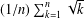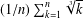In Guatemala prior to control initiatives, the main vectors of Trypanosoma cruzi, the causative agent of Chagas disease, were Rhodnius prolixus and Triatoma dimidiata. This study conducted in 2006 in the department of Chiquimula recorded a high level of T. dimidiata infestation and an absence of R. prolixus in all surveyed communities. In Guatemala, the presence of T. dimidiata as domestic, peridomestic and sylvatic populations results in control difficulties as houses are re-infested from the surrounding environment. Entomological surveys, the current method used to select houses in need of control efforts, are labour intensive and time consuming. A time- and cost-effective way to prioritize houses for evaluation and subsequent treatment is the stratification of houses based on the risk of triatomine infestation. In the present study, 17 anthropogenic risk factors were evaluated for associations with house infestation of T. dimidiata including: wall, floor and roof type. There was an increased likelihood of domestic infestation with T. dimidiata associated with the presence of dirt floors (18/29; OR 8.075, 95% CI 2.13–30.6), uncoated bajareque walls (12/17; OR 4.80, 95% CI 1.35–17.1) and triatomine-like faeces on walls (16/26; OR 3.89, 95% CI 1.19–12.7). These factors could be used to target control of T. dimidiata to communities with an increased risk of being infested.
 $n$ INTEGERS
$n$ INTEGERS