Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Tao, Terence
2007.
Structure and Randomness in Combinatorics.
p.
3.
Kohlenbach, Ulrich
2008.
Gödel's Functional Interpretation and its Use in Current Mathematics*.
Dialectica,
Vol. 62,
Issue. 2,
p.
223.
del Junco, Andrés
2009.
Ergodic Theory.
p.
79.
TOWSNER, HENRY
2009.
Convergence of diagonal ergodic averages.
Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 4,
p.
1309.
KOHLENBACH, U.
and
LEUŞTEAN, L.
2009.
A quantitative mean ergodic theorem for uniformly convex Banach spaces.
Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 6,
p.
1907.
Junco, Andrés del
2009.
Encyclopedia of Complexity and Systems Science.
p.
2933.
Johnson, Michael C. R.
2009.
Convergence of polynomial ergodic averages of several variables for some commuting transformations.
Illinois Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 53,
Issue. 3,
Avigad, Jeremy
2009.
The metamathematics of ergodic theory.
Annals of Pure and Applied Logic,
Vol. 157,
Issue. 2-3,
p.
64.
Gerhardy, Philipp
2010.
Logic Colloquium 2007.
p.
82.
AUSTIN, TIM
2010.
On the norm convergence of non-conventional ergodic averages.
Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 2,
p.
321.
Frantzikinakis, Nikos
2010.
Multiple recurrence and convergence for hardy sequences of polynomial growth.
Journal d'Analyse Mathématique,
Vol. 112,
Issue. 1,
p.
79.
Шкредов, Илья Дмитриевич
and
Shkredov, Il'ya Dmitrievich
2010.
Анализ Фурье в комбинаторной теории чисел.
Успехи математических наук,
Vol. 65,
Issue. 3,
p.
127.
Austin, Tim
2010.
Deducing the multidimensional Szemerédi theorem from an infinitary removal lemma.
Journal d'Analyse Mathématique,
Vol. 111,
Issue. 1,
p.
131.
Kohlenbach, Ulrich
2011.
On the asymptotic behavior of odd operators.
Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications,
Vol. 382,
Issue. 2,
p.
615.
Kohlenbach, Ulrich
2011.
On quantitative versions of theorems due to F.E. Browder and R. Wittmann.
Advances in Mathematics,
Vol. 226,
Issue. 3,
p.
2764.
Austin, Tim
Eisner, Tanja
and
Tao, Terence
2011.
Nonconventional ergodic averages and multiple recurrence for von Neumann dynamical systems.
Pacific Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 250,
Issue. 1,
p.
1.
CHU, QING
2011.
Multiple recurrence for two commuting transformations.
Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 03,
p.
771.
Kra, Bryna
2011.
Poincaré recurrence and number theory: thirty years later.
Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 4,
p.
497.
Kohlenbach, U.
and
Leuştean, L.
2012.
On the computational content of convergence proofs via Banach limits.
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 370,
Issue. 1971,
p.
3449.
Shkredov, I. D.
2012.
On the gowers norms of certain functions.
Mathematical Notes,
Vol. 92,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
554.
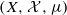 . We show that the multiple ergodic averages
. We show that the multiple ergodic averages 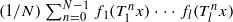 are convergent in
are convergent in 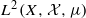 as
as 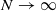 for all
for all 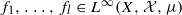 ; this was previously established for l=2 by Conze and Lesigne [J. P. Conze and E. Lesigne. Théorèmes ergodique por les mesures diagonales. Bull. Soc. Math. France112 (1984), 143–175] and for general l assuming some additional ergodicity hypotheses on the maps Ti and TiTj−1 by Frantzikinakis and Kra [N. Frantzikinakis and B. Kra. Convergence of multiple ergodic averages for some commuting transformations. Ergod. Th. & Dynam. Sys.25 (2005), 799–809] (with the l=3 case of this result established earlier by Zhang [Q. Zhang. On the convergence of the averages
; this was previously established for l=2 by Conze and Lesigne [J. P. Conze and E. Lesigne. Théorèmes ergodique por les mesures diagonales. Bull. Soc. Math. France112 (1984), 143–175] and for general l assuming some additional ergodicity hypotheses on the maps Ti and TiTj−1 by Frantzikinakis and Kra [N. Frantzikinakis and B. Kra. Convergence of multiple ergodic averages for some commuting transformations. Ergod. Th. & Dynam. Sys.25 (2005), 799–809] (with the l=3 case of this result established earlier by Zhang [Q. Zhang. On the convergence of the averages 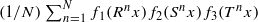 . Mh. Math.122 (1996), 275–300]). Our approach is combinatorial and finitary in nature, inspired by recent developments regarding the hypergraph regularity and removal lemmas, although we will not need the full strength of those lemmas. In particular, the l=2 case of our arguments is a finitary analogue of those by Conze and Lesigne.
. Mh. Math.122 (1996), 275–300]). Our approach is combinatorial and finitary in nature, inspired by recent developments regarding the hypergraph regularity and removal lemmas, although we will not need the full strength of those lemmas. In particular, the l=2 case of our arguments is a finitary analogue of those by Conze and Lesigne.