Article contents
Convergence Rates of Cascade Algorithms with Infinitely Supported Masks
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Abstract
We investigate the solutions of refinement equations of the form
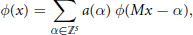 $$\phi (x)\,=\,\sum\limits_{\alpha \in {{\mathbb{Z}}^{S}}}{a(\alpha )\,}\phi (Mx\,-\,\alpha ),$$
$$\phi (x)\,=\,\sum\limits_{\alpha \in {{\mathbb{Z}}^{S}}}{a(\alpha )\,}\phi (Mx\,-\,\alpha ),$$
where the function 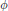 $\phi $ is in
$\phi $ is in 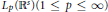 ${{L}_{p}}({{\mathbb{R}}^{s}})(1\,\le \,p\,\le \,\infty )$,
${{L}_{p}}({{\mathbb{R}}^{s}})(1\,\le \,p\,\le \,\infty )$,  $a$ is an infinitely supported sequence on
$a$ is an infinitely supported sequence on 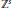 ${{\mathbb{Z}}^{s}}$ called a refinement mask, and
${{\mathbb{Z}}^{s}}$ called a refinement mask, and 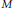 $M$ is an
$M$ is an  $s\,\times \,s$ integer matrix such that
$s\,\times \,s$ integer matrix such that 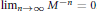 ${{\lim }_{n\to \infty }}\,{{M}^{-n}}\,=\,0$. Associated with the mask
${{\lim }_{n\to \infty }}\,{{M}^{-n}}\,=\,0$. Associated with the mask  $a$ and
$a$ and 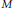 $M$ is a linear operator
$M$ is a linear operator 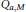 ${{\text{Q}}_{a,M}}$ defined on
${{\text{Q}}_{a,M}}$ defined on 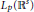 ${{L}_{p}}({{\mathbb{R}}^{s}})$ by
${{L}_{p}}({{\mathbb{R}}^{s}})$ by 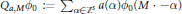 ${{\text{Q}}_{a,M}}{{\phi }_{0}}\,:=\,{{\sum }_{\alpha \in {{\mathbb{Z}}^{s}}}}\,a(\alpha ){{\phi }_{0}}(M\,\cdot \,-\alpha )$. Main results of this paper are related to the convergence rates of
${{\text{Q}}_{a,M}}{{\phi }_{0}}\,:=\,{{\sum }_{\alpha \in {{\mathbb{Z}}^{s}}}}\,a(\alpha ){{\phi }_{0}}(M\,\cdot \,-\alpha )$. Main results of this paper are related to the convergence rates of 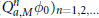 ${{(\text{Q}_{a,M}^{n}{{\phi }_{o}})}_{n=1,2,\ldots }}$ in
${{(\text{Q}_{a,M}^{n}{{\phi }_{o}})}_{n=1,2,\ldots }}$ in 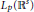 ${{L}_{p}}({{\mathbb{R}}^{s}})$ with mask
${{L}_{p}}({{\mathbb{R}}^{s}})$ with mask  $a$ being infinitely supported. It is proved that under some appropriate conditions on the initial function
$a$ being infinitely supported. It is proved that under some appropriate conditions on the initial function 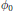 ${{\phi }_{0}}$,
${{\phi }_{0}}$, 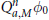 $\text{Q}_{a,M}^{n}{{\phi }_{0}}$ converges in
$\text{Q}_{a,M}^{n}{{\phi }_{0}}$ converges in 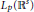 ${{L}_{p}}({{\mathbb{R}}^{s}})$ with an exponential rate.
${{L}_{p}}({{\mathbb{R}}^{s}})$ with an exponential rate.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Mathematical Society 2012
References
- 1
- Cited by


