overline {\mathbb {F}}_p}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\overline {\mathbb {F}}_p}$
is
![]() $\infty $
-connected at p.
$\infty $
-connected at p.
Connectedness and higher semiadditivity
We shall, however, be interested in higher connectedness primarily in the higher semiadditive setting. In this case, we first observe that the semiadditive height gives an upper bound on connectedness.
Proposition 6.32. Let ![]() . If the height of
. If the height of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
at p is
${\mathscr {C}}$
at p is
![]() $\le n$
, then
$\le n$
, then
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is not (
${\mathscr {C}}$
is not (
![]() $n+1$
)-connected at p.
$n+1$
)-connected at p.
Proof. Since the height of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
at p is at most n, the n-connected space
${\mathscr {C}}$
at p is at most n, the n-connected space
![]() $B^{n+1}C_p$
is
$B^{n+1}C_p$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-acyclic, so that
${\mathscr {C}}$
-acyclic, so that ![]() ; see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.1]. Thus, the canonical map
; see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.1]. Thus, the canonical map
is not an isomorphism.
To further analyze the collection of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective spaces, we use the Eilenberg–Moore property of affine spaces.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective spaces, we use the Eilenberg–Moore property of affine spaces.
Proposition 6.33. Let ![]() . The functor
. The functor
preserves pullbacks of diagrams
![]() $ A \to B \leftarrow C $
of
$ A \to B \leftarrow C $
of
![]() $\pi $
-finite spaces, where B is
$\pi $
-finite spaces, where B is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine.
Proof. As pushouts in
![]() $\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
are given by relative tensor products, this follows from Theorem 2.38 and the fact that representable functors take pushouts to pullbacks.
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
are given by relative tensor products, this follows from Theorem 2.38 and the fact that representable functors take pushouts to pullbacks.
This implies that under the assumption of affineness
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective spaces are closed under extensions and formation of fibers.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective spaces are closed under extensions and formation of fibers.
Proposition 6.34. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $f\colon A \to B$
be a map of
$f\colon A \to B$
be a map of
![]() $\pi $
-finite spaces, where B is
$\pi $
-finite spaces, where B is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective and
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective and
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Then, A is
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Then, A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective if and only if all the fibers of f are
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective if and only if all the fibers of f are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective.
Proof. Consider the canonical natural transformation
of functors
![]() $\mathcal{S} \to \mathcal{S}$
. The domain, being the identity functor, clearly preserves pullbacks. By Proposition 6.33, the codomain preserves the pullbacks of all diagrams of the form
$\mathcal{S} \to \mathcal{S}$
. The domain, being the identity functor, clearly preserves pullbacks. By Proposition 6.33, the codomain preserves the pullbacks of all diagrams of the form
![]() $A \xrightarrow {f} B \xleftarrow {\:b\:} \textrm {pt}.$
Now, consider the commutative diagram
$A \xrightarrow {f} B \xleftarrow {\:b\:} \textrm {pt}.$
Now, consider the commutative diagram

where the bottom arrow is an isomorphism since B is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective. It follows that the induced map on the fibers of the vertical maps at
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective. It follows that the induced map on the fibers of the vertical maps at
![]() $b\in B$
can be identified with the canonical map
$b\in B$
can be identified with the canonical map
Thus, A is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective if and only if
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective if and only if
![]() $f^{-1}(b)$
is
$f^{-1}(b)$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective for all
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective for all
![]() $b\in B$
.
$b\in B$
.
Assuming the affineness of all d-finite p-spaces, d-connectedness can be reduced to the
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflectivity of a single space.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflectivity of a single space.
Proposition 6.35. Let ![]() such that all d-finite p-spaces are
such that all d-finite p-spaces are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Then,
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Then,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p if and only if
${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p if and only if
![]() $B^d C_p$
is
$B^d C_p$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective.
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective.
Proof. If
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p, then by definition, all d-finite p-spaces are
${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p, then by definition, all d-finite p-spaces are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective and, in particular,
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective and, in particular,
![]() $B^d C_p$
. Conversely, assume that
$B^d C_p$
. Conversely, assume that
![]() $B^d C_p$
is
$B^d C_p$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective. The functor
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective. The functor
takes
![]() $\textrm {pt}$
to
$\textrm {pt}$
to
![]() $\textrm {pt}$
and preserves pullbacks of
$\textrm {pt}$
and preserves pullbacks of
![]() $\pi $
-finite spaces with a
$\pi $
-finite spaces with a
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine base (Proposition 6.33). Hence, it commutes with taking loops for d-finite p-spaces. It follows that
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine base (Proposition 6.33). Hence, it commutes with taking loops for d-finite p-spaces. It follows that
![]() $B^\ell C_p$
is
$B^\ell C_p$
is
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective for all
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective for all
![]() $\ell = 0,\dots d$
. Finally, by Proposition 6.34, the
$\ell = 0,\dots d$
. Finally, by Proposition 6.34, the
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective d-finite p-spaces are closed under extensions. Since all the d-finite p-spaces are generated under extensions by the spaces
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective d-finite p-spaces are closed under extensions. Since all the d-finite p-spaces are generated under extensions by the spaces
![]() $C_p, BC_p,\dots ,B^d C_p,$
it follows that all of them are
$C_p, BC_p,\dots ,B^d C_p,$
it follows that all of them are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective, so
${\mathscr {C}}$
-reflective, so
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p.
${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p.
It will be useful for the sequel to have a slight variant of the above.
Proposition 6.36. Let ![]() such that all d-finite p-spaces are
such that all d-finite p-spaces are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Then,
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Then,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p if and only if
${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p if and only if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is 0-connected and the space
${\mathscr {C}}$
is 0-connected and the space ![]() is d-connected, which then in particular implies that
is d-connected, which then in particular implies that
The subtle difference from Proposition 6.35 is that we do not, a priori, require the above isomorphism to be provided by the canonical map, at the expense of requiring
![]() $0$
-connectedness in advance.
$0$
-connectedness in advance.
Proof. The ‘only if’ part is clear. For the ‘if’ part, consider the canonical map
By assumption, both the source and target are
![]() $(d-1)$
-connected, so it suffices to show that we get an isomorphism after applying the d-fold loop space functor. Now, as in the proof of Proposition 6.35, the functor
$(d-1)$
-connected, so it suffices to show that we get an isomorphism after applying the d-fold loop space functor. Now, as in the proof of Proposition 6.35, the functor ![]() commutes with taking loops for d-finite p-spaces. Thus, applying
commutes with taking loops for d-finite p-spaces. Thus, applying
![]() $\Omega ^d$
we get the canonical map
$\Omega ^d$
we get the canonical map
which is an isomorphism by the assumption that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $0$
-connected.
$0$
-connected.
Connectedness and orientations
The notions of connectedness at p and
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientability interact in a nontrivial way.
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientability interact in a nontrivial way.
Proposition 6.37. Let ![]() . If
. If
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then it is not
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then it is not
![]() $(n+1)$
-connected at p.
$(n+1)$
-connected at p.
Furthermore, by Theorem 6.2, when
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, all n-finite p-spaces are
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, all n-finite p-spaces are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Hence, by Proposition 6.36, for every
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine. Hence, by Proposition 6.36, for every
![]() $d\le n$
, the d-connectedness of
$d\le n$
, the d-connectedness of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
depends only on the properties of the commutative algebra
${\mathscr {C}}$
depends only on the properties of the commutative algebra ![]() . When
. When
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is actually
${\mathscr {C}}$
is actually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-oriented, we can further reformulate the d-connectedness property in terms of the space
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-oriented, we can further reformulate the d-connectedness property in terms of the space
of p-th roots of unity of ![]() .
.
Proposition 6.38. Let ![]() be
be
![]() $0$
-connected and
$0$
-connected and
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. For every
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. For every
![]() $d\le n$
, the
$d\le n$
, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p if and only if
${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p if and only if
Proof. From the
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability, we deduce that all the d-finite p-spaces are
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability, we deduce that all the d-finite p-spaces are
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine (Theorem 6.2). Thus, by Proposition 6.36,
${\mathscr {C}}$
-affine (Theorem 6.2). Thus, by Proposition 6.36,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected if and only if it is 0-connected, and the space
${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected if and only if it is 0-connected, and the space ![]() is isomorphic to
is isomorphic to
![]() $B^d C_p$
. Using the Fourier transform, we get
$B^d C_p$
. Using the Fourier transform, we get
Now, applying the various adjunctions, we get
Thus,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected if and only if it is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected if and only if it is
![]() $0$
-connected and the space
$0$
-connected and the space ![]() is isomorphic to
is isomorphic to
![]() $B^d C_p$
, which completes the proof.
$B^d C_p$
, which completes the proof.
Remark 6.39. In particular, for ![]() which is
which is
![]() $0$
-connected and
$0$
-connected and
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-oriented, the space of
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-oriented, the space of
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-pre-orientations of height n is isomorphic to the discrete set
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-pre-orientations of height n is isomorphic to the discrete set
![]() $C_p$
. Its subspace of orientations consists of the nonzero elements
$C_p$
. Its subspace of orientations consists of the nonzero elements
![]() $C_p \smallsetminus \{0\}$
and is a torsor for the action of
$C_p \smallsetminus \{0\}$
and is a torsor for the action of
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p^\times $
by scaling.
$\mathbb {F}_p^\times $
by scaling.
The characterization of d-connectedness in terms of p-th roots of unity also implies that it interacts well with categorification.
Corollary 6.40. Let
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
be
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\textrm {Pr}})$
be
![]() $0$
-connected and
$0$
-connected and
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. For every
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. For every
![]() $d\leq n$
, the
$d\leq n$
, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p if and only if
${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p if and only if
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p.
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected at p.
Proof. By Corollary 6.30,
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $0$
-connected, and by Corollary 5.16,
$0$
-connected, and by Corollary 5.16,
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n+1)$
orientable. In addition, we have
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n+1)$
orientable. In addition, we have
Hence,
So the claim follows from Proposition 6.38.
Remark 6.41. While an
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is at most n-connected, its categorification
${\mathscr {C}}$
is at most n-connected, its categorification
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
can be
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
can be
![]() $(n+1)$
-connected. Furthermore, we shall see that
$(n+1)$
-connected. Furthermore, we shall see that
![]() $(n+1)$
-connectedness of
$(n+1)$
-connectedness of
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
can have interesting implications for
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
can have interesting implications for
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
itself.
${\mathscr {C}}$
itself.
Extending orientations
Our interest in d-connectedness stems from the fact that it allows one to extend
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientations to truncated
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientations to truncated
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientations. We begin with the somewhat more general setting. In Theorem 4.39, we have seen that given a strict map of local ring spectra
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientations. We begin with the somewhat more general setting. In Theorem 4.39, we have seen that given a strict map of local ring spectra
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
, an
$f\colon \mathfrak {R}\to \mathfrak {S}$
, an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-preorientation
$\mathfrak {R}$
-preorientation
![]() $\omega $
is an orientation if and only if
$\omega $
is an orientation if and only if
![]() $f_*\omega $
is an orientation. We shall now show that under more restrictive assumptions on f, the property of d-connectedness implies the stronger conclusion that every
$f_*\omega $
is an orientation. We shall now show that under more restrictive assumptions on f, the property of d-connectedness implies the stronger conclusion that every
![]() $\mathfrak {S}$
-orientation can be lifted to an
$\mathfrak {S}$
-orientation can be lifted to an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation.
Definition 6.42. Let
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
be a strict map of local rings in
$f\colon \mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
be a strict map of local rings in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
. We say that f is d-small if the fiber of f is
$\textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
. We say that f is d-small if the fiber of f is
![]() $[0,d-1]$
-finite and admits an
$[0,d-1]$
-finite and admits an
![]() $\mathfrak {S}$
-module structure.
$\mathfrak {S}$
-module structure.
Proposition 6.43. Let ![]() be d-connected at p, and let
be d-connected at p, and let
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
be a d-small map between local ring spectra with residue field
$f\colon \mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
be a d-small map between local ring spectra with residue field
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
. For
$\mathbb {F}_p$
. For
![]() $n\ge d$
, every
$n\ge d$
, every
![]() $\mathfrak {S}$
-orientation of
$\mathfrak {S}$
-orientation of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
of height n extends to an
${\mathscr {C}}$
of height n extends to an
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation.
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientation.
Proof. Let ![]() be an
be an
![]() $\mathfrak {S}$
-orientation. By Theorem 4.39, it would suffice to construct a lift as in the following diagram:
$\mathfrak {S}$
-orientation. By Theorem 4.39, it would suffice to construct a lift as in the following diagram:

See Remark 4.40. Let X be the fiber of
![]() $f\colon \mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
, as a map of spectra. The obstruction for the existence of
$f\colon \mathfrak {R} \to \mathfrak {S}$
, as a map of spectra. The obstruction for the existence of
![]() $\overline {\omega }$
lies in the group
$\overline {\omega }$
lies in the group
By the assumption that f is d-small, X is, in particular, connective and
![]() $(n-1)$
-truncated. Hence,
$(n-1)$
-truncated. Hence,
![]() $\Sigma ^{-1}(I_p^{(n)}{X}) \simeq I_p^{(n)}{(\Sigma X)}$
is connective. Consequently, we have
$\Sigma ^{-1}(I_p^{(n)}{X}) \simeq I_p^{(n)}{(\Sigma X)}$
is connective. Consequently, we have
By assumption, X is
![]() $\pi $
-finite and admits an
$\pi $
-finite and admits an
![]() $\mathfrak {S}$
-module structure. Thus, by the Fourier transform associated with
$\mathfrak {S}$
-module structure. Thus, by the Fourier transform associated with
![]() $\omega $
, we have
$\omega $
, we have
Finally, by our assumptions,
![]() $\lfloor {X}\rfloor $
is a
$\lfloor {X}\rfloor $
is a
![]() $(d-1)$
-finite p-space, so
$(d-1)$
-finite p-space, so
![]() $\lfloor {\Sigma X}\rfloor $
is a d-finite p-space, and hence, the d-connectedness of
$\lfloor {\Sigma X}\rfloor $
is a d-finite p-space, and hence, the d-connectedness of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
implies that
${\mathscr {C}}$
implies that
Since
![]() $\pi _0(\lfloor { \Sigma X}\rfloor )= \pi _0(\Sigma X) \simeq 0$
, we see that there is no obstruction to construct
$\pi _0(\lfloor { \Sigma X}\rfloor )= \pi _0(\Sigma X) \simeq 0$
, we see that there is no obstruction to construct
![]() $\overline {\omega }$
.
$\overline {\omega }$
.
