Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 March 2017
We show that for every ergodic measure-preserving system 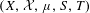 $(X,{\mathcal{X}},\unicode[STIX]{x1D707},S,T)$ with commuting transformations
$(X,{\mathcal{X}},\unicode[STIX]{x1D707},S,T)$ with commuting transformations  $S$ and
$S$ and  $T$, the average
$T$, the average 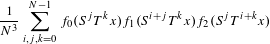 $$\begin{eqnarray}\frac{1}{N^{3}}\mathop{\sum }_{i,j,k=0}^{N-1}f_{0}(S^{j}T^{k}x)f_{1}(S^{i+j}T^{k}x)f_{2}(S^{j}T^{i+k}x)\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\frac{1}{N^{3}}\mathop{\sum }_{i,j,k=0}^{N-1}f_{0}(S^{j}T^{k}x)f_{1}(S^{i+j}T^{k}x)f_{2}(S^{j}T^{i+k}x)\end{eqnarray}$$ $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}$-almost every
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}$-almost every 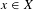 $x\in X$ as
$x\in X$ as 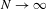 $N\rightarrow \infty$ for all
$N\rightarrow \infty$ for all 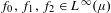 $f_{0},f_{1},f_{2}\in L^{\infty }(\unicode[STIX]{x1D707})$. We also show that if
$f_{0},f_{1},f_{2}\in L^{\infty }(\unicode[STIX]{x1D707})$. We also show that if 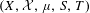 $(X,{\mathcal{X}},\unicode[STIX]{x1D707},S,T)$ is an ergodic measurable distal system, then the average
$(X,{\mathcal{X}},\unicode[STIX]{x1D707},S,T)$ is an ergodic measurable distal system, then the average 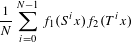 $$\begin{eqnarray}\frac{1}{N}\mathop{\sum }_{i=0}^{N-1}f_{1}(S^{i}x)f_{2}(T^{i}x)\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\frac{1}{N}\mathop{\sum }_{i=0}^{N-1}f_{1}(S^{i}x)f_{2}(T^{i}x)\end{eqnarray}$$ $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}$-almost every
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}$-almost every 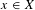 $x\in X$ as
$x\in X$ as 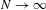 $N\rightarrow \infty$ for all
$N\rightarrow \infty$ for all 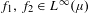 $f_{1},f_{2}\in L^{\infty }(\unicode[STIX]{x1D707})$.
$f_{1},f_{2}\in L^{\infty }(\unicode[STIX]{x1D707})$.