One in four of the Cu-filled cation sites in clinoatacamite, the monoclinic polymorph of atacamite and botallackite, is angle- rather than Jahn-Teller-distorted. Experiments show that this site alone is susceptible to substitution by a non-Jahn-Teller distorting cation of suitable radius and charge, such as Zn2+, and also Ni2+, Co2+, Fe2+, Cd2+ and Mg2+. The crystal symmetry changes to rhombohedral when ∼⅓ of the Cu in this site is substituted by e.g. Zn, thus giving paratacamite; the Zn is essential for stability and forms, with larger proportions of Zn, a series to the end-member in which the site is fully occupied by Zn. This end-member, rhombohedral stoichiometric Cu3Zn(OH)6Cl2, has been characterized using natural specimens from Chile and Iran and is named herbertsmithite. The other cations mentioned behave similarly, producing stabilized rhombohedral paratacamites and end-members analogous to herbertsmithite, which if found in nature, as the Ni analogue has been, should be named species. Clinoatacamite, paratacamite and herbertsmithite have rather similar X-ray powder diffraction patterns, but are readily distinguished by infrared spectroscopy.
Zn-stabilized paratacamite forms blue-green crystals of rhombohedral habit, with vitreous lustre, e = 1.828-1.830, o = 1.835, uniaxial negative, weakly pleochroic O > E, density: 3.75 g cm-3, Mohs hardness: 3-3½; space group R , a = 13.654(5), c = 14.041(6) Å, Z = 24, with pronounced R
, a = 13.654(5), c = 14.041(6) Å, Z = 24, with pronounced R m substructure; six strongest XRD lines 5.452 (100), 2.895 (20), 2.760 (74), 2.262 (52), 1.817 (18), 1.708 (21).
m substructure; six strongest XRD lines 5.452 (100), 2.895 (20), 2.760 (74), 2.262 (52), 1.817 (18), 1.708 (21).
Herbertsmithite forms dark green crystals of rhombohedral habit, with vitreous lustre, e = 1.817, o = 1.825, uniaxial negative, weakly pleochroic O > E, density: 3.95 g cm-3, Mohs hardness: 3-3½;; space group R m with no superstructure observed, a = 6.834(1), c = 14.075(2) Å, Z = 3; six strongest XRD lines 5.466 (55), 4.702 (14), 2.764 (100), 2.266 (36), 1.820 (13), 1.709 (18).
m with no superstructure observed, a = 6.834(1), c = 14.075(2) Å, Z = 3; six strongest XRD lines 5.466 (55), 4.702 (14), 2.764 (100), 2.266 (36), 1.820 (13), 1.709 (18).


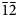

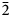
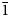
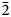
 ,
, 