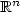2 results
Asymptotic behaviour, nodal lines and symmetry properties forsolutions of superlinear elliptic equations nearan eigenvalue
-
- Journal:
- ESAIM: Control, Optimisation and Calculus of Variations / Volume 11 / Issue 4 / October 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 September 2005, pp. 508-521
- Print publication:
- October 2005
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the Instantaneous Spreading for the Navier–Stokes System in the Whole Space
-
- Journal:
- ESAIM: Control, Optimisation and Calculus of Variations / Volume 8 / 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2002, pp. 273-285
- Print publication:
- 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation