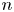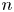1 results
An adaptive strategy for offering m-out-of-n insurance policies
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 37 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2022, pp. 106-134
-
- Article
- Export citation