This specializes to the following criterion for extending
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientations to truncated
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientations to truncated
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientations:
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientations:
Proposition 6.44. Let ![]() be d-connected at p. Every
be d-connected at p. Every
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of height n of
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of height n of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
extends to a
${\mathscr {C}}$
extends to a
![]() $\tau _{\leq d-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation.
$\tau _{\leq d-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation.
Proof. The claim holds vacuously for
![]() $d=0$
, so we may assume
$d=0$
, so we may assume
![]() $d \ge 1$
. Let
$d \ge 1$
. Let ![]() be an
be an
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. First, we extend
${\mathscr {C}}$
. First, we extend
![]() $\omega $
to a
$\omega $
to a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientation. For all
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientation. For all
![]() $r\ge 1$
, the quotient map
$r\ge 1$
, the quotient map
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^{r+1} \twoheadrightarrow \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
satisfies the assumptions of Proposition 6.43. Thus, applying it iteratively, we obtain a compatible sequence of
$\mathbb {Z}/p^{r+1} \twoheadrightarrow \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
satisfies the assumptions of Proposition 6.43. Thus, applying it iteratively, we obtain a compatible sequence of
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-orientations extending
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-orientations extending
![]() $\omega $
. Since
$\omega $
. Since
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}} \simeq \underrightarrow {\operatorname {lim}}\, I_p^{(n)}{{(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)}}$
by Lemma 6.15, and
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}} \simeq \underrightarrow {\operatorname {lim}}\, I_p^{(n)}{{(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)}}$
by Lemma 6.15, and
the colimit of the associated diagram is the desired extension of
![]() $\omega $
to a
$\omega $
to a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientation:
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientation:

Next, we proceed by induction on the Postnikov tower
Again, each map in the tower satisfies the conditions of Proposition 6.43, and thus, the
![]() $\tau _{\leq 0}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation
$\tau _{\leq 0}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation
![]() $\omega _{\le 0}$
can be extended inductively all the way to a
$\omega _{\le 0}$
can be extended inductively all the way to a
![]() $\tau _{\leq d-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation.
$\tau _{\leq d-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation.
If
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
admits an
${\mathscr {C}}$
admits an
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of height n, then it is not
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of height n, then it is not
![]() $(n+1)$
-connected (Proposition 6.37). Thus, the most we can get from Proposition 6.44 is when
$(n+1)$
-connected (Proposition 6.37). Thus, the most we can get from Proposition 6.44 is when
![]() $d=n$
, which when combined with Proposition 6.38 gives us the following:
$d=n$
, which when combined with Proposition 6.38 gives us the following:
Corollary 6.45. Let ![]() such that
such that
If
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then it is
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then it is
![]() $(\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable.
$(\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable.
This raises a natural question: When does a spectrum
![]() $M \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}_{(p)}$
admit an action of
$M \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}_{(p)}$
admit an action of
![]() $\tau _{\leq n-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
?
$\tau _{\leq n-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
?
In general, being a module over a truncated sphere is a (rather subtle) structure. However, for spectra concentrated in degrees
![]() $0$
to n, this structure degenerates to a property, which can moreover be detected on the level of homotopy groups.
$0$
to n, this structure degenerates to a property, which can moreover be detected on the level of homotopy groups.
Proposition 6.46. A spectrum
![]() $M\in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
admits a module structure over
$M\in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
admits a module structure over
![]() $\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
if and only if the action map
$\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
if and only if the action map
is zero. Moreover, this module structure is then unique.
Proof. The
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
admits a symmetric monoidal structure for which the truncation functor
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
admits a symmetric monoidal structure for which the truncation functor
![]() $\tau _{\le n}\colon \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}} \to \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
is symmetric monoidal. In particular, the unit is
$\tau _{\le n}\colon \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}} \to \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
is symmetric monoidal. In particular, the unit is
![]() $\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S} \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
, and the tensor product of
$\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S} \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
, and the tensor product of
![]() $X, Y \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
is given by
$X, Y \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
is given by
![]() $\tau _{\le n} (X\otimes Y) \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
. We divide the claim into two parts:
$\tau _{\le n} (X\otimes Y) \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
. We divide the claim into two parts:
-
(1)
 $\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
is an idempotent algebra in
$\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
is an idempotent algebra in
 $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
, in the sense of [Reference LurieLur, Definition 4.8.2.8];
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
, in the sense of [Reference LurieLur, Definition 4.8.2.8]; -
(2)
 $\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
classifies the property that
$\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
classifies the property that
 $\alpha _M$
is zero, in the sense that
$\alpha _M$
is zero, in the sense that
 $M \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
is an
$M \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
is an
 $\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
-module if and only if
$\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
-module if and only if
 $\alpha _M=0$
.
$\alpha _M=0$
.
Consider the exact sequence
where the truncation map u is the unit map for
![]() $\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
as a commutative algebra in
$\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
as a commutative algebra in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
. For every
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
. For every
![]() $M\in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
, we get an exact sequence
$M\in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
, we get an exact sequence
The leftmost spectrum is
![]() $n-1$
connected, and on
$n-1$
connected, and on
![]() $\pi _n$
, the map
$\pi _n$
, the map
![]() $1_M\otimes f$
induces the map
$1_M\otimes f$
induces the map
Thus, by the long exact sequence in homotopy groups, the map
![]() $1_M \otimes u$
becomes an isomorphism after applying
$1_M \otimes u$
becomes an isomorphism after applying
![]() $\tau _{\le n}$
if and only if
$\tau _{\le n}$
if and only if
![]() $\alpha _M = 0$
. Now, for
$\alpha _M = 0$
. Now, for
![]() $M=\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
, the target of
$M=\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
, the target of
![]() $\alpha _M$
is the zero group, and hence, it is the zero map. Thus,
$\alpha _M$
is the zero group, and hence, it is the zero map. Thus,
![]() $1_{\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}} \otimes u\colon \tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S} \otimes \tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S} \to \tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S} \otimes \tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
is an isomorphism, so
$1_{\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}} \otimes u\colon \tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S} \otimes \tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S} \to \tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S} \otimes \tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
is an isomorphism, so
![]() $\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
is an idempotent algebra in
$\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}$
is an idempotent algebra in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
; this verifies (1). By [Reference LurieLur, Proposition 4.8.2.10], this implies that the forgetful functor
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
; this verifies (1). By [Reference LurieLur, Proposition 4.8.2.10], this implies that the forgetful functor
is fully faithful, and the essential image is precisely the objects
![]() $M \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
, whose tensor with u in
$M \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
, whose tensor with u in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
is an isomorphism, which by the above is equivalent to
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]}$
is an isomorphism, which by the above is equivalent to
![]() $\alpha _M = 0$
. Therefore, we have shown that (2) holds as well.
$\alpha _M = 0$
. Therefore, we have shown that (2) holds as well.
Corollary 6.47. A spectrum
![]() $M \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}_{(p)}$
admits a module structure over
$M \in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}_{(p)}$
admits a module structure over
![]() $\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
if and only if the action map
$\tau _{\le n-1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
if and only if the action map
is zero. Moreover, this module structure is then unique.
Proof. In view of [Reference LurieLur, Proposition 4.8.2.10], this follows immediately from Proposition 6.46.
Sadly, Corollary 6.45 stops short from implying
![]() $(\tau _{\leq n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability, which will be already the same as
$(\tau _{\leq n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability, which will be already the same as
![]() $(\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability. This obstacle, however, can be overcome using categorification.
$(\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability. This obstacle, however, can be overcome using categorification.
Proposition 6.48. Let ![]() such that
such that
If
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then it is
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then it is
![]() $(\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable.
$(\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable.
Proof. By Corollary 5.16, if
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n+1)$
-orientable. Since we can identify
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n+1)$
-orientable. Since we can identify
![]() $\operatorname{{Map}}_{\textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}}(C_p,\textrm {pic}({\mathscr {C}}))$
with
$\operatorname{{Map}}_{\textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}}(C_p,\textrm {pic}({\mathscr {C}}))$
with ![]() , we get by Proposition 6.38, that
, we get by Proposition 6.38, that
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(n+1)$
-connected. Hence, by Proposition 6.44, the
$(n+1)$
-connected. Hence, by Proposition 6.44, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n+1)$
-orientable. It follows, by Corollary 5.16 again, that
$(\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n+1)$
-orientable. It follows, by Corollary 5.16 again, that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable and hence, by Remark 3.4, is
$(\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable and hence, by Remark 3.4, is
![]() $(\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable.
$(\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable.
Torsion units and
 $(d+\frac {1}{2})$
-connectedness
$(d+\frac {1}{2})$
-connectedness
To further study extensions of
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation to truncated
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation to truncated
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientations, it will be convenient to use the following terminology:
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientations, it will be convenient to use the following terminology:
Definition 6.49. Let ![]() be
be
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. We say that
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. We say that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(d+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected if it is d-connected and
$(d+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected if it is d-connected and
![]() $(\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable.
$(\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable.
Remark 6.50. If ![]() is
is
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-oriented and
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-oriented and
![]() $0$
-connected, then by Remark 6.39, the space of its
$0$
-connected, then by Remark 6.39, the space of its
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientations of height n is a torsor for the group
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientations of height n is a torsor for the group
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}/p)^\times $
. Thus, if any of the
$(\mathbb {Z}/p)^\times $
. Thus, if any of the
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientations of
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientations of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
extends to a
${\mathscr {C}}$
extends to a
![]() $\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation, then all of them do.
$\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation, then all of them do.
As a sanity check, we observe that
![]() $(d+1)$
-connectedness implies
$(d+1)$
-connectedness implies
![]() $(d+\frac {1}{2})$
-connectedness by Proposition 6.44, which, in turn, implies d-connectedness by definition. We further note that while an
$(d+\frac {1}{2})$
-connectedness by Proposition 6.44, which, in turn, implies d-connectedness by definition. We further note that while an
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
cannot be
${\mathscr {C}}$
cannot be
![]() $(n+1)$
-connected (Proposition 6.37), it can be
$(n+1)$
-connected (Proposition 6.37), it can be
![]() $(n+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected. The following is a useful criterion for that:
$(n+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected. The following is a useful criterion for that:
Proposition 6.51. Let ![]() such that
such that
If
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, then
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(n+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected.
$(n+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected.
Proof. By Proposition 6.48, we get that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable. By looping once the isomorphism in the hypothesis, we get
$(\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable. By looping once the isomorphism in the hypothesis, we get
Thus,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is n-connected by Proposition 6.38.
${\mathscr {C}}$
is n-connected by Proposition 6.38.
Our next goal is to show that just like d-connectedness can be characterized in terms of the p-th roots of unity of ![]() (Proposition 6.38), the property of
(Proposition 6.38), the property of
![]() $(d+\frac {1}{2})$
-connectedness can be similarly characterized in terms of all of the ‘p-local
$(d+\frac {1}{2})$
-connectedness can be similarly characterized in terms of all of the ‘p-local
![]() $\pi $
-finite units’ of
$\pi $
-finite units’ of ![]() .
.
Definition 6.52. Let
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}} \subseteq \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
be the full subcategory generated under (filtered) colimits by
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}} \subseteq \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
be the full subcategory generated under (filtered) colimits by
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {fin}} \subseteq \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
and denote the right adjoint of the embedding by
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {fin}} \subseteq \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
and denote the right adjoint of the embedding by
We say that a spectrum
![]() $X \in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
is (p-local)
$X \in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
is (p-local)
![]() $\pi $
-torsion if it belongs to
$\pi $
-torsion if it belongs to
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
.
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
.
The above notion of ‘p-local
![]() $\pi $
-torsion’ is related to p-torsion in the usual sense by the following:
$\pi $
-torsion’ is related to p-torsion in the usual sense by the following:
Proposition 6.53. Let
![]() $X \in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
. If
$X \in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
. If
![]() $X\in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
, then
$X\in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
, then
![]() $X[p^{-1}]= 0$
. The converse holds if X is bounded above.
$X[p^{-1}]= 0$
. The converse holds if X is bounded above.
Proof. For the ‘if’ part, observe that the collection of spectra X for which
![]() $X[p^{-1}]= 0$
, contains
$X[p^{-1}]= 0$
, contains
![]() $C_p$
and is closed under colimits in
$C_p$
and is closed under colimits in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}$
. Since all p-local
$\textrm {Sp}$
. Since all p-local
![]() $\pi $
-finite spectra are generated by
$\pi $
-finite spectra are generated by
![]() $C_p$
under colimits, the same holds for all p-local
$C_p$
under colimits, the same holds for all p-local
![]() $\pi $
-torsion spectra, and the claim follows. Conversely, if
$\pi $
-torsion spectra, and the claim follows. Conversely, if
![]() $X\in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
is p-torsion and bounded above, it is the colimit of its Postnikov truncations, for which the successive fibers are (de)suspensions of p-torsion abelian groups, which, in turn, are all generated from
$X\in \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
is p-torsion and bounded above, it is the colimit of its Postnikov truncations, for which the successive fibers are (de)suspensions of p-torsion abelian groups, which, in turn, are all generated from
![]() $C_p$
by colimits in
$C_p$
by colimits in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}$
.
$\textrm {Sp}$
.
Remark 6.54. Some additional hypothesis is necessary for the converse part in Proposition 6.53, as
![]() $X= \mathbb {S}/p$
is an example of a connective spectrum with
$X= \mathbb {S}/p$
is an example of a connective spectrum with
![]() $X[p^{-1}] = 0$
, but
$X[p^{-1}] = 0$
, but
![]() $X \notin \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
.
$X \notin \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
.
Definition 6.55. For
![]() ${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
and
${\mathscr {C}} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\operatorname{{Cat}}_\infty )$
and
![]() $S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the p-local
$S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
, the p-local
![]() $\pi $
-torsion units of S are given by
$\pi $
-torsion units of S are given by
In many examples of interest, such as
![]() $\mathfrak {R}= \tau _{\le d} \mathbb {S}_{(p)},$
the spectrum
$\mathfrak {R}= \tau _{\le d} \mathbb {S}_{(p)},$
the spectrum
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
belongs to
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}}$
belongs to
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
. In these cases, pre-orientations
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
. In these cases, pre-orientations
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}} \rightarrow S^\times $
factor uniquely through
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}} \rightarrow S^\times $
factor uniquely through
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(S) \to S^\times $
and are thus in bijection with maps
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(S) \to S^\times $
and are thus in bijection with maps
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}} \rightarrow \mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(S)$
. As with ordinary roots of unity, the semiadditive height gives an upper bound on the truncatedness of the spectrum
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathfrak {R}} \rightarrow \mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(S)$
. As with ordinary roots of unity, the semiadditive height gives an upper bound on the truncatedness of the spectrum
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(S)$
.
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(S)$
.
