Food-based standards (FBS) for school lunches were introduced in England in April 2001 to improve the quality and nutritional balance of school lunches(1). However, a survey in 2005 showed that lunchtime food provision and consumption in primary schools in England did not accord with healthy eating guidelines(Reference Nelson, Nicholas and Suleiman2). This, and other factors, triggered a response from the government to establish the School Meal Review Panel(3), which recommended the introduction of a combination of FBS and nutrient-based standards (NBS) for school lunches. In September 2006, interim FBS were introduced, and from September 2008, lunchtime catering in all maintained primary schools in England was required by law to be compliant with the final FBS and NBS for school lunches(4–7).
The FBS for school lunches set minimum requirements for providing healthier items such as fruit, vegetables and bread, and restrictions on less healthy items such as confectionery, deep-fried food, savoury snacks and drinks high in sugar. While the FBS on their own may help to increase intake of fruit, vegetables and oily fish, they may not be sufficient in helping control the intake of specific nutrients. The NBS were introduced to limit the provision of total fat, saturated fat, salt and non-milk extrinsic sugars, and to promote the increased provision of food or drink containing essential nutrients such as fibre, Ca, Fe and Zn. A combination of FBS and NBS was predicted to have a greater impact on improving the nutritional quality of school lunches than FBS alone.
The present report shows how NBS complement FBS to promote the provision and consumption of healthier school lunches in primary schools in England.
Experimental methods
In September 2008, a nationally representative sample of 136 maintained primary schools in England was recruited to participate in a survey of school food provision and consumption at lunchtime. Over five consecutive days, fieldworkers recorded the type, number of portions and portion size of all food and drink provided by schools at lunchtime, and the food and drink choices and consumption of 6696 pupils aged between 3 and 12 years inclusive who were taking a school lunch on that day. Since the standards apply only to primary-aged pupils, sixteen pupils aged 3 years who were at nursery school were excluded from the analysis. Details on data collection tools and methods can be found in the Primary School Food Survey 2009 report(8).
Compliance with the FBS and NBS was assessed against published regulations(4). By law, compliance with the standards relates to planned provision over a full menu cycle (typically 3–4 weeks). In the present study, however, compliance was assessed in relation to the actual provision collected over a 1-week inventory. FBS requiring assessment over either 2 weeks (meat products) or 3 weeks (oily fish) could therefore not be assessed.
For the present report, compliance of schools with three FBS (deep-fried food; starchy food cooked in fat or oil; and salt and condiments) and five related NBS (total fat; saturated fat; percentage of energy from fat; percentage of energy from saturated fat; and Na) was assessed. These FBS restrict the number of times or the amounts that the schools can serve particular food types across the school day: no more than two deep-fried items (e.g. chips) per week; starchy food cooked in fat or oil (e.g. roast potatoes) on no more than 3 d/week; no salt available at tables or service counters, and condiments such as ketchup available only in sachets or controlled portions of no more than 10 g or one tablespoon. The five NBS give a maximum value for the nutrient content of an average school lunch. A comparison of the average nutrient content of a school lunch as eaten was made between schools that met only the FBS and schools that met both the FBS and related NBS. To allow for the clustered nature of the data, differences were estimated using a multilevel modelling approach, taking the school into account.
Ethics approval was granted from King's College London Research Ethics Committee (CREC/07/08-211). Data were analysed using SPSS version 15.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and MLwiN version 2.02(Reference Rasbash, Charlton and Browne10).
Results
Of the 136 schools, thirty-two met just one of the three FBS (two met the deep-fried FBS and fifteen met each of the starchy food and condiment standards); thirty-nine schools met two of the FBS; fifty-three met all three; and the remaining twelve met none of the three. Table 1 shows the relationship between the numbers of schools meeting the FBS and the NBS discussed in the present report. Even when the FBS was met, a large number of schools failed to provide food that met the related NBS. For example, of the seventy-two schools that did not serve deep-fried items more than twice a week (i.e. met the FBS), thirty (42 %) and fifty-two (72 %), respectively, provided an average school lunch with fat and saturated fat content above the maximum recommended levels (Table 2). Of the 101 schools that successfully restricted the availability of salt and condiments to pupils, 77 % provided an average lunch that exceeded the maximum recommended level for Na. This clearly shows that schools meeting only the FBS did not necessarily provide an average school lunch that was within the recommended nutrient levels.
Table 1 Relationship between the number of schools meeting food-based standards (FBS) and related nutrient-based standards (NBS), by number of standards met
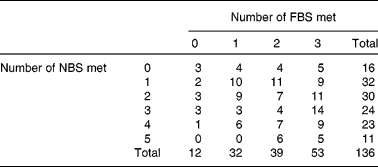
Table 2 Mean nutrient intake from school lunches in schools that met the food-based standards (FBS) but not the nutrient-based standards (NBS) v. those that met the FBS and the NBS*
(Mean values with their standard errors, number of pupils, number of schools and 95 % confidence intervals)

* FBS, NBS, SE and 95 % CI are based on multilevel modelling (see text).
† All means to 1 decimal place.
The impact of meeting both the FBS and the NBS was that pupils tended to choose meals more likely to reflect healthy eating guidance. For example, 9 % fewer pupils chose a starchy food cooked in fat or oil item in schools that met the FBS for starchy food cooked in fat or oil and the NBS for fat compared with pupils from schools that met only the FBS. Similarly, 6·5 % fewer pupils chose salt and condiments at lunchtime in schools that met the FBS for salt and condiments and the NBS for Na compared with those from schools that met only the FBS.
Pupils' nutrient intake from school lunches was then compared between schools that met only the FBS and schools that met both the FBS and the related NBS (Table 2). In all cases, the average nutrient intake from lunch in schools that met both the FBS and the related NBS was significantly lower (P < 0·01) than that in schools that met only the FBS. For example, in schools that met the FBS for restricting salt and condiments and the NBS for Na, the average consumption of Na at lunchtime was roughly one-third lower than in schools that met only the FBS (316·4 mg compared with 462·2 mg; mean difference − 145·8 mg; 95 % CI − 191·2, − 100·4).
An examination of the other two groups of schools (those meeting the NBS only and those not meeting either the FBS or the NBS) shows that the average nutrient intake from school meals by pupils in schools meeting only the NBS was not different from that of pupils in schools where the FBS and associated NBS were met (table not shown). At schools where neither the FBS nor NBS was met, pupils' nutrient intake of fat, saturated fat and Na was significantly higher than pupils in the other groups of schools (table not shown).
Conclusion
The present findings suggest that compliance with both the FBS and NBS is likely to result in lower average intake from school lunches of fat, saturated fat, percentage of energy from fat and saturated fat, and Na than compliance with FBS alone. Average nutrient intake by pupils in schools meeting just the NBS was not dissimilar to those meeting both the FBS and NBS, but those that met both the FBS and NBS provided greater dietary variety than those meeting the NBS alone. This greater variety is likely to encourage the consumption of school lunches with greater food diversity, in line with healthy eating guidelines.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to all the schools and pupils who took part in the present survey. There were no conflicts of interest in the preparation of the present report. The present study was funded by the School Food Trust. D. H. prepared the first draft of the manuscript. L. W. carried out the statistical analysis of the data. All authors contributed to the final revisions.




