No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
We study complex commutative Banach algebras (and, more generally, continuous inverse algebras) in which the holomorphic functions of a fixed  $n$-tuple of elements are dense. In particular, we characterize the compact subsets of
$n$-tuple of elements are dense. In particular, we characterize the compact subsets of 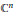 ${{\mathbb{C}}^{n}}$ which appear as joint spectra of such
${{\mathbb{C}}^{n}}$ which appear as joint spectra of such  $n$
-tuples. The characterization is compared with several established notions of holomorphic convexity by means of approximation conditions.
$n$
-tuples. The characterization is compared with several established notions of holomorphic convexity by means of approximation conditions.