Proposition 6.56. Let ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() $S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. If S is of height
$S\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}({\mathscr {C}})$
. If S is of height
![]() $\le n$
at p, then the spectrum
$\le n$
at p, then the spectrum
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(S)$
is n-truncated.
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(S)$
is n-truncated.
Proof. For every
![]() $M\in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the fold map
$M\in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, the fold map
![]() $S[\Sigma ^{n+1} M] \to S$
is an isomorphism by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.3]. Thus, applying the various adjunctions, we have
$S[\Sigma ^{n+1} M] \to S$
is an isomorphism by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Proposition 3.2.3]. Thus, applying the various adjunctions, we have
Since
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
generates
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
generates
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
under colimits, it follows that
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
under colimits, it follows that
![]() $\Omega ^{n+1}\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(S)= 0$
, and hence,
$\Omega ^{n+1}\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(S)= 0$
, and hence,
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(S)$
is n-truncated.
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(S)$
is n-truncated.
We therefore focus on the full subcategory
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)} \subseteq \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
of n-truncated objects. Furthermore, passing from
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)} \subseteq \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
of n-truncated objects. Furthermore, passing from
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}_{(p)}$
to
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}_{(p)}$
to
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)}$
is a purely formal operation.
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)}$
is a purely formal operation.
Lemma 6.57. For every prime p and integer
![]() $n\ge 0$
, we have an equivalence of
$n\ge 0$
, we have an equivalence of
![]() $\infty $
-categories
$\infty $
-categories
Proof. By definition, the
![]() $\pi $
-finite objects in
$\pi $
-finite objects in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
generate it under colimits. Since n-truncation preserves colimits and the property of being
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
generate it under colimits. Since n-truncation preserves colimits and the property of being
![]() $\pi $
-finite, the same holds for
$\pi $
-finite, the same holds for
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)}$
. It hence remains to show that the
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)}$
. It hence remains to show that the
![]() $\pi $
-finite objects are compact in
$\pi $
-finite objects are compact in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)}$
. This follows from the fact that any n-truncated
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)}$
. This follows from the fact that any n-truncated
![]() $\pi $
-finite spectrum can be represented as the n-truncation of a finite spectrum.
$\pi $
-finite spectrum can be represented as the n-truncation of a finite spectrum.
With these preliminaries, we are ready to prove the following analogue of Proposition 6.38:
Theorem 6.58. Let ![]() be
be
![]() $0$
-connected and
$0$
-connected and
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-oriented. For every
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-oriented. For every
![]() $d\le n$
, the
$d\le n$
, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(d+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected at p if and only if
$(d+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected at p if and only if
Proof. Throughout the proof, we shall write
![]() $\Omega \colon \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}} \to \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
for the loops functor from the
$\Omega \colon \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}} \to \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
for the loops functor from the
![]() $\infty $
-category of connective spectra to itself. With this convention, the above isomorphism is equivalent to the following one:
$\infty $
-category of connective spectra to itself. With this convention, the above isomorphism is equivalent to the following one:
We begin with the ‘if’ part. Assuming the above isomorphism, we get
Hence, by Proposition 6.38,
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected. It remains to show that
${\mathscr {C}}$
is d-connected. It remains to show that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable. Let
$(\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable. Let
![]() $\omega $
be an
$\omega $
be an
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of height n for
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientation of height n for
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
. By Theorem 4.39, it suffices to solve the lifting problem
${\mathscr {C}}$
. By Theorem 4.39, it suffices to solve the lifting problem

Since
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {F}_p}$
is
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {F}_p}$
is
![]() $(n-1)$
-connected, it is, in particular,
$(n-1)$
-connected, it is, in particular,
![]() $(n-d-1)$
-connected. Hence,
$(n-d-1)$
-connected. Hence,
![]() $\omega $
factors through
$\omega $
factors through ![]() , which we assumed to be isomorphic to
, which we assumed to be isomorphic to
![]() $\tau _{\ge n-d}(I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {S}_{(p)}}) \simeq I_p^{(n)}{\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}}$
. We shall be done by showing that every two nonzero maps
$\tau _{\ge n-d}(I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {S}_{(p)}}) \simeq I_p^{(n)}{\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}}$
. We shall be done by showing that every two nonzero maps
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {F}_p} \rightarrow \tau _{\ge n-d}(I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {S}_{(p)}})$
differ by an automorphism of the target. Indeed, we have
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {F}_p} \rightarrow \tau _{\ge n-d}(I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {S}_{(p)}})$
differ by an automorphism of the target. Indeed, we have
The nonzero maps correspond to
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p^\times $
, and multiplication by the Teichmuller lifts
$\mathbb {F}_p^\times $
, and multiplication by the Teichmuller lifts
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p^\times \to \mathbb {S}_{p}^\times $
permutes them.
$\mathbb {F}_p^\times \to \mathbb {S}_{p}^\times $
permutes them.
We now show the ‘only if’ part. Assume that
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
is
${\mathscr {C}}$
is
![]() $(d+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected. We have
$(d+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected. We have
by definition and Proposition 6.56, respectively. By the Yoneda lemma, it would thus suffice to show that both objects represent the same functor on
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,d]\text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)}$
. In fact, since
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,d]\text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)}$
. In fact, since
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,d]\text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)} \simeq \operatorname{{Ind}}(\textrm {Sp}^{[0,d]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}_{(p)})$
(Lemma 6.57), it suffices to show that on
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,d]\text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)} \simeq \operatorname{{Ind}}(\textrm {Sp}^{[0,d]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}_{(p)})$
(Lemma 6.57), it suffices to show that on
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{[0,d]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}_{(p)}$
, both objects represent the functor
$\textrm {Sp}^{[0,d]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}_{(p)}$
, both objects represent the functor
![]() $\lfloor {I_p^{(d)}{(-)}}\rfloor $
. Given
$\lfloor {I_p^{(d)}{(-)}}\rfloor $
. Given
![]() $M\in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,d]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}_{(p)}$
, we have on the one hand a chain of natural isomorphisms
$M\in \textrm {Sp}^{[0,d]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}_{(p)}$
, we have on the one hand a chain of natural isomorphisms
On the other hand, we have a chain of natural isomorphisms
We now use the assumption that
![]() $\omega $
extends to a
$\omega $
extends to a
![]() $\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation. This gives a Fourier transform natural isomorphism
$\tau _{\le d}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientation. This gives a Fourier transform natural isomorphism
Using this, and the d-connectedness of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}$
at p, we can extend the above chain of natural isomorphisms by
${\mathscr {C}}$
at p, we can extend the above chain of natural isomorphisms by
Corollary 6.59.
![]() is
is
![]() $(n+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected if and only if it is
$(n+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected if and only if it is
![]() $0$
-connected,
$0$
-connected,
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable and
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable and
Proof. This follows immediately from the case
![]() $n=d$
in Theorem 6.58.
$n=d$
in Theorem 6.58.
7 Chromatic applications
In this final section, we apply the general theory of Fourier transforms and orientations to chromatic homotopy theory, specifically to the study of the monochromatic categories
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
,
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
,
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
, and
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
, and ![]() . In particular, we deduce theorems A–F stated in the introduction of the paper.
. In particular, we deduce theorems A–F stated in the introduction of the paper.
7.1 Chromatic preliminaries
We begin with a rapid review of some material from chromatic stable homotopy theory, geared towards our applications in the subsequent subsections. For a more comprehensive survey, we refer the interested to [Reference Barthel and BeaudryBB20]. In the end of this section, we also review briefly the theory of higher cyclotomic extensions in the monochromatic categories from [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b] and their relationship with Westerland’s ring spectrum
![]() $R_n$
introduced and studied in [Reference WesterlandWes17].
$R_n$
introduced and studied in [Reference WesterlandWes17].
Telescopic localizations
Let
![]() $\textrm {Sp}$
be the symmetric monoidal
$\textrm {Sp}$
be the symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category of spectra, and let p be a fixed prime. The thick subcategory theorem of Hopkins and Smith [Reference Hopkins and SmithHS98] classifies the thick subcategories of the
$\infty $
-category of spectra, and let p be a fixed prime. The thick subcategory theorem of Hopkins and Smith [Reference Hopkins and SmithHS98] classifies the thick subcategories of the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^\omega $
of finite p-local spectra. These subcategories assemble into a strictly ascending chromatic filtration
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^\omega $
of finite p-local spectra. These subcategories assemble into a strictly ascending chromatic filtration
which plays a fundamental role in chromatic stable homotopy theory. The objects of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}^\omega _n \smallsetminus {\mathscr {C}}^\omega _{n+1}$
are said to be (p-local) finite spectra of type n; by the thick subcategory theorem, any choice of finite type n spectrum generates
${\mathscr {C}}^\omega _n \smallsetminus {\mathscr {C}}^\omega _{n+1}$
are said to be (p-local) finite spectra of type n; by the thick subcategory theorem, any choice of finite type n spectrum generates
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}^\omega _n$
as a thick subcategory. Furthermore, the periodicity theorem says that any finite spectrum
${\mathscr {C}}^\omega _n$
as a thick subcategory. Furthermore, the periodicity theorem says that any finite spectrum
![]() $F(n)$
of type n admits a
$F(n)$
of type n admits a
![]() $v_n$
-self map
$v_n$
-self map
![]() $\nu \colon \Sigma ^{|\nu |}F(n) \to F(n)$
of some nonnegative degree
$\nu \colon \Sigma ^{|\nu |}F(n) \to F(n)$
of some nonnegative degree
![]() $|\nu |$
depending on
$|\nu |$
depending on
![]() $F(n)$
. We will denote the corresponding height n telescope by
$F(n)$
. We will denote the corresponding height n telescope by
![]() $T(n)= F(n)[\nu ^{-1}]$
. For
$T(n)= F(n)[\nu ^{-1}]$
. For
![]() $n=0$
, we use the convention that the self-map is taken to be multiplication by p. In particular, one can take
$n=0$
, we use the convention that the self-map is taken to be multiplication by p. In particular, one can take
![]() $F(0) = \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
and
$F(0) = \mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
and ![]() .
.
The chromatic filtration extends to the category of all p-local spectra
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
by considering for each height n the subcategory
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
by considering for each height n the subcategory
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_n \subseteq \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
generated by
${\mathscr {C}}_n \subseteq \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
generated by
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}^\omega _n$
(equivalently, by
${\mathscr {C}}^\omega _n$
(equivalently, by
![]() $F(n)$
)) under all colimits. The ‘complement’ of
$F(n)$
)) under all colimits. The ‘complement’ of
![]() ${\mathscr {C}}_{n+1}$
is given by the Verdier quotient
${\mathscr {C}}_{n+1}$
is given by the Verdier quotient
and we write
for the corresponding finite localization functor (leaving the prime p implicit). The subcategory
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_n^f \subseteq \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
consists of the
$\textrm {Sp}_n^f \subseteq \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
consists of the
![]() $(T(0)\oplus \cdots \oplus T(n))$
-local spectra in the sense of Bousfield. In particular, if
$(T(0)\oplus \cdots \oplus T(n))$
-local spectra in the sense of Bousfield. In particular, if
![]() $X\in \textrm {Sp}$
is
$X\in \textrm {Sp}$
is
![]() $T(m)$
-acyclic for
$T(m)$
-acyclic for
![]() $0<m\le n$
, then
$0<m\le n$
, then
For example, as we shall repeatedly use, this is the case when X is bounded above.
We denote by
![]() $C_n^f$
the
$C_n^f$
the
![]() $L_n^f$
-acyclification functor. Thus, for every
$L_n^f$
-acyclification functor. Thus, for every
![]() $X\in \textrm {Sp}$
, we have a canonical fiber sequence of spectra
$X\in \textrm {Sp}$
, we have a canonical fiber sequence of spectra
Finally, we note that the functors
![]() $L_n^f$
and
$L_n^f$
and
![]() $(-)_{(p)}$
, and hence
$(-)_{(p)}$
, and hence
![]() $C_n^f$
, are smashing. This means that they preserve all colimits (as endofunctors of
$C_n^f$
, are smashing. This means that they preserve all colimits (as endofunctors of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}$
).
$\textrm {Sp}$
).
The
![]() $\infty $
-categories
$\infty $
-categories
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{n}^f$
form a strictly ascending filtration
$\textrm {Sp}_{n}^f$
form a strictly ascending filtration
interpolating between the
![]() $\infty $
-categories of rational and p-local spectra. The n-th filtration quotient can then be identified with the Bousfield localization of
$\infty $
-categories of rational and p-local spectra. The n-th filtration quotient can then be identified with the Bousfield localization of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
at a height n telescope
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
at a height n telescope
![]() $T(n)$
:
$T(n)$
:
The localization
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
inherits a symmetric monoidal structure, given by the
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
inherits a symmetric monoidal structure, given by the
![]() $T(n)$
-localized smash product. Moreover, by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Theorem A],
$T(n)$
-localized smash product. Moreover, by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Theorem A],
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditive of height n.
$\infty $
-semiadditive of height n.
 $K(n)$
-local homotopy
$K(n)$
-local homotopy
There is a variant of the chromatic filtration that is constructed from the Morava K-theories. Continuing to work with an implicit fixed prime p, for every finite height
![]() $n\ge 1$
, let
$n\ge 1$
, let
![]() $K(n)$
denote the n-th Morava K-theory spectrum associated to a formal group law
$K(n)$
denote the n-th Morava K-theory spectrum associated to a formal group law
![]() $\Gamma $
of height n over
$\Gamma $
of height n over
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
. It has the structure of a complex oriented
$\mathbb {F}_p$
. It has the structure of a complex oriented
![]() $\mathbb {E}_1$
-ring spectrum, and its coefficient ring is given by
$\mathbb {E}_1$
-ring spectrum, and its coefficient ring is given by
where
![]() $v_n$
is of degree
$v_n$
is of degree
![]() $2(p^n-1)$
. By convention, we set
$2(p^n-1)$
. By convention, we set
![]() $K(0) = \mathbb {Q}$
and
$K(0) = \mathbb {Q}$
and
![]() $K(\infty ) = \mathbb {F}_p$
. As a consequence of the nilpotence theorem [Reference Devinatz, Hopkins and SmithDHS88, Reference Hopkins and SmithHS98], the Morava K-theories form the prime fields of
$K(\infty ) = \mathbb {F}_p$
. As a consequence of the nilpotence theorem [Reference Devinatz, Hopkins and SmithDHS88, Reference Hopkins and SmithHS98], the Morava K-theories form the prime fields of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
.
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
.
Let
![]() $L_n\colon \textrm {Sp} \to \textrm {Sp}$
be the Bousfield localization functor with respect to
$L_n\colon \textrm {Sp} \to \textrm {Sp}$
be the Bousfield localization functor with respect to
![]() $(K(0)\oplus \cdots \oplus K(n))$
. Hopkins and Ravenel proved that
$(K(0)\oplus \cdots \oplus K(n))$
. Hopkins and Ravenel proved that
![]() $L_n$
is smashing as well. Setting
$L_n$
is smashing as well. Setting
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{n} = L_n\textrm {Sp}$
, we obtain a filtration
$\textrm {Sp}_{n} = L_n\textrm {Sp}$
, we obtain a filtration
which is compatible with the chromatic filtration discussed above, in the sense that
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_n \subseteq \textrm {Sp}_n^f$
. The n-th filtration quotients of this filtration are symmetric monoidally equivalent to the
$\textrm {Sp}_n \subseteq \textrm {Sp}_n^f$
. The n-th filtration quotients of this filtration are symmetric monoidally equivalent to the
![]() $K(n)$
-local categories:
$K(n)$
-local categories:
The question whether the localization functor
![]() $L_{K(n)}\colon \textrm {Sp}_{T(n)} \to \textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is an equivalence is the content of Ravenel’s telescope conjecture.
$L_{K(n)}\colon \textrm {Sp}_{T(n)} \to \textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is an equivalence is the content of Ravenel’s telescope conjecture.
By construction, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is compactly generated by the
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is compactly generated by the
![]() $K(n)$
-localization of
$K(n)$
-localization of
![]() $F(n)$
for any finite spectrum
$F(n)$
for any finite spectrum
![]() $F(n)$
of type n. However, for
$F(n)$
of type n. However, for
![]() $n\ge 1$
, the unit
$n\ge 1$
, the unit
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)} \in \textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is not compact. Finally, as the telescopic categories, each
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)} \in \textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is not compact. Finally, as the telescopic categories, each
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditive of height n as well, as was proven previously by Hopkins and Lurie in [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13].
$\infty $
-semiadditive of height n as well, as was proven previously by Hopkins and Lurie in [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13].
Lubin–Tate spectra and cyclotomic extensions
For
![]() $n\ge 1$
, let
$n\ge 1$
, let
![]() $E_n$
be the n-th Lubin–Tate spectrum (or Morava E-theory spectrum) at the prime p associated to a formal group law
$E_n$
be the n-th Lubin–Tate spectrum (or Morava E-theory spectrum) at the prime p associated to a formal group law
![]() $\Gamma $
of height n over
$\Gamma $
of height n over
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
. Namely, it is the Landweber exact ring spectrum attached to the universal deformation of the base-change
$\mathbb {F}_p$
. Namely, it is the Landweber exact ring spectrum attached to the universal deformation of the base-change
![]() $\overline {\Gamma }$
of
$\overline {\Gamma }$
of
![]() $\Gamma $
over
$\Gamma $
over
![]() $\overline {\mathbb {F}}_p$
and has ring of coefficients
$\overline {\mathbb {F}}_p$
and has ring of coefficients
Here,
![]() $\mathbb {W}(\overline {\mathbb {F}}_p)$
denotes the ring of Witt vector on
$\mathbb {W}(\overline {\mathbb {F}}_p)$
denotes the ring of Witt vector on
![]() $\overline {\mathbb {F}}_p$
, the power series variables
$\overline {\mathbb {F}}_p$
, the power series variables
![]() $u_i$
have degree 0, and u has degree
$u_i$
have degree 0, and u has degree
![]() $-2$
. The spectrum
$-2$
. The spectrum
![]() $E_n$
is
$E_n$
is
![]() $K(n)$
-local and has the same Bousfield class as
$K(n)$
-local and has the same Bousfield class as
![]() $\bigoplus _{i=0}^nK(i)$
; in particular, there is a natural equivalence of localization functors
$\bigoplus _{i=0}^nK(i)$
; in particular, there is a natural equivalence of localization functors
![]() $L_{n} \simeq L_{E_n}$
. By Goerss–Hopkins obstruction theory [Reference Goerss and HopkinsGH04],
$L_{n} \simeq L_{E_n}$
. By Goerss–Hopkins obstruction theory [Reference Goerss and HopkinsGH04],
![]() $E_n$
admits an essentially unique
$E_n$
admits an essentially unique
![]() $\mathbb {E}_{\infty }$
-ring spectrum structure (see also [Reference LurieLur18a]). We write
$\mathbb {E}_{\infty }$
-ring spectrum structure (see also [Reference LurieLur18a]). We write ![]() for the
for the
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditive height n symmetric monoidal
$\infty $
-semiadditive height n symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-category of
$\infty $
-category of
![]() $K(n)$
-local modules over
$K(n)$
-local modules over
![]() $E_n$
.
$E_n$
.
While other conventions exist in the literature, for the purposes of this paper, it is convenient to define the Lubin–Tate spectrum at height
![]() $0$
to be the even periodic commutative ring spectrumFootnote
5
$0$
to be the even periodic commutative ring spectrumFootnote
5
where u is in degree
![]() $-2$
.
$-2$
.
For
![]() $n\ge 1$
, the n-th Morava stabilizer group, defined as the profinite group
$n\ge 1$
, the n-th Morava stabilizer group, defined as the profinite group
acts continuously on
![]() $E_n$
through
$E_n$
through
![]() $\mathbb {E}_{\infty }$
-ring maps, in a sense made precise by Devinatz and Hopkins in [Reference Devinatz and HopkinsDH04]. In fact,
$\mathbb {E}_{\infty }$
-ring maps, in a sense made precise by Devinatz and Hopkins in [Reference Devinatz and HopkinsDH04]. In fact,
![]() $E_n$
is algebraically closed, and the canonical unit map
$E_n$
is algebraically closed, and the canonical unit map
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)} \to E_n$
exhibits the target as a
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)} \to E_n$
exhibits the target as a
![]() $K(n)$
-local pro-Galois extension with Galois group
$K(n)$
-local pro-Galois extension with Galois group
![]() $\mathbb {G}_n$
(in fact, the algebraic closure); see, for example, [Reference RognesRog08]. Note, however, that
$\mathbb {G}_n$
(in fact, the algebraic closure); see, for example, [Reference RognesRog08]. Note, however, that
![]() $E_0$
is not a Galois extension of
$E_0$
is not a Galois extension of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(0)} = \mathbb {Q}$
.
$\mathbb {S}_{K(0)} = \mathbb {Q}$
.
This brings into focus intermediate extensions of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
. One particularly relevant such extension appeared in the work of Westerland [Reference WesterlandWes17], where he constructed a certain
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
. One particularly relevant such extension appeared in the work of Westerland [Reference WesterlandWes17], where he constructed a certain
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_p^{\times }$
-extension
$\mathbb {Z}_p^{\times }$
-extension
![]() $R_n$
of
$R_n$
of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
for all odd primes and positive heights. In fact, as explained in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b], this extension identifies with the (infinite) higher cyclotomic extension
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
for all odd primes and positive heights. In fact, as explained in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b], this extension identifies with the (infinite) higher cyclotomic extension
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}[\omega _{p^\infty }^{(n)}]$
, which we therefore denote by
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}[\omega _{p^\infty }^{(n)}]$
, which we therefore denote by
![]() $R_n$
at all primes and heights (including
$R_n$
at all primes and heights (including
![]() $p=2$
and
$p=2$
and
![]() $n=0$
). The cyclotomic extensions
$n=0$
). The cyclotomic extensions
![]() $R_n$
are given as the filtered colimits of the corresponding finite cyclotomic extensions
$R_n$
are given as the filtered colimits of the corresponding finite cyclotomic extensions
![]() $R_{n,r}:=\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}[\omega _{p^r}^{(n)}]$
,
$R_{n,r}:=\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}[\omega _{p^r}^{(n)}]$
,
where
![]() $R_{n,r}$
is a
$R_{n,r}$
is a
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^\times $
-Galois extension in
$(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^\times $
-Galois extension in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
. For
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
. For
![]() $n\ge 1$
, under the
$n\ge 1$
, under the
![]() $K(n)$
-local Galois correspondence of [Reference RognesRog08, Theorem 11.2.2] (see also [Reference MathewMat16, Theorem 10.9]), the Galois extensions
$K(n)$
-local Galois correspondence of [Reference RognesRog08, Theorem 11.2.2] (see also [Reference MathewMat16, Theorem 10.9]), the Galois extensions
![]() $R_{n,r}$
correspond to group homomorphisms
$R_{n,r}$
correspond to group homomorphisms
![]() $\chi _{p,r}\colon \mathbb {G}_n \to (\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^{\times }$
. Consequently,
$\chi _{p,r}\colon \mathbb {G}_n \to (\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^{\times }$
. Consequently,
![]() $R_n$
corresponds to a continuous homomorphism
$R_n$
corresponds to a continuous homomorphism
called the p-adic cyclotomic character of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
; see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, §5.2]. The kernel of
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
; see [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, §5.2]. The kernel of
![]() $\chi _p$
, denoted by
$\chi _p$
, denoted by
![]() $\mathbb {G}_n^0 \triangleleft \mathbb {G}_n$
, is a closed subgroup, and we have an equivalence
$\mathbb {G}_n^0 \triangleleft \mathbb {G}_n$
, is a closed subgroup, and we have an equivalence
![]() $ R_n \simeq E_n^{h\mathbb {G}_n^0} $
of faithful
$ R_n \simeq E_n^{h\mathbb {G}_n^0} $
of faithful
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_p^{\times }$
-Galois extensions of
$\mathbb {Z}_p^{\times }$
-Galois extensions of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
; here,
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
; here,
![]() $(-)^{h\mathbb {G}_n^0}$
stands for the continuous fixed points. For
$(-)^{h\mathbb {G}_n^0}$
stands for the continuous fixed points. For
![]() $n=0$
, the ring
$n=0$
, the ring
![]() $R_n$
is the classical cyclotomic extension
$R_n$
is the classical cyclotomic extension
![]() $\mathbb {Q}(\omega _{p^\infty })$
, and it corresponds to the usual p-adic cyclotomic character of the absolute Galois group of
$\mathbb {Q}(\omega _{p^\infty })$
, and it corresponds to the usual p-adic cyclotomic character of the absolute Galois group of
![]() $\mathbb {Q}$
.
$\mathbb {Q}$
.
One advantage of the cyclotomic approach from [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b] is that it allows for a telescopic lifts of
![]() $R_{n,r}$
and
$R_{n,r}$
and
![]() $R_n$
. The corresponding
$R_n$
. The corresponding
![]() $p^r$
-th finite cyclotomic extensions
$p^r$
-th finite cyclotomic extensions
![]() $R_{n,r}^f:=\mathbb {S}_{T(n)}[\omega _{p^r}^{(n)}]$
, constructed in parallel to the finite cyclotomic extensions
$R_{n,r}^f:=\mathbb {S}_{T(n)}[\omega _{p^r}^{(n)}]$
, constructed in parallel to the finite cyclotomic extensions
![]() $R_{n,r}$
, are again faithful
$R_{n,r}$
, are again faithful
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^\times $
-Galois for every r ([Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Proposition 5.2]). They assemble into an infinite cyclotomic extension
$(\mathbb {Z}/p^r)^\times $
-Galois for every r ([Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Proposition 5.2]). They assemble into an infinite cyclotomic extension
which is a pro-finite
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_p^\times $
-Galois extension in
$\mathbb {Z}_p^\times $
-Galois extension in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
. It is, however, not known whether
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
. It is, however, not known whether
![]() $R_n^f$
is a faithful Galois extension; we return to this point at the end of Section 7.3.
$R_n^f$
is a faithful Galois extension; we return to this point at the end of Section 7.3.
7.2 Orientations of the Lubin–Tate ring spectrum
We begin our discussion of the Fourier transform in chromatic homotopy theory with the case of
![]() $E_n$
-modules. After reinterpreting Theorem 1.1 of Hopkins and Lurie as providing
$E_n$
-modules. After reinterpreting Theorem 1.1 of Hopkins and Lurie as providing
![]() $E_n$
with a
$E_n$
with a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientation and descending it to
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientation and descending it to
![]() $R_n$
, we apply the results of Section 6 to extend it to a spherical orientation (Theorem D), and the results of Section 5 to further categorify it (Theorem G). We then construct the pro-
$R_n$
, we apply the results of Section 6 to extend it to a spherical orientation (Theorem D), and the results of Section 5 to further categorify it (Theorem G). We then construct the pro-
![]() $\pi $
-finite Galois
$\pi $
-finite Galois
![]() $K(n)$
-local spherical cyclotomic extension (Theorem F) and conclude the subsection with the computation of the connective cover of the p-localized discrepancy spectrum of
$K(n)$
-local spherical cyclotomic extension (Theorem F) and conclude the subsection with the computation of the connective cover of the p-localized discrepancy spectrum of
![]() $E_n$
(Theorem E).
$E_n$
(Theorem E).
 $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-Orientability
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-Orientability
As we shall now explain, the
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability of
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability of
![]() $E_n$
is essentially equivalent to the following result of Hopkins and Lurie:
$E_n$
is essentially equivalent to the following result of Hopkins and Lurie:
Theorem 7.1 [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Corollary 5.3.26].
For every
![]() $n\ge 1$
, there is a natural isomorphism
$n\ge 1$
, there is a natural isomorphism
for connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local
$\pi $
-finite p-local
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-modules M, where
$\mathbb {Z}$
-modules M, where
![]() $M^*= \hom _{\mathbb {Z}}(M,\mathbb {Q}/\mathbb {Z})$
.
$M^*= \hom _{\mathbb {Z}}(M,\mathbb {Q}/\mathbb {Z})$
.
Indeed, while this isomorphism is not constructed in [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13] using Fourier theory, all natural transformations of the above form are essentially Fourier transforms. Thus, this result can be reformulated (and extended to height
![]() $n=0$
) as follows:
$n=0$
) as follows:
Corollary 7.2. For every
![]() $n\ge 0$
, the
$n\ge 0$
, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category ![]() is
is
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable.
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable.
Proof. We start with the case
![]() $n=0$
. The commutative ring spectrum
$n=0$
. The commutative ring spectrum
![]() $E_0$
is an algebra over
$E_0$
is an algebra over
![]() $\overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
, and hence, it suffices to show that
$\overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
, and hence, it suffices to show that
![]() $\overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
is
$\overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},0)$
-orientable by Proposition 4.5. Using Lemma 6.15, the compatible system of p-power roots of unity
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},0)$
-orientable by Proposition 4.5. Using Lemma 6.15, the compatible system of p-power roots of unity
![]() $\exp (\frac {2\pi i}{p^k})\in \overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
(viewed as a subfield of
$\exp (\frac {2\pi i}{p^k})\in \overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
(viewed as a subfield of
![]() $\mathbb {C}$
) gives a
$\mathbb {C}$
) gives a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-pre-orientation of
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-pre-orientation of
![]() $\overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
of height
$\overline {\mathbb {Q}}$
of height
![]() $0$
. For a finite abelian p-group M, the resulting Fourier transform
$0$
. For a finite abelian p-group M, the resulting Fourier transform
![]() $\overline {\mathbb {Q}}[M]\to \overline {\mathbb {Q}}^{M^*}$
is the classical discrete Fourier transform, and hence an isomorphism.
