Article contents
HETEROGENEOUS SYSTEMS IN 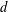 $d$ DIMENSIONS: LOWER SPECTRUM
$d$ DIMENSIONS: LOWER SPECTRUM
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 November 2015
Abstract
The lower part of the spectrum of the Helmholtz equation for a heterogeneous system in a finite region in 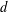 $d$ dimensions, where the solutions to the corresponding homogeneous system are known, can be systematically approximated by means of iterative methods. These methods only require the specification of an arbitrary ansatz and converge to the desired solution, regardless of the strength of the inhomogeneities, provided the ansatz has a finite overlap with it. In this paper, different boundary conditions at the borders of the domain are assumed, and some applications are used to illustrate the methods.
$d$ dimensions, where the solutions to the corresponding homogeneous system are known, can be systematically approximated by means of iterative methods. These methods only require the specification of an arbitrary ansatz and converge to the desired solution, regardless of the strength of the inhomogeneities, provided the ansatz has a finite overlap with it. In this paper, different boundary conditions at the borders of the domain are assumed, and some applications are used to illustrate the methods.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2015 Australian Mathematical Society
References
- 1
- Cited by


