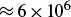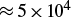We used the PW high-repetition laser facility VEGA-3 at Centro de Láseres Pulsados in Salamanca, with the goal of studying the generation of radioisotopes using laser-driven proton beams. Various types of targets have been irradiated, including in particular several targets containing boron to generate α-particles through the hydrogen–boron fusion reaction. We have successfully identified γ-ray lines from several radioisotopes created by irradiation using laser-generated α-particles or protons including 43Sc, 44Sc, 48Sc, 7Be, 11C and 18F. We show that radioisotope generation can be used as a diagnostic tool to evaluate α-particle generation in laser-driven proton–boron fusion experiments. We also show the production of 11C radioisotopes, 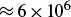 $\approx 6 \times 10^{6}$, and of 44Sc radioisotopes,
$\approx 6 \times 10^{6}$, and of 44Sc radioisotopes, 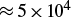 $\approx 5 \times 10^{4}$ per laser shot. This result can open the way to develop laser-driven radiation sources of radioisotopes for medical applications.
$\approx 5 \times 10^{4}$ per laser shot. This result can open the way to develop laser-driven radiation sources of radioisotopes for medical applications.