$\overline {\mathbb {Q}}[M]\to \overline {\mathbb {Q}}^{M^*}$
is the classical discrete Fourier transform, and hence an isomorphism.
We turn to the case
![]() $n\ge 1$
. First, a
$n\ge 1$
. First, a
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local
$\pi $
-finite p-local
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-module is the same thing as a
$\mathbb {Z}$
-module is the same thing as a
![]() $\pi $
-finite
$\pi $
-finite
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-module. Furthermore, if M is concentrated between degrees
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-module. Furthermore, if M is concentrated between degrees
![]() $0$
and n, then
$0$
and n, then
![]() $\Sigma ^n M^*\simeq I_p^{(n)}{M}$
. Hence, an isomorphism as in Theorem 7.1 restricts to a natural isomorphism
$\Sigma ^n M^*\simeq I_p^{(n)}{M}$
. Hence, an isomorphism as in Theorem 7.1 restricts to a natural isomorphism
![]() $E_n[-]\simeq E_n^{\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{-}}\rfloor }$
of functors
$E_n[-]\simeq E_n^{\lfloor {I_p^{(n)}{-}}\rfloor }$
of functors
![]() ${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathbb {Z}/p^r}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}} \rightarrow \operatorname {CAlg}(\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)})$
for every
${\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathbb {Z}/p^r}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}} \rightarrow \operatorname {CAlg}(\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)})$
for every
![]() $r\in \mathbb {N}$
. By Proposition 3.10 (and Remark 3.13), such an isomorphism is the Fourier transform associated with an essentially unique
$r\in \mathbb {N}$
. By Proposition 3.10 (and Remark 3.13), such an isomorphism is the Fourier transform associated with an essentially unique
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-orientation
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-orientation
![]() $\omega \colon \Sigma ^n \mathbb {Z}/p^r \to E_n^\times $
. Since these orientations are compatible with each other, they assemble into a
$\omega \colon \Sigma ^n \mathbb {Z}/p^r \to E_n^\times $
. Since these orientations are compatible with each other, they assemble into a
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientation of
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientation of
![]() $E_n$
of height n by Proposition 6.17.
$E_n$
of height n by Proposition 6.17.
Remark 7.3. The construction of the isomorphism in Theorem 7.1 depends on a choice of a normalization
![]() $\nu $
of the p-divisible group
$\nu $
of the p-divisible group
![]() $\Gamma $
associated with
$\Gamma $
associated with
![]() $E_n$
, in the sense of [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Definition 5.3.1]. Hence, identifying this isomorphism with the Fourier transform, we associate to a normalization
$E_n$
, in the sense of [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Definition 5.3.1]. Hence, identifying this isomorphism with the Fourier transform, we associate to a normalization
![]() $\nu $
of
$\nu $
of
![]() $\Gamma $
a
$\Gamma $
a
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientation
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientation
![]() $\omega _\nu $
. It is not hard to show that the association
$\omega _\nu $
. It is not hard to show that the association
![]() $\nu \mapsto \omega _\nu $
furnishes a bijection between normalizations of
$\nu \mapsto \omega _\nu $
furnishes a bijection between normalizations of
![]() $\Gamma $
and
$\Gamma $
and
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientations of
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientations of
![]() $E_n$
.
$E_n$
.
The orientability of ![]() implies virtual orientability of
implies virtual orientability of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
.
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
.
Corollary 7.4. For every
![]() $n\ge 0$
, the
$n\ge 0$
, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is virtually
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable (hence, in particular, virtually
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable (hence, in particular, virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable).
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable).
Proof. Since
![]() $E_n$
is faithful in
$E_n$
is faithful in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
, this follows from Corollary 7.2.
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
, this follows from Corollary 7.2.
While
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is virtually
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable, it is not
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable, it is not
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable. Namely, one cannot replace
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable. Namely, one cannot replace
![]() $E_n$
with
$E_n$
with
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
in the isomorphism of Theorem 7.1. However, the Fourier theoretic point of view does allow us to descend this isomorphism from
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
in the isomorphism of Theorem 7.1. However, the Fourier theoretic point of view does allow us to descend this isomorphism from
![]() $E_n$
to the intermediate extension
$E_n$
to the intermediate extension
![]() $R_n$
.
$R_n$
.
Theorem 7.5. For every
![]() $n\ge 0$
, there is a natural isomorphism
$n\ge 0$
, there is a natural isomorphism
for connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local
$\pi $
-finite p-local
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-module spectra M.
$\mathbb {Z}$
-module spectra M.
Proof. Since
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is virtually
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, by Corollary 6.18, we obtain that
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, by Corollary 6.18, we obtain that
In particular, the universal
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientation on
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientation on
![]() $R_n$
provides the desired isomorphism.
$R_n$
provides the desired isomorphism.
Remark 7.6. The fact that
![]() $R_n$
carries the universal
$R_n$
carries the universal
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientation among
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientation among
![]() $K(n)$
-local commutative ring spectra shows that for
$K(n)$
-local commutative ring spectra shows that for
![]() $n\ge 1$
, the isomorphism in Theorem 7.1 is obtained from the one in Theorem 7.5 by scalar extension along a map
$n\ge 1$
, the isomorphism in Theorem 7.1 is obtained from the one in Theorem 7.5 by scalar extension along a map
![]() $R_n \to E_n$
. This map identifies with the inclusion of the fixed point algebra
$R_n \to E_n$
. This map identifies with the inclusion of the fixed point algebra
![]() $R_n \simeq E_n^{h\mathbb {G}_n^0} \to E_n$
, up to possibly pre-composing with an automorphism of
$R_n \simeq E_n^{h\mathbb {G}_n^0} \to E_n$
, up to possibly pre-composing with an automorphism of
![]() $R_n$
(that is, an element of
$R_n$
(that is, an element of
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{p}^\times $
). Hence, Theorem 7.5 is essentially the claim that the isomorphism in Theorem 7.1 is
$\mathbb {Z}_{p}^\times $
). Hence, Theorem 7.5 is essentially the claim that the isomorphism in Theorem 7.1 is
![]() $\mathbb {G}_n^0$
-equivariant.
$\mathbb {G}_n^0$
-equivariant.
 $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientability
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientability
Since
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is virtually
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is virtually
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientable (by Corollary 7.4), it is also virtually
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientable (by Corollary 7.4), it is also virtually
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientable (by Proposition 6.20). Namely, the
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientable (by Proposition 6.20). Namely, the
![]() $K(n)$
-local spherical cyclotomic extension
$K(n)$
-local spherical cyclotomic extension
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}[\omega _{\mathbb {S}_{(p)}}^{(n)}]$
is faithful. Our general results imply that it is a pro-
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}[\omega _{\mathbb {S}_{(p)}}^{(n)}]$
is faithful. Our general results imply that it is a pro-
![]() $\pi $
-finite Galois extension of
$\pi $
-finite Galois extension of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
.
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
.
Theorem 7.7. For every
![]() $n \ge 0$
, the commutative algebra
$n \ge 0$
, the commutative algebra
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}[\omega _{\mathbb {S}_{(p)}}^{(n)}]$
is a pro-Galois extension of
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}[\omega _{\mathbb {S}_{(p)}}^{(n)}]$
is a pro-Galois extension of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
for the group
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
for the group
![]() $\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}^\times $
, viewed as a pro-
$\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}^\times $
, viewed as a pro-
![]() $\pi $
-finite group.
$\pi $
-finite group.
Proof. By Corollary 7.4,
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is virtually
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. Thus, the result follows from Theorem 6.24.
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. Thus, the result follows from Theorem 6.24.
While
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}[\omega _{\mathbb {S}_{(p)}}^{(n)}]$
is the universal spherically oriented
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}[\omega _{\mathbb {S}_{(p)}}^{(n)}]$
is the universal spherically oriented
![]() $K(n)$
-local commutative algebra, we do not have an explicit description of it. In contrast, combining the theory of categorical connectedness from Section 6 with the results on
$K(n)$
-local commutative algebra, we do not have an explicit description of it. In contrast, combining the theory of categorical connectedness from Section 6 with the results on
![]() $\textrm {pic}(E_n)$
from [Reference Burklund, Schlank and YuanBSY22], we can also construct a (nonuniversal) spherical orientation on
$\textrm {pic}(E_n)$
from [Reference Burklund, Schlank and YuanBSY22], we can also construct a (nonuniversal) spherical orientation on
![]() $E_n$
, which for
$E_n$
, which for
![]() $n\ge 1$
is an ordinary (pro-finite) Galois extension of
$n\ge 1$
is an ordinary (pro-finite) Galois extension of
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
.
$\mathbb {S}_{K(n)}$
.
Theorem 7.8. For every
![]() $n\ge 0$
, the
$n\ge 0$
, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category ![]() is
is
![]() $(n+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected, and hence, in particular,
$(n+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected, and hence, in particular,
![]() $(\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable.
$(\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable.
Proof. We check the assumptions of Proposition 6.51. By Corollary 7.2, ![]() is
is
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, and by [Reference Burklund, Schlank and YuanBSY22, Proposition 8.14], we have
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, and by [Reference Burklund, Schlank and YuanBSY22, Proposition 8.14], we have
Applying the general results on categorification of orientations from Section 5, we also get the following:
Corollary 7.9. There is a natural equivalence of symmetric monoidal
![]() $\infty $
-categories:
$\infty $
-categories:
for M a connective
![]() $(n+1)$
-finite p-local spectrum, provided that the action map
$(n+1)$
-finite p-local spectrum, provided that the action map
is zero.
Proof. Since ![]() is
is
![]() $(\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable (by Theorem 7.8), we get by Corollary 5.16 that
$(\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable (by Theorem 7.8), we get by Corollary 5.16 that ![]() is
is
![]() $(\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n+1)$
-orientable. By Corollary 6.47, this translates to the above.
$(\tau _{\le n}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n+1)$
-orientable. By Corollary 6.47, this translates to the above.
We expect that the technical condition on M can be removed:
Conjecture 7.10. The
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category ![]() is
is
![]() $(\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n+1)$
-orientable.
$(\mathbb {S}_{(p)},n+1)$
-orientable.
At least in height
![]() $0$
, this conjecture can be verified by an explicit computation:
$0$
, this conjecture can be verified by an explicit computation:
Proposition 7.11. The
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{E_0}}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{E_0}}$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {S}_{(p)},1)$
-orientable (for every prime p).
$(\mathbb {S}_{(p)},1)$
-orientable (for every prime p).
Proof. It suffices to show that
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{E_0}}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{E_0}}$
is
![]() $(\tau _{\le 1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},1)$
-orientable (see Remark 3.4). By Corollary 7.2,
$(\tau _{\le 1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},1)$
-orientable (see Remark 3.4). By Corollary 7.2,
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{E_0}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{E_0}$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},0)$
-orientatable, and hence, by Corollary 5.16,
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},0)$
-orientatable, and hence, by Corollary 5.16,
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{E_0}}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{E_0}}$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},1)$
-orientable. For
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},1)$
-orientable. For
![]() $p\neq 2$
, we have
$p\neq 2$
, we have
![]() $\tau _{\le 1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}\simeq \mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
, so the result holds for odd primes. It remains to treat the case
$\tau _{\le 1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)}\simeq \mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
, so the result holds for odd primes. It remains to treat the case
![]() $p=2$
. In fact, we shall show that
$p=2$
. In fact, we shall show that
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{E_0}}$
is
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{E_0}}$
is
![]() $(1+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected at
$(1+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected at
![]() $p=2$
, which implies
$p=2$
, which implies
![]() $(\tau _{\le 1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},1)$
-orientability, by definition.
$(\tau _{\le 1}\mathbb {S}_{(p)},1)$
-orientability, by definition.
By Theorem 6.58 applied to
![]() ${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{E_0}}$
, it would suffice to show that
${{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{{{\operatorname {Mod}}}_{E_0}}$
, it would suffice to show that
![]() $ \textrm {pic}(E_0)^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(2)} \:\simeq \: I_2^{(1)}\mathbb {S}_{(2)}. $
Since
$ \textrm {pic}(E_0)^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(2)} \:\simeq \: I_2^{(1)}\mathbb {S}_{(2)}. $
Since
![]() $\pi _*E_0$
is a 2-periodic even graded field,
$\pi _*E_0$
is a 2-periodic even graded field,
![]() $\pi _0\textrm {pic}(E_0) \simeq \mathbb {Z}/2$
, with the nonzero element given by the isomorphism class of
$\pi _0\textrm {pic}(E_0) \simeq \mathbb {Z}/2$
, with the nonzero element given by the isomorphism class of
![]() $\Sigma E_0$
(see, for example, [Reference Baker and RichterBR05, Theorem 37]). Since
$\Sigma E_0$
(see, for example, [Reference Baker and RichterBR05, Theorem 37]). Since
![]() $\Omega \textrm {pic}(E_0) \simeq E_0^\times $
, we conclude that
$\Omega \textrm {pic}(E_0) \simeq E_0^\times $
, we conclude that
 $$\begin{align*}\pi_t(\textrm{pic}(E_0)) = \left\{\begin{array}{lr} \mathbb{Z}/2\mathbb{Z} & t=0 \\ \overline{\mathbb{Q}}^\times & t = 1\\ \overline{\mathbb{Q}} & t>1 \text{ odd} \\ 0 & \text{otherwise} \end{array} \right. \end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\pi_t(\textrm{pic}(E_0)) = \left\{\begin{array}{lr} \mathbb{Z}/2\mathbb{Z} & t=0 \\ \overline{\mathbb{Q}}^\times & t = 1\\ \overline{\mathbb{Q}} & t>1 \text{ odd} \\ 0 & \text{otherwise} \end{array} \right. \end{align*}$$
Let X denote the fiber of the map ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() we obtain that
we obtain that
![]() $\textrm {pic}(E_0)^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(2)}\simeq X^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(2)},$
and we shall compute the latter.
$\textrm {pic}(E_0)^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(2)}\simeq X^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(2)},$
and we shall compute the latter.
From the long exact sequence of homotopy groups associated with the fiber sequence
we see that the homotopy groups of X are as follows:
 $$\begin{align*}\pi_t(X) = \left\{\begin{array}{lr} \mathbb{Z}/2\mathbb{Z} & t=0 \\ \mathbb{Q}_2/\mathbb{Z}_2 & t = 1\\ 0 & t\ge 2. \end{array} \right. \end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\pi_t(X) = \left\{\begin{array}{lr} \mathbb{Z}/2\mathbb{Z} & t=0 \\ \mathbb{Q}_2/\mathbb{Z}_2 & t = 1\\ 0 & t\ge 2. \end{array} \right. \end{align*}$$
In particular, by Proposition 6.53,
![]() $X \simeq X^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(2)}$
, so it remains to show that
$X \simeq X^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(2)}$
, so it remains to show that
![]() $X\simeq I_2^{(1)}\mathbb {S}_{(2)}$
.
$X\simeq I_2^{(1)}\mathbb {S}_{(2)}$
.
Since X is an extension of
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/2\mathbb {Z}$
by
$\mathbb {Z}/2\mathbb {Z}$
by
![]() $\Sigma \mathbb {Q}_2/\mathbb {Z}_2$
, it is classified by a map
$\Sigma \mathbb {Q}_2/\mathbb {Z}_2$
, it is classified by a map
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/2\mathbb {Z} \to \Sigma ^2 \mathbb {Q}_2 /\mathbb {Z}_2$
in
$\mathbb {Z}/2\mathbb {Z} \to \Sigma ^2 \mathbb {Q}_2 /\mathbb {Z}_2$
in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}$
. The collection of homotopy classes of such maps is given by
$\textrm {Sp}$
. The collection of homotopy classes of such maps is given by
where the last isomorphism follows from the classical computation of the integral (dual) Steenrod algebra. Consequently, there are only two possible extensions of
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/2\mathbb {Z}$
by
$\mathbb {Z}/2\mathbb {Z}$
by
![]() $\Sigma \mathbb {Q}_2/\mathbb {Z}_2$
, and we want to show that X is the nonsplit one.
$\Sigma \mathbb {Q}_2/\mathbb {Z}_2$
, and we want to show that X is the nonsplit one.
These two extensions can be distinguished using the multiplication-by-
![]() $\eta $
map from
$\eta $
map from
![]() $\pi _0$
to
$\pi _0$
to
![]() $\pi _1$
, which is
$\pi _1$
, which is
![]() $0$
for the split extension and the inclusion
$0$
for the split extension and the inclusion
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/2\mathbb {Z}\hookrightarrow \mathbb {Q}_2/\mathbb {Z}_2$
for the nonsplit one. Since the morphism
$\mathbb {Z}/2\mathbb {Z}\hookrightarrow \mathbb {Q}_2/\mathbb {Z}_2$
for the nonsplit one. Since the morphism
![]() $X\to \textrm {pic}(E_0)$
induces an isomorphism on
$X\to \textrm {pic}(E_0)$
induces an isomorphism on
![]() $\pi _0$
and an injection on
$\pi _0$
and an injection on
![]() $\pi _1$
, it suffices to show that multiplication by
$\pi _1$
, it suffices to show that multiplication by
![]() $\eta $
is nonzero already on
$\eta $
is nonzero already on
![]() $\pi _0\textrm {pic}(E_0)$
. This follows from the fact that, for the class
$\pi _0\textrm {pic}(E_0)$
. This follows from the fact that, for the class
![]() $[\Sigma E_0]\in \pi _0(P)$
, we have (e.g., by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Proposition 3.20]),
$[\Sigma E_0]\in \pi _0(P)$
, we have (e.g., by [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Proposition 3.20]),
which is nontrivial.
The discrepancy spectrum
Another application of the categorical connectedness result of Theorem 7.8 is an explicit description of the spectrum
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(E_n)$
.
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(E_n)$
.
Theorem 7.12. For every
![]() $n\ge 0$
, there is an isomorphism
$n\ge 0$
, there is an isomorphism
Proof. The
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category ![]() is
is
![]() $(n+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected by Theorem 7.8, so the claim follows by Corollary 6.59, keeping in mind that
$(n+\frac {1}{2})$
-connected by Theorem 7.8, so the claim follows by Corollary 6.59, keeping in mind that
![]() $I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {S}_{(p)}} \simeq \tau _{\ge 0}(\Sigma ^n I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p})$
.
$I_p^{(n)}{\mathbb {S}_{(p)}} \simeq \tau _{\ge 0}(\Sigma ^n I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p})$
.
The spectrum
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(E_n)$
turns out to be closely related to the discrepancy spectrum of
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(E_n)$
turns out to be closely related to the discrepancy spectrum of
![]() $E_n$
. In [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10], Ando, Hopkins and Rezk defined the discrepancy spectrum of an arbitrary
$E_n$
. In [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10], Ando, Hopkins and Rezk defined the discrepancy spectrum of an arbitrary
![]() $L_n$
-local commutative ring spectrum R as the fiber of the localization map
$L_n$
-local commutative ring spectrum R as the fiber of the localization map
![]() $R^\times \to L_n R^\times $
. For such a ring spectrum R, it essentially follows from [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10, Theorem 4.11] that its discrepancy spectrum agrees with its p-torsion
$R^\times \to L_n R^\times $
. For such a ring spectrum R, it essentially follows from [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10, Theorem 4.11] that its discrepancy spectrum agrees with its p-torsion
![]() $\pi $
-finite units
$\pi $
-finite units
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
, after taking the connective cover and p-localizing. As explained in [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10] (see the discussion below [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10, Lemma 4.12]), if R is
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
, after taking the connective cover and p-localizing. As explained in [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10] (see the discussion below [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10, Lemma 4.12]), if R is
![]() $L_n$
-local, then
$L_n$
-local, then
![]() $L_nR^\times \simeq L_n^fR^\times $
, so one can use
$L_nR^\times \simeq L_n^fR^\times $
, so one can use
![]() $L_n^fR^\times $
instead of
$L_n^fR^\times $
instead of
![]() $L_nR^\times $
in the definition of the discrepancy spectrum. This variant has the advantage of providing a well-behaved notion of a discrepancy spectrum defined for all
$L_nR^\times $
in the definition of the discrepancy spectrum. This variant has the advantage of providing a well-behaved notion of a discrepancy spectrum defined for all
![]() $L_n^f$
-local commutative ring spectra. In particular, for this definition, the p-localization of the discrepancy spectrum of
$L_n^f$
-local commutative ring spectra. In particular, for this definition, the p-localization of the discrepancy spectrum of
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(L_n^f\textrm {Sp})$
is given by
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(L_n^f\textrm {Sp})$
is given by
![]() $C_n^fR^\times $
.
$C_n^fR^\times $
.
Our goal in this subsection is to review the relation between the discrepancy spectrum and the p-torsion
![]() $\pi $
-finite units of
$\pi $
-finite units of
![]() $L_n$
-local commutative ring spectra from [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10], and generalize it to the context of
$L_n$
-local commutative ring spectra from [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10], and generalize it to the context of
![]() $L_n^f$
-local commutative ring spectra. In fact, we will even work in the wider generality of almost
$L_n^f$
-local commutative ring spectra. In fact, we will even work in the wider generality of almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local commutative ring spectra, in the following sense:
$L_n^f$
-local commutative ring spectra, in the following sense:
Definition 7.13. A p-local spectrum X is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local if
$L_n^f$
-local if
![]() $\hom (Z,X)$
is bounded above for some (and hence all) finite spectra Z of type
$\hom (Z,X)$
is bounded above for some (and hence all) finite spectra Z of type
![]() $n+1$
.
$n+1$
.
Equivalently, X is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local if
$L_n^f$
-local if
![]() $X\otimes Z$
is bounded above for some (and hence all) finite spectra Z of type
$X\otimes Z$
is bounded above for some (and hence all) finite spectra Z of type
![]() $n+1$
. Indeed,
$n+1$
. Indeed,
![]() $\hom (Z,X) \simeq \mathbb {D} Z \otimes X$
and
$\hom (Z,X) \simeq \mathbb {D} Z \otimes X$
and
![]() $\mathbb {D} Z$
is of type
$\mathbb {D} Z$
is of type
![]() $n+1$
if and only if Z is. Note also that the collection of almost
$n+1$
if and only if Z is. Note also that the collection of almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local spectra itself forms a thick subcategory of
$L_n^f$
-local spectra itself forms a thick subcategory of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
.
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
.
Remark 7.14. If we replace in Definition 7.13 ‘bounded above’ with ‘
![]() $\pi $
-finite’, we arrive at the stronger notion of fp-type n in the sense of Mahowald and Rezk [Reference Mahowald and RezkMR99]. Indeed, a
$\pi $
-finite’, we arrive at the stronger notion of fp-type n in the sense of Mahowald and Rezk [Reference Mahowald and RezkMR99]. Indeed, a
![]() $\pi $
-finite spectrum is connective by convention, and if it is p-local, it must also be p-complete.
$\pi $
-finite spectrum is connective by convention, and if it is p-local, it must also be p-complete.
Example 7.15. Every
![]() $L_n^f$
-local (and in particular
$L_n^f$
-local (and in particular
![]() $L_n$
-local) spectrum is almost
$L_n$
-local) spectrum is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local. Indeed, a p-local spectrum X is
$L_n^f$
-local. Indeed, a p-local spectrum X is
![]() $L_n^f$
-local if and only if
$L_n^f$
-local if and only if
![]() $\hom (Z,X)= 0$
for some finite spectrum Z of type
$\hom (Z,X)= 0$
for some finite spectrum Z of type
![]() $n+1$
.
$n+1$
.
Example 7.16. Every p-local bounded above spectrum is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local. Indeed, if X is a bounded above spectrum and Z is any (in particular, type
$L_n^f$
-local. Indeed, if X is a bounded above spectrum and Z is any (in particular, type
![]() $n+1$
) finite spectrum, then
$n+1$
) finite spectrum, then
![]() $Z\otimes X$
is also bounded above.
$Z\otimes X$
is also bounded above.
The example above implies that the almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-locality of a spectrum can be checked after passing to an arbitrary connected cover of it. In fact, one can verify this property using only an arbitrary connected cover of its underlying space.
$L_n^f$
-locality of a spectrum can be checked after passing to an arbitrary connected cover of it. In fact, one can verify this property using only an arbitrary connected cover of its underlying space.
Proposition 7.17. Let
![]() $X,Y \in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
be such that
$X,Y \in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
be such that
for some (and hence all sufficiently large)
![]() $d \ge 0$
. Then, X is almost
$d \ge 0$
. Then, X is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local if and only if Y is.
$L_n^f$
-local if and only if Y is.
Proof. Let
![]() $A\in \mathcal{S}_*$
be a finite pointed space whose reduced suspension spectrum
$A\in \mathcal{S}_*$
be a finite pointed space whose reduced suspension spectrum
![]() $Z:= \overline {\mathbb {S}}[A]$
is of type
$Z:= \overline {\mathbb {S}}[A]$
is of type
![]() $n+1$
. Then, by definition, a spectrum W is almost
$n+1$
. Then, by definition, a spectrum W is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local if and only if
$L_n^f$
-local if and only if
![]() $\hom (Z,W)$
is bounded above. This is the case if and only if there exists
$\hom (Z,W)$
is bounded above. This is the case if and only if there exists
![]() $e\in \mathbb {N}$
such that
$e\in \mathbb {N}$
such that
By applying the functor
![]() $\Omega $
to the above isomorphism, if
$\Omega $
to the above isomorphism, if
![]() $(*)$
holds for some e, then it holds for any larger value of e as well. Unwinding the definitions, we get
$(*)$
holds for some e, then it holds for any larger value of e as well. Unwinding the definitions, we get
Now, if
![]() $\Omega ^{\infty + d} X \simeq \Omega ^{\infty +d} Y$
and X is almost
$\Omega ^{\infty + d} X \simeq \Omega ^{\infty +d} Y$
and X is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local, we may choose e satisfying
$L_n^f$
-local, we may choose e satisfying
![]() $(*)$
for X such that
$(*)$
for X such that
![]() $e \ge d$
. But then
$e \ge d$
. But then
and we deduce that Y is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local as well. By symmetry, if Y is almost
$L_n^f$
-local as well. By symmetry, if Y is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local, then so is X, and therefore, they are almost
$L_n^f$
-local, then so is X, and therefore, they are almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local together.
$L_n^f$
-local together.
Given
![]() $R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)})$
, in addition to the ‘additive’ underlying p-local spectrum
$R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)})$
, in addition to the ‘additive’ underlying p-local spectrum
![]() $R\in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
, we can form the ‘multiplicative’ p-localized spectrum of units
$R\in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
, we can form the ‘multiplicative’ p-localized spectrum of units
![]() $R^\times _{(p)}\in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
. Although these are very different p-local spectra in general, Proposition 7.17 implies that they are almost
$R^\times _{(p)}\in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
. Although these are very different p-local spectra in general, Proposition 7.17 implies that they are almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local together.
$L_n^f$
-local together.
Corollary 7.18. A p-local commutative ring spectrum R is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local if and only if the p-localization of its spectrum of units
$L_n^f$
-local if and only if the p-localization of its spectrum of units
![]() $R^\times $
is almost
$R^\times $
is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local.
$L_n^f$
-local.
Proof. This follows from Proposition 7.17 and the fact that
Note that, in particular,
![]() $R^\times _{(p)}$
is almost
$R^\times _{(p)}$
is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local for every
$L_n^f$
-local for every
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_n)$
. We thus obtain the following:
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_n)$
. We thus obtain the following:
Example 7.19. The spectrum
![]() $(E_n^\times )_{(p)}$
is almost
$(E_n^\times )_{(p)}$
is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local.
$L_n^f$
-local.
We proceed by analyzing the behavior of the functor
![]() $C_n^f$
on arbitrary almost
$C_n^f$
on arbitrary almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local spectra.
$L_n^f$
-local spectra.
Proposition 7.20. For an almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local spectrum X, the spectrum
$L_n^f$
-local spectrum X, the spectrum
![]() $C_n^fX$
is a filtered colimit of bounded above p-torsion spectra.
$C_n^fX$
is a filtered colimit of bounded above p-torsion spectra.
Proof. This follows from the standard fact (see [Reference Hovey and StricklandHS99, Proposition 7.10]) that
![]() $C_n^fX$
can be written as
$C_n^fX$
can be written as
![]() $ \underrightarrow {\operatorname {lim}}\, \hom (Z_\alpha , X), $
where
$ \underrightarrow {\operatorname {lim}}\, \hom (Z_\alpha , X), $
where
![]() $(Z_\alpha )$
is a cofiltered diagram of finite spectra of type
$(Z_\alpha )$
is a cofiltered diagram of finite spectra of type
![]() $n+1$
. Since X is almost
$n+1$
. Since X is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local and the spectra
$L_n^f$
-local and the spectra
![]() $Z_\alpha $
are finite p-torsion, each
$Z_\alpha $
are finite p-torsion, each
![]() $\hom (Z_\alpha , X) \simeq \hom (Z_\alpha ,C_n^fX)$
is bounded above and p-torsion.
