Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Bloom, Walter R.
and
Fournier, John J. F.
1987.
Generalized Lipschitz Spaces on Vilenkin Groups.
Mathematische Nachrichten,
Vol. 132,
Issue. 1,
p.
67.


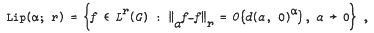
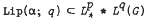 , where 1 ≤
, where 1 ≤ 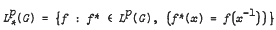 . It is also shown that for
. It is also shown that for 