Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 March 2020
Several evidences support the hypothesis that glutamatergic dysfunction may be implicated in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia and in the last few year great interest has been focused on the role of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). Memantine is a noncompetitive NMDARs antagonist, binds the same site of NMDARs of Mg2+, endogenous blocker of NMDARs, with moderate affinity, rapid unblocking kinetics and strong functional voltage-dependency. Memantine does not affect the physiological activation of NMDARs whereas it blocks the sustained activation under pathological conditions. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that memantine at high concentrations targets many receptors, including serotonin, nicotinic acetylcholine, sigma-1 and serotonin and dopamine receptors.
Increasing interest in memantine add-on therapy in schizophrenic patients with negative and cognitive symptoms may suggest that memantine could be a new promising treatment in schizophrenia.
The aim of this update was to evaluate clinical data about the memantine effectiveness in schizophrenic patients.
We searched on PubMed to identify original studies about the use of memantine in treatment of schizophrenic patients. The search conducted on June 16th, 2016 yielded 135 records. Neuf papers met our inclusion criteria.
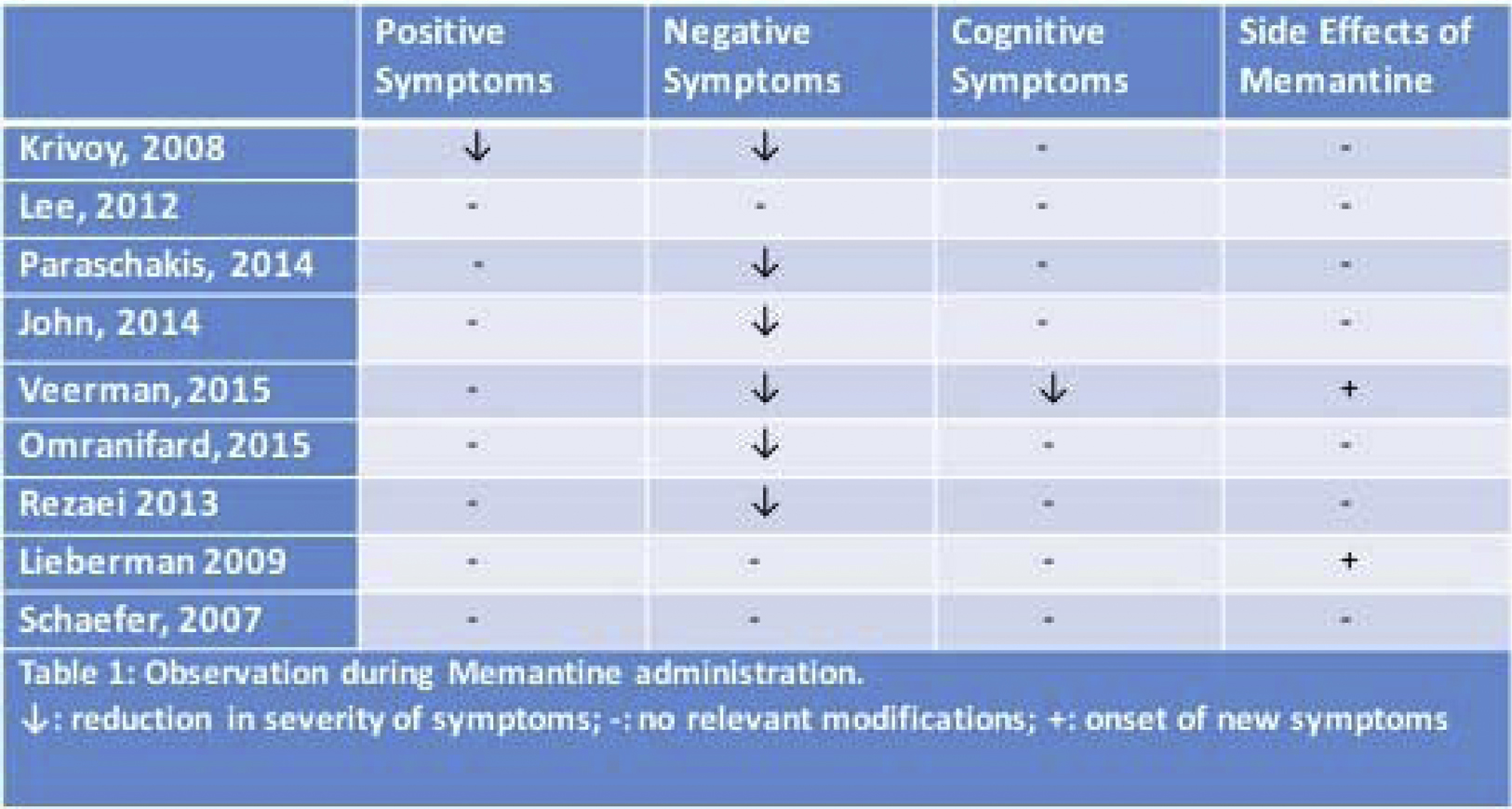
Negative symptoms improved in the large majority of patients treated, however there is not a clear evidence on cognitive and positive symptoms (Table 1)
Memantine therapy in schizophrenic patients has given unclear results. It seems that memantine improves mainly negative symptoms, while cognitive and positive symptoms did not improve significantly. Further trials with a more numerous sample are required obtain an objective result.
Table 1
Observation during Memantime administration.
↓: reduction in severity of symptoms; -: no relevant modifications; +: onset of new symptoms
The authors have not supplied their declaration of competing interest.
Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.