$\hom (Z_\alpha , X) \simeq \hom (Z_\alpha ,C_n^fX)$
is bounded above and p-torsion.
The functor
![]() $C_n^f$
is compatible with connective covers in the following sense:
$C_n^f$
is compatible with connective covers in the following sense:
Lemma 7.21. For
![]() $X\in \textrm {Sp}$
, the canonical map
$X\in \textrm {Sp}$
, the canonical map
is an isomorphism.
Proof. Since
![]() $C_n^f$
is an exact functor, we have a cofiber sequence
$C_n^f$
is an exact functor, we have a cofiber sequence
Applying the limit-preserving functor
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}\colon \textrm {Sp}_{(p)} \to \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}}$
, we obtain a fiber sequence
$\tau _{\ge 0}\colon \textrm {Sp}_{(p)} \to \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}}$
, we obtain a fiber sequence
Thus, to show that the first map is an isomorphism, it suffices to show that
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^f \tau _{\leq -1} X \simeq 0$
. Equivalently, for
$\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^f \tau _{\leq -1} X \simeq 0$
. Equivalently, for
![]() $Y\in \textrm {Sp}$
, we wish to show that if
$Y\in \textrm {Sp}$
, we wish to show that if
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}Y=0$
, then
$\tau _{\ge 0}Y=0$
, then
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^f Y = 0$
. First, such a Y is bounded above, so
$\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^f Y = 0$
. First, such a Y is bounded above, so
![]() $L_n^fY\simeq \mathbb {Q} \otimes Y$
(as explained in Section 7.1). Consequently,
$L_n^fY\simeq \mathbb {Q} \otimes Y$
(as explained in Section 7.1). Consequently,
and similarly,
Finally,
![]() $C_n^fY$
is the fiber of a map
$C_n^fY$
is the fiber of a map
![]() $Y_{(p)}\to L_n^fY$
, and since the functor
$Y_{(p)}\to L_n^fY$
, and since the functor
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}\colon \textrm {Sp}\to \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
preserves fibers, we get
$\tau _{\ge 0}\colon \textrm {Sp}\to \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
preserves fibers, we get
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0} C_n^fY \simeq 0$
.
$\tau _{\ge 0} C_n^fY \simeq 0$
.
Recall that
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
is defined as the p-local
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
is defined as the p-local
![]() $\pi $
-torsion part of
$\pi $
-torsion part of
![]() $R^\times $
. The relation between
$R^\times $
. The relation between
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
and the discrepancy spectrum of R is deduced from the following general fact:
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
and the discrepancy spectrum of R is deduced from the following general fact:
Proposition 7.22. Let X be an almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local spectrum. Then
$L_n^f$
-local spectrum. Then
Proof. First, we can assume without loss of generality that X is connective, by replacing it with
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}X$
. Indeed, by Example 7.16, the spectrum
$\tau _{\ge 0}X$
. Indeed, by Example 7.16, the spectrum
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}X$
is also almost
$\tau _{\ge 0}X$
is also almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local, and by Lemma 7.21, we have
$L_n^f$
-local, and by Lemma 7.21, we have
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0} (C_n^f X) \simeq \tau _{\ge 0} (C_n^f \tau _{\ge 0}X)$
. Now, by the definition of
$\tau _{\ge 0} (C_n^f X) \simeq \tau _{\ge 0} (C_n^f \tau _{\ge 0}X)$
. Now, by the definition of
![]() $(-)_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
, it would suffice to show that
$(-)_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
, it would suffice to show that
-
(1)
 $\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^fX \in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
.
$\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^fX \in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
. -
(2) For every
 $Z\in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
, the map
$Z\in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
, the map
 $\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^fX \to X$
induces an isomorphism
$\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^fX \to X$
induces an isomorphism  $$\begin{align*}\operatorname{{Map}}(Z,\tau_{\ge 0}C_n^fX)\simeq \operatorname{{Map}}(Z,X). \end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\operatorname{{Map}}(Z,\tau_{\ge 0}C_n^fX)\simeq \operatorname{{Map}}(Z,X). \end{align*}$$
For
![]() $(1)$
, by Proposition 7.20, there is a filtered colimit presentation
$(1)$
, by Proposition 7.20, there is a filtered colimit presentation
![]() $C_n^f X \simeq \underrightarrow {\operatorname {lim}}\, X_\alpha $
such that each
$C_n^f X \simeq \underrightarrow {\operatorname {lim}}\, X_\alpha $
such that each
![]() $X_\alpha $
is bounded above and p-torsion. Since the formation of connective covers preserves filtered colimits, we obtain that
$X_\alpha $
is bounded above and p-torsion. Since the formation of connective covers preserves filtered colimits, we obtain that
Each
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}X_\alpha $
is connective, bounded above and p-torsion. By Proposition 6.53,
$\tau _{\ge 0}X_\alpha $
is connective, bounded above and p-torsion. By Proposition 6.53,
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}X_\alpha $
belongs to
$\tau _{\ge 0}X_\alpha $
belongs to
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
, and hence, so does
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
, and hence, so does
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0} (C_n^f X)$
.
$\tau _{\ge 0} (C_n^f X)$
.
For
![]() $(2)$
, by definition, every
$(2)$
, by definition, every
![]() $Z \in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
is a filtered colimit of bounded above p-torsion spectra. A bounded above spectrum Y satisfies
$Z \in \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
is a filtered colimit of bounded above p-torsion spectra. A bounded above spectrum Y satisfies
![]() $L_n^f Y \simeq Y\otimes \mathbb {Q}$
, and if Y is also p-torsion, then it is
$L_n^f Y \simeq Y\otimes \mathbb {Q}$
, and if Y is also p-torsion, then it is
![]() $L_n^f$
-acyclic. Since
$L_n^f$
-acyclic. Since
![]() $L_n^f$
-acyclic spectra are closed under colimits, we deduce that Z itself is
$L_n^f$
-acyclic spectra are closed under colimits, we deduce that Z itself is
![]() $L_n^f$
-acyclic; hence,
$L_n^f$
-acyclic; hence,
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}} \subseteq C_n^f(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)})$
. Consequently,
$\textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}} \subseteq C_n^f(\textrm {Sp}_{(p)})$
. Consequently,
where the composite of these isomorphisms is given by post-composing with the canonical map
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^fX \to X$
.
$\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^fX \to X$
.
Putting everything together, we get the main result of this subsection.
Theorem 7.23 cf. [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10, Theorem 4.11].
For all
![]() $n \ge 0$
and for every almost
$n \ge 0$
and for every almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local commutative ring spectrum R, we have
$L_n^f$
-local commutative ring spectrum R, we have
Proof. By Corollary 7.18, the p-localization of the spectrum
![]() $R^\times $
is almost
$R^\times $
is almost
![]() $L_n^f$
-local as well. Hence, by Proposition 7.22, we have
$L_n^f$
-local as well. Hence, by Proposition 7.22, we have
Corollary 7.24. The connective cover of the p-localized discrepancy spectrum of
![]() $E_n$
is isomorphic to
$E_n$
is isomorphic to
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}(\Sigma ^n I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p})$
.
$\tau _{\ge 0}(\Sigma ^n I_{\mathbb {Q}_p/\mathbb {Z}_p})$
.
Proof. Recall that the connective cover of the p-localized discrepancy spectrum of
![]() $E_n$
is isomorphic to
$E_n$
is isomorphic to
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^f(E_n^\times )$
. By Theorem 7.23, we have
$\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^f(E_n^\times )$
. By Theorem 7.23, we have
![]() $\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^f(E_n^\times ) \simeq \mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(E_n)$
. Hence, the result follows from Theorem 7.12.
$\tau _{\ge 0}C_n^f(E_n^\times ) \simeq \mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(E_n)$
. Hence, the result follows from Theorem 7.12.
Remark 7.25. Using the vanishing of the telescopic homology of sufficiently connected Eilenberg–MacLane spaces, established in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Theorem E], the same argument as in the proof of Proposition 6.56 shows that
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
is n-truncated for every
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)$
is n-truncated for every
![]() $R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(L_n^f \textrm {Sp})$
. Together with Theorem 7.23, this constitutes a telescopic generalization of [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10, Theorem 4.11].
$R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(L_n^f \textrm {Sp})$
. Together with Theorem 7.23, this constitutes a telescopic generalization of [Reference Ando, Hopkins and RezkAHR10, Theorem 4.11].
As another consequence of Theorem 7.23, we obtain the following property of the functor
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(-)$
.
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(-)$
.
Corollary 7.26. The functor
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(-)\colon \operatorname{{CAlg}}(L_n^f\textrm {Sp})\to \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
preserves filtered colimits.
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(-)\colon \operatorname{{CAlg}}(L_n^f\textrm {Sp})\to \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}$
preserves filtered colimits.
Proof. First, observe that the fully faithful embedding
![]() $\textrm {Sp}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)} \hookrightarrow \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}}$
is conservative and preserves filtered colimits, so it suffices to prove the claim when regarding
$\textrm {Sp}^{\pi \text {-}\textrm {tor}}_{(p)} \hookrightarrow \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}}$
is conservative and preserves filtered colimits, so it suffices to prove the claim when regarding
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(-)$
as a functor into p-local connective spectra.
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(-)$
as a functor into p-local connective spectra.
By Theorem 7.23, we have
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)\simeq \tau _{\ge 0}C_n^f(R^\times )$
for
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(R)\simeq \tau _{\ge 0}C_n^f(R^\times )$
for
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(L_n^f\textrm {Sp})$
. Namely, we may write the functor
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(L_n^f\textrm {Sp})$
. Namely, we may write the functor
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(-)$
as the composition
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(-)$
as the composition
We will proceed by showing that each of the functors in this composite preserve filtered colimits.
-
(1) The embedding
 $\operatorname{{CAlg}}(L_n^f\textrm {Sp}) \hookrightarrow \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp})$
is obtained from the lax symmetric monoidal, colimit-preserving, fully faithful embedding
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}(L_n^f\textrm {Sp}) \hookrightarrow \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp})$
is obtained from the lax symmetric monoidal, colimit-preserving, fully faithful embedding
 $L_n^f\textrm {Sp} \hookrightarrow \textrm {Sp}$
by applying
$L_n^f\textrm {Sp} \hookrightarrow \textrm {Sp}$
by applying
 $\operatorname{{CAlg}}(-)$
, and hence, it preserves filtered colimits.
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}(-)$
, and hence, it preserves filtered colimits. -
(2) The argument for the functor
 $(-)^\times \colon \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}) \to \textrm {Sp}$
is similar to [Reference Mathew and StojanoskaMS16, Proposition 2.3.3], and we give it for completeness. The lax symmetric monoidal functor
$(-)^\times \colon \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}) \to \textrm {Sp}$
is similar to [Reference Mathew and StojanoskaMS16, Proposition 2.3.3], and we give it for completeness. The lax symmetric monoidal functor
 $\Omega ^\infty \colon \textrm {Sp} \to \mathcal{S}$
preserves filtered colimits, and therefore, so does the induced functor
$\Omega ^\infty \colon \textrm {Sp} \to \mathcal{S}$
preserves filtered colimits, and therefore, so does the induced functor
 $\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}) \to \operatorname{{CMon}}(\mathcal{S}),$
taking a commutative algebra to its underlying space with the multiplicative commutative monoid structure. Furthermore, the functor
$\operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}) \to \operatorname{{CMon}}(\mathcal{S}),$
taking a commutative algebra to its underlying space with the multiplicative commutative monoid structure. Furthermore, the functor
 $\operatorname{{CMon}}(\mathcal{S}) \to \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
, right adjoint to the inclusion of connective spectra as group-like commutative monoids, also preserves filtered colimits. Indeed, this can be checked after composing with the conservative filtered colimit-preserving forgetful functor
$\operatorname{{CMon}}(\mathcal{S}) \to \textrm {Sp}^{\textrm {cn}}$
, right adjoint to the inclusion of connective spectra as group-like commutative monoids, also preserves filtered colimits. Indeed, this can be checked after composing with the conservative filtered colimit-preserving forgetful functor
 $\operatorname{{CMon}}(\mathcal{S}) \to \mathcal{S}$
, and the invertible elements form a connected summand, so the claim can be easily verified on
$\operatorname{{CMon}}(\mathcal{S}) \to \mathcal{S}$
, and the invertible elements form a connected summand, so the claim can be easily verified on
 $\pi _0$
.
$\pi _0$
. -
(3) The functor
 $C_n^f\colon \textrm {Sp}\to \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
is the acyclification functor associated with the smashing localization
$C_n^f\colon \textrm {Sp}\to \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}$
is the acyclification functor associated with the smashing localization
 $L_n^f$
, and hence, it preserves all small colimits.
$L_n^f$
, and hence, it preserves all small colimits. -
(4) The functor
 $\tau _{\ge 0} \colon \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}\to \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}}$
preserves filtered colimits since the formation of homotopy groups preserves filtered colimits.
$\tau _{\ge 0} \colon \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}\to \textrm {Sp}_{(p)}^{\textrm {cn}}$
preserves filtered colimits since the formation of homotopy groups preserves filtered colimits.
We deduce that their composition
![]() $\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(-)$
preserves filtered colimits.
$\mu _{\mathbb {S}_{p}}(-)$
preserves filtered colimits.
7.3 Virtual orientability of
 $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
We now turn to the application of the theory of orientations and the Fourier transform to the
![]() $T(n)$
-local setting. In particular, we construct a
$T(n)$
-local setting. In particular, we construct a
![]() $T(n)$
-local lift of the chromatic Fourier transform (Theorem A) and prove the corresponding
$T(n)$
-local lift of the chromatic Fourier transform (Theorem A) and prove the corresponding
![]() $T(n)$
-local affineness, Eilenberg–Moore and Galois results (Theorem B and Theorem C).
$T(n)$
-local affineness, Eilenberg–Moore and Galois results (Theorem B and Theorem C).
Virtual
 $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientability & applications
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientability & applications
In [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, §5], the
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability of
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientability of
![]() $E_n$
was used to prove affineness results for
$E_n$
was used to prove affineness results for
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
, as well as Eilenberg–Moore type formulas for the cohomology of
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
, as well as Eilenberg–Moore type formulas for the cohomology of
![]() $\pi $
-finite spaces with
$\pi $
-finite spaces with
![]() $K(n)$
-local coefficients. From the Fourier-theoretic perspective, this is a formal consequence of
$K(n)$
-local coefficients. From the Fourier-theoretic perspective, this is a formal consequence of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
being virtually
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
being virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. Similarly, the next proposition allows us to lift all of these results to
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. Similarly, the next proposition allows us to lift all of these results to
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
.
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
.
Proposition 7.27. For all
![]() $n \ge 0$
, the
$n \ge 0$
, the
![]() $\infty $
-category
$\infty $
-category
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is virtually
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable.
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable.
Proof. The
![]() $T(n)$
-local commutative ring spectrum
$T(n)$
-local commutative ring spectrum
![]() $E_n$
is
$E_n$
is
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable by Proposition 7.2 and hence, in particular,
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable by Proposition 7.2 and hence, in particular,
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable by Proposition 4.4. Since the functor
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable by Proposition 4.4. Since the functor
is nil-conservative (see, for example, [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Corollary 5.1.17]Footnote
6
), we deduce from Proposition 6.9 that
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is virtually
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable.
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable.
Remark 7.28. The virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability of
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
depends crucially on the fact that it is
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
depends crucially on the fact that it is
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditive of semiadditive height n ([Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Theorem 4.4.5]). However, those properties alone do not suffice to guarantee that a stable
$\infty $
-semiadditive of semiadditive height n ([Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Theorem 4.4.5]). However, those properties alone do not suffice to guarantee that a stable
![]() $\infty $
-category is virtually
$\infty $
-category is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. Indeed, for
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable. Indeed, for
![]() $n=1$
, the universal example of such an
$n=1$
, the universal example of such an
![]() $\infty $
-category is
$\infty $
-category is ![]() (constructed in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Theorem 5.3.6]). In [Reference YuanYua22], Yuan constructs a commutative algebra
(constructed in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21a, Theorem 5.3.6]). In [Reference YuanYua22], Yuan constructs a commutative algebra ![]() , whose p-th cyclotomic extension is not Galois ([Reference YuanYua22, Proposition 3.9]). By Proposition 6.11, this implies that
, whose p-th cyclotomic extension is not Galois ([Reference YuanYua22, Proposition 3.9]). By Proposition 6.11, this implies that ![]() is not virtually
is not virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,1)$
-orientable.
$(\mathbb {F}_p,1)$
-orientable.
The virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability of
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
implies the following affineness result:
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
implies the following affineness result:
Theorem 7.29. Let
![]() $n\ge 0$
, and let A be a
$n\ge 0$
, and let A be a
![]() $\pi $
-finite space for which
$\pi $
-finite space for which
![]() $\pi _1(A,a)$
is a p-group and
$\pi _1(A,a)$
is a p-group and
![]() $\pi _{n+1}(A,a)$
is of order prime to p, for every
$\pi _{n+1}(A,a)$
is of order prime to p, for every
![]() $a\in A$
. Then, A is
$a\in A$
. Then, A is
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
-affine.
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
-affine.
Recall that by Proposition 2.5, this implies that for every
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})^A$
, the global sections functor induces an isomorphism
$R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})^A$
, the global sections functor induces an isomorphism
Proof. By Proposition 7.27,
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is virtually
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is virtually
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, and as it is also stable and p-local, the
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientable, and as it is also stable and p-local, the
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
-affineness of A follows from Theorem 6.2 and Remark 6.3.
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
-affineness of A follows from Theorem 6.2 and Remark 6.3.
The affineness of the spaces in Theorem 7.29 gives, in turn, corresponding Eilenberg–Moore type results:
Corollary 7.30. Let A be as in Theorem 7.29 (e.g., an n-finite p-space), and let
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})$
. For every
$R\in \operatorname{{Alg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})$
. For every
![]() $\pi $
-finite space B and an arbitrary space
$\pi $
-finite space B and an arbitrary space
![]() $B'$
mapping to A, we have
$B'$
mapping to A, we have
Proof. The space A and the map
![]() $B \to A$
are
$B \to A$
are
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
-ambidextrous by the
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
-ambidextrous by the
![]() $\infty $
-semiadditivity of
$\infty $
-semiadditivity of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
([Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Theorem A]), and A is
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
([Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY22, Theorem A]), and A is
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
-affine, by Theorem 7.29. Thus, the claim follows from Theorem 2.38.
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
-affine, by Theorem 7.29. Thus, the claim follows from Theorem 2.38.
We also obtain the following result on the ubiquity of
![]() $T(n)$
-local Galois extensions:
$T(n)$
-local Galois extensions:
Corollary 7.31. Let A be as in Theorem 7.29 (e.g., an n-finite p-space). Every
![]() $R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})^A$
is an A-Galois extension of
$R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})^A$
is an A-Galois extension of
![]() $A_*R$
, in the sense of Definition 2.25.
$A_*R$
, in the sense of Definition 2.25.
In particular, for
![]() $n \ge 1$
and G a finite p-group, every
$n \ge 1$
and G a finite p-group, every
![]() $R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})^{BG}$
is a G-Galois extension of its fixed point algebra
$R \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})^{BG}$
is a G-Galois extension of its fixed point algebra
![]() $R^{hG}$
.
$R^{hG}$
.
Proof. By Theorem 7.29, A is
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
-affine. Hence, the claim follows from Corollary 2.28.
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
-affine. Hence, the claim follows from Corollary 2.28.
Remark 7.32. The
![]() $K(n)$
-local analogues of the above results follow easily, either using the colimit-preserving symmetric monoidal functor
$K(n)$
-local analogues of the above results follow easily, either using the colimit-preserving symmetric monoidal functor
![]() $L_{K(n)}\colon \textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}\to \textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
or by an identical argument starting from the virtual
$L_{K(n)}\colon \textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}\to \textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
or by an identical argument starting from the virtual
![]() $(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability of
$(\mathbb {F}_p,n)$
-orientability of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
. In particular, we recover the affineness result of [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Theorem 5.4.3] and the Eilenberg–Moore type result of [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Theorem 5.4.8].
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
. In particular, we recover the affineness result of [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Theorem 5.4.3] and the Eilenberg–Moore type result of [Reference Hopkins and LurieHL13, Theorem 5.4.8].
The virtual
![]() $\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientability of
$\mathbb {F}_p$
-orientability of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
, given by Proposition 7.27, bootstraps automatically to virtual
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
, given by Proposition 7.27, bootstraps automatically to virtual
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-orientability for every connective n-truncated
$\mathfrak {R}$
-orientability for every connective n-truncated
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local commutative ring spectrum
$\pi $
-finite p-local commutative ring spectrum
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
, by Corollary 6.5. Namely, the corresponding
$\mathfrak {R}$
, by Corollary 6.5. Namely, the corresponding
![]() $\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extensions, over which we have a Fourier transform isomorphism, are faithful. Specializing to
$\mathfrak {R}$
-cyclotomic extensions, over which we have a Fourier transform isomorphism, are faithful. Specializing to
![]() $\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
, these are precisely the
$\mathfrak {R} = \mathbb {Z}/p^r$
, these are precisely the
![]() $T(n)$
-local higher cyclotomic extensions
$T(n)$
-local higher cyclotomic extensions
![]() $R_{n,r}^f$
constructed in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b]. We thus obtain Fourier isomorphisms over these extensions.
$R_{n,r}^f$
constructed in [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b]. We thus obtain Fourier isomorphisms over these extensions.
Theorem 7.33. For every
![]() $n\ge 0$
and
$n\ge 0$
and
![]() $r\ge 1$
, there is a natural isomorphism of
$r\ge 1$
, there is a natural isomorphism of
![]() $T(n)$
-local commutative
$T(n)$
-local commutative
![]() $R^f_{n,r}$
-algebras
$R^f_{n,r}$
-algebras
where M is a connective
![]() $\pi $
-finite
$\pi $
-finite
![]() $\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-module and
$\mathbb {Z}/p^r$
-module and
![]() $M^*$
is its Pontryagin dual.
$M^*$
is its Pontryagin dual.
Proof. By Corollary 6.7,
![]() $R_{n,r}^f$
is the universal
$R_{n,r}^f$
is the universal
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}/p^r,n)$
-oriented commutative algebra in
$(\mathbb {Z}/p^r,n)$
-oriented commutative algebra in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
.
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
.
Finally, we also obtain a higher chromatic height analogue of Kummer theory.
Theorem 7.34. For every
![]() $n\ge 0$
, every
$n\ge 0$
, every
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})$
admitting a primitive higher
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})$
admitting a primitive higher
![]() $p^r$
-th root of unity, and every
$p^r$
-th root of unity, and every
![]() $M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathbb {Z}/p^r}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, there is a natural isomorphism of spaces
$M \in {\operatorname {Mod}}_{\mathbb {Z}/p^r}^{[0,n]\text {-}\textrm {fin}}$
, there is a natural isomorphism of spaces
Proof. This is a special case of Proposition 4.32.
Classically, Kummer theory is used to classify abelian Galois extensions. Applying Theorem 7.34 to the case of finite abelian p-groups, we get a similar classification in arbitrary chromatic heights.
Corollary 7.35. For every
![]() $n\ge 0$
, every
$n\ge 0$
, every
![]() $R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})$
admitting a primitive higher
$R\in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})$
admitting a primitive higher
![]() $p^r$
-th root of unity, and every finite abelian
$p^r$
-th root of unity, and every finite abelian
![]() $p^r$
-torsion group M, there is a natural isomorphism
$p^r$
-torsion group M, there is a natural isomorphism
Proof. The case
![]() $n=0$
follows from [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Theorem 3.18]. For
$n=0$
follows from [Reference Carmeli, Schlank and YanovskiCSY21b, Theorem 3.18]. For
![]() $n\ge 1$
, we have
$n\ge 1$
, we have
By Theorem 7.34, the last space identifies with
Virtual
 $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientability & speculations
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientability & speculations
By Corollary 6.18, the infinite cyclotomic extension
![]() $R_n^f$
is the universal
$R_n^f$
is the universal
![]() $(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable
$(\mathbb {Z}_{(p)},n)$
-orientable
![]() $T(n)$
-local commutative ring spectrum, so, in particular, it supports a Fourier transform for all
$T(n)$
-local commutative ring spectrum, so, in particular, it supports a Fourier transform for all
![]() $\pi $
-finite p-local
$\pi $
-finite p-local
![]() $\mathbb {Z}$
-modules. Note that by universality, this lifts the
$\mathbb {Z}$
-modules. Note that by universality, this lifts the
![]() $K(n)$
-local Fourier transform over
$K(n)$
-local Fourier transform over
![]() $R_n$
from Theorem 7.5. However, in contrast with
$R_n$
from Theorem 7.5. However, in contrast with
![]() $R_n$
, we do not know whether
$R_n$
, we do not know whether
![]() $R_n^f$
is faithful (even though all the extensions
$R_n^f$
is faithful (even though all the extensions
![]() $R_{n,r}^f$
are). This question can be re-formulated in a way that might shed some light on the relationship between
$R_{n,r}^f$
are). This question can be re-formulated in a way that might shed some light on the relationship between
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
and
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
and
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
.
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
.
By Proposition 4.27, the Bousfield localization of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
with respect to
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
with respect to
![]() $R_n^f$
is the universal virtually
$R_n^f$
is the universal virtually
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientable symmetric monoidal localization of
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientable symmetric monoidal localization of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
. Proposition 6.19 tells us that this localization
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
. Proposition 6.19 tells us that this localization
![]() $\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)} := (\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})_{R_n^f}$
is smashing and that its unit is given by
$\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)} := (\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})_{R_n^f}$
is smashing and that its unit is given by
![]() $(R_n^f)^{hG} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})$
, where
$(R_n^f)^{hG} \in \operatorname{{CAlg}}(\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)})$
, where
We also observe that since, essentially by construction,
![]() $\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)}$
is virtually
$\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)}$
is virtually
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientable, it is, in fact, virtually
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientable, it is, in fact, virtually
![]() $\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientable, by Proposition 6.20. Now, since
$\mathbb {S}_{(p)}$
-orientable, by Proposition 6.20. Now, since
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is a virtually
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
is a virtually
![]() $\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientable localization of
$\mathbb {Z}_{(p)}$
-orientable localization of
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
, we obtain a chain of fully faithful embeddings
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
, we obtain a chain of fully faithful embeddings
The gap between
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
and
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
and
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is the subject of Ravenel’s celebrated telescope conjecture, which would imply that all the above inclusions are, in fact, equalities. However, this conjecture is not only open but also believed by many experts to be false for heights greater than
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
is the subject of Ravenel’s celebrated telescope conjecture, which would imply that all the above inclusions are, in fact, equalities. However, this conjecture is not only open but also believed by many experts to be false for heights greater than
![]() $1$
. It is also not known whether there can be any Bousfield localization strictly in between
$1$
. It is also not known whether there can be any Bousfield localization strictly in between
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
and
$\textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
and
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
. In this light, we propose the following:
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
. In this light, we propose the following:
Question 7.36. What can be said about the location of the intermediate localization
![]() $\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)}$
? In particular, is
$\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)}$
? In particular, is
![]() $\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)} = \textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
? Is
$\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)} = \textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
? Is
![]() $\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)} = \textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
?
$\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)} = \textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
?
On the one hand,
![]() $\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)} = \textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
if and only if
$\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)} = \textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
if and only if
![]() $R_n^f$
is faithful in
$R_n^f$
is faithful in
![]() $\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
. On the other,
$\textrm {Sp}_{T(n)}$
. On the other,
![]() $\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)} = \textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
if and only if
$\widehat {\textrm {Sp}}_{T(n)} = \textrm {Sp}_{K(n)}$
if and only if
![]() $R_n^f$
is itself
$R_n^f$
is itself
![]() $K(n)$
-local – namely,
$K(n)$
-local – namely,
![]() $R_n^f \simeq L_{K(n)}R_n^f \simeq R_n$
. Thus, the failure of the telescope conjecture is equivalent to at least one of these assertions being false, while the failure of both would produce a strictly intermediate localization.
$R_n^f \simeq L_{K(n)}R_n^f \simeq R_n$
. Thus, the failure of the telescope conjecture is equivalent to at least one of these assertions being false, while the failure of both would produce a strictly intermediate localization.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Robert Burklund, Gijs Heuts, Michael Hopkins and Allen Yuan for useful discussions, and Shai Keidar, Shay Ben Moshe, Maxime Ramzi, John Rognes and the anonymous referee for helpful comments on an earlier version of this paper. The first author is supported by the European Research Council (ERC) under Horizon Europe (grant No. 101042990). The second author is partially supported by the Danish National Research Foundation through the Copenhagen Centre for Geometry and Topology (DNRF151). The third author is supported by ISF1588/18 and BSF 2018389. The first and fourth authors thank the Max Planck Institute for its hospitality. The first author would also like to thank the Hausdorff Center for Mathematics, and the third author would like to thank the Massachusetts Institute of Technology for its hospitality.
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interest